16.8: The General Mechanism
- Page ID
- 30768
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)The General Mechanism
Step 1 (Slow)
The e- in the pi bond attacks the electrophile
One carbon gets a positive charge the other forms a C-E bond
This forms the arenium ion.
The arenium ion is conjugated but not aromatic.
Step 2 (Fast)
The LPE on a base attacks the hydrogen.
This causes the e- in the C-H bond to form a C-C double bond and aromaticity is reformed
A Detailed discussion of the Mechanism for Electrophilic Substitution Reactions of Benzene
A two-step mechanism has been proposed for these electrophilic substitution reactions. In the first, slow or rate-determining, step the electrophile forms a sigma-bond to the benzene ring, generating a positively charged benzenonium intermediate. In the second, fast step, a proton is removed from this intermediate, yielding a substituted benzene ring. The following four-part illustration shows this mechanism for the bromination reaction. Also, an animated diagram may be viewed.

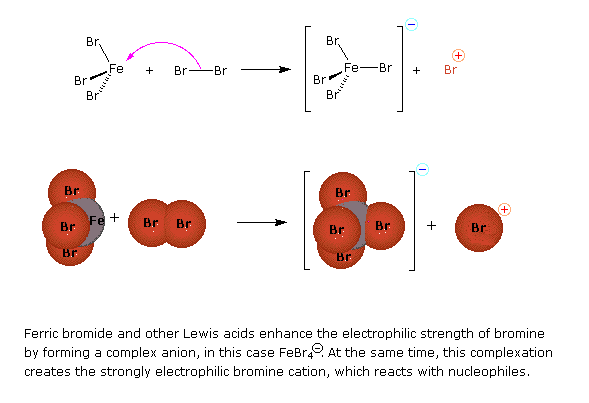
Preliminary step: Formation of the strongly electrophilic bromine cation
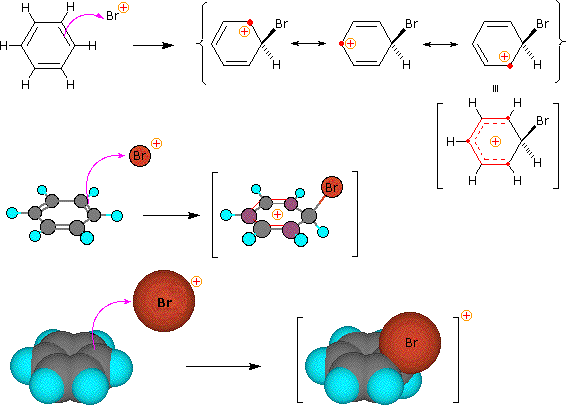
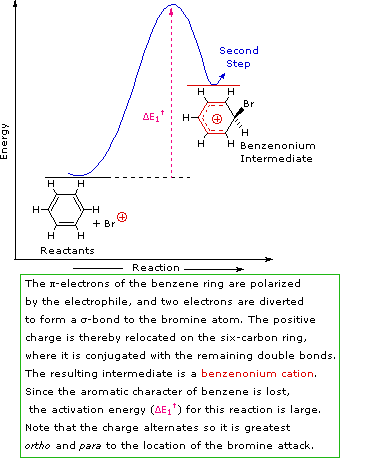
Step 1: The electrophile forms a sigma-bond to the benzene ring, generating a positively charged benzenonium intermediate
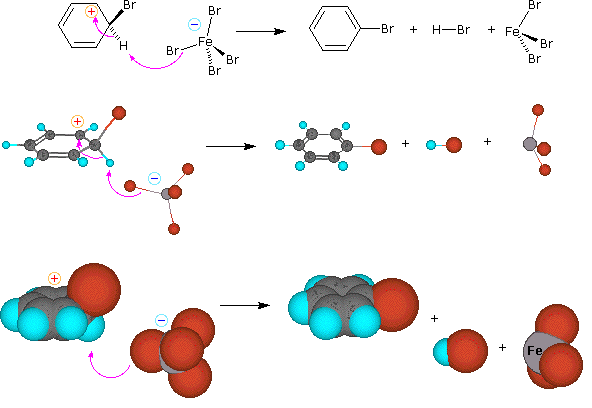
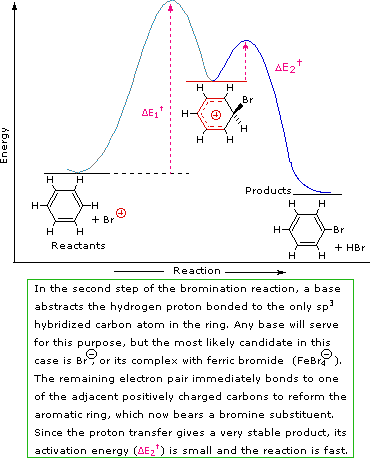
Step 2: A proton is removed from this intermediate, yielding a substituted benzene ring
This mechanism for electrophilic aromatic substitution should be considered in context with other mechanisms involving carbocation intermediates. These include SN1 and E1 reactions of alkyl halides, and Brønsted acid addition reactions of alkenes.
To summarize, when carbocation intermediates are formed one can expect them to react further by one or more of the following modes:
1. The cation may bond to a nucleophile to give a substitution or addition product.
2. The cation may transfer a proton to a base, giving a double bond product.
3. The cation may rearrange to a more stable carbocation, and then react by mode #1 or #2.
SN1 and E1 reactions are respective examples of the first two modes of reaction. The second step of alkene addition reactions proceeds by the first mode, and any of these three reactions may exhibit molecular rearrangement if an initial unstable carbocation is formed. The carbocation intermediate in electrophilic aromatic substitution (the benzenonium ion) is stabilized by charge delocalization (resonance) so it is not subject to rearrangement. In principle it could react by either mode 1 or 2, but the energetic advantage of reforming an aromatic ring leads to exclusive reaction by mode 2 (ie. proton loss).
Other Examples of Electophilic Aromatic Substitution
Many other substitution reactions of benzene have been observed, the five most useful are listed below (chlorination and bromination are the most common halogenation reactions). Since the reagents and conditions employed in these reactions are electrophilic, these reactions are commonly referred to as Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. The catalysts and co-reagents serve to generate the strong electrophilic species needed to effect the initial step of the substitution. The specific electrophile believed to function in each type of reaction is listed in the right hand column.
| Reaction Type | Typical Equation | Electrophile E(+) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Halogenation: | C6H6 | + Cl2 & heat FeCl3 catalyst | ——> | C6H5Cl + HCl Chlorobenzene | Cl(+) or Br(+) |
| Nitration: | C6H6 | + HNO3 & heat H2SO4 catalyst | ——> | C6H5NO2 + H2O Nitrobenzene | NO2(+) |
| Sulfonation: | C6H6 | + H2SO4 + SO3 & heat | ——> | C6H5SO3H + H2O Benzenesulfonic acid | SO3H(+) |
| Alkylation: Friedel-Crafts | C6H6 | + R-Cl & heat AlCl3 catalyst | ——> | C6H5-R + HCl An Arene | R(+) |
| Acylation: Friedel-Crafts | C6H6 | + RCOCl & heat AlCl3 catalyst | ——> | C6H5COR + HCl An Aryl Ketone | RCO(+) |
Contributors
Prof. Steven Farmer (Sonoma State University)
- William Reusch, Professor Emeritus (Michigan State U.), Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry

