Glossary
- Page ID
- 338702
| Words (or words that have the same definition) | The definition is case sensitive | (Optional) Image to display with the definition [Not displayed in Glossary, only in pop-up on pages] | (Optional) Caption for Image | (Optional) External or Internal Link | (Optional) Source for Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Eg. "Genetic, Hereditary, DNA ...") | (Eg. "Relating to genes or heredity") |  |
The infamous double helix | https://bio.libretexts.org/ | CC-BY-SA; Delmar Larsen |
|
Word(s) |
Definition |
Image | Caption | Link | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| organic chemistry | study of the chemistry of the carbon compounds | ||||
| organic molecule | Compound that contains carbon and hydrogen | ||||
| molecular formula | shows the type and number of atoms in a molecule | 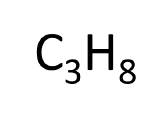 |
|||
| structural formula | shows all atoms and the bonds attaching them | 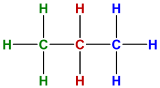 |
|||
| Lewis Structure | shows all atoms and electrons (bonding and nonbonding) attaching them |  |
|||
| Condensed structural formulas | an abbreviated formula that shows all the atoms in a molecule, without showing all of the bonds |  |
|||
| Skeletal Structures (or line-angle structures) | shows all the bonds between carbon atoms, but omits some atom labels |  |
|||
| hydrocarbons | Organic molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms | ||||
| alkane | hydrocarbons with only C–C and C–H single bonds. | ||||
| saturated | maximum number of H atoms | ||||
| conformers | different rotational forms of a molecule |  |
|||
| Structural (or constitutional) isomers | molecules with the same molecular formula but a different connectivity. | 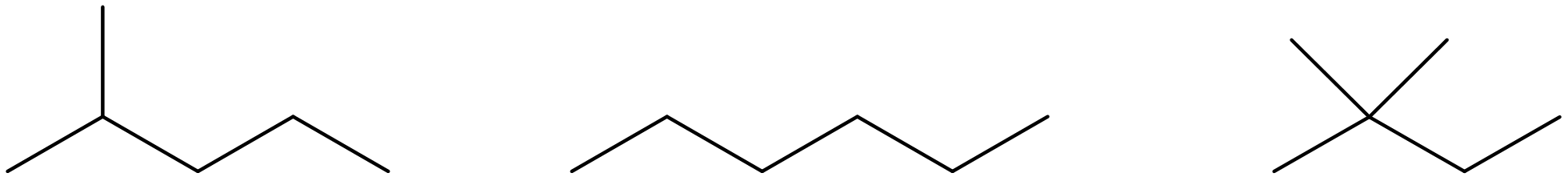 |
|||
| cycloalkane | Three or more carbon atoms arranged in a ring with only C-C and C-H bonds | 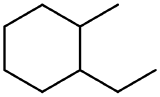 |
|||
| substituents | groups that replace at least one H in order to branch from the alkane chain. | ||||
| alkenes | Molecules that contain a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C) and general molecular formula: CnH2n | ||||
| parent chain | longest continuous chain of carbon atoms | ||||
| diene | molecule that contains two C=C | ||||
| polyene | molecule that contains more than two C=C | ||||
| cycloalkene | cyclic molecule that contains a C=C | 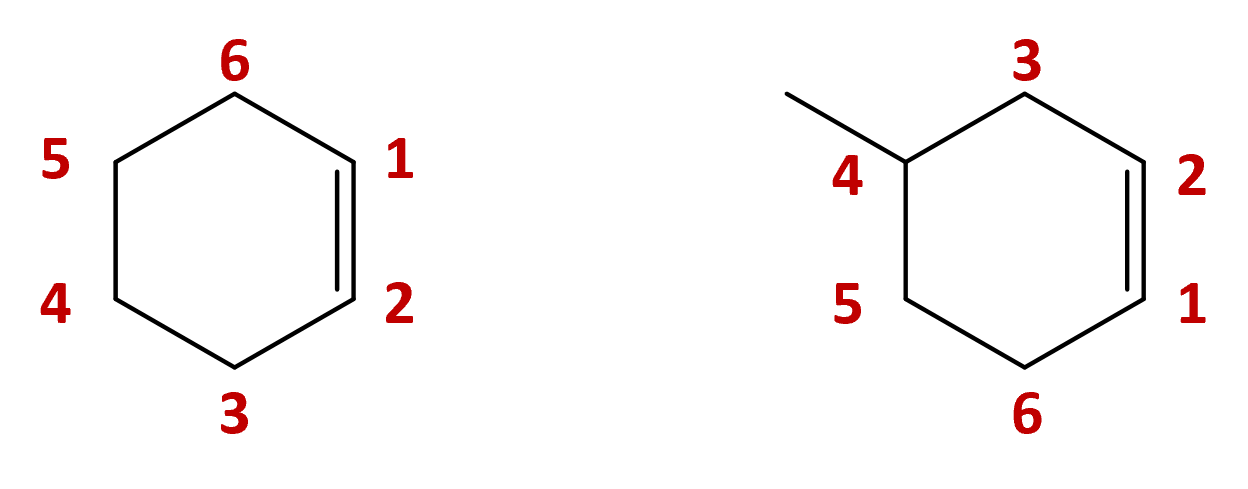 |
|||
| alkyl halide | organic molecules where a halogen (F, Cl, Br, or I) has replaced a hydrogen | ||||
| geometric (cis-trans) isomers | molecues that have different arrangements because of restricted rotation around a carbon-carbon double bond (or ring) | 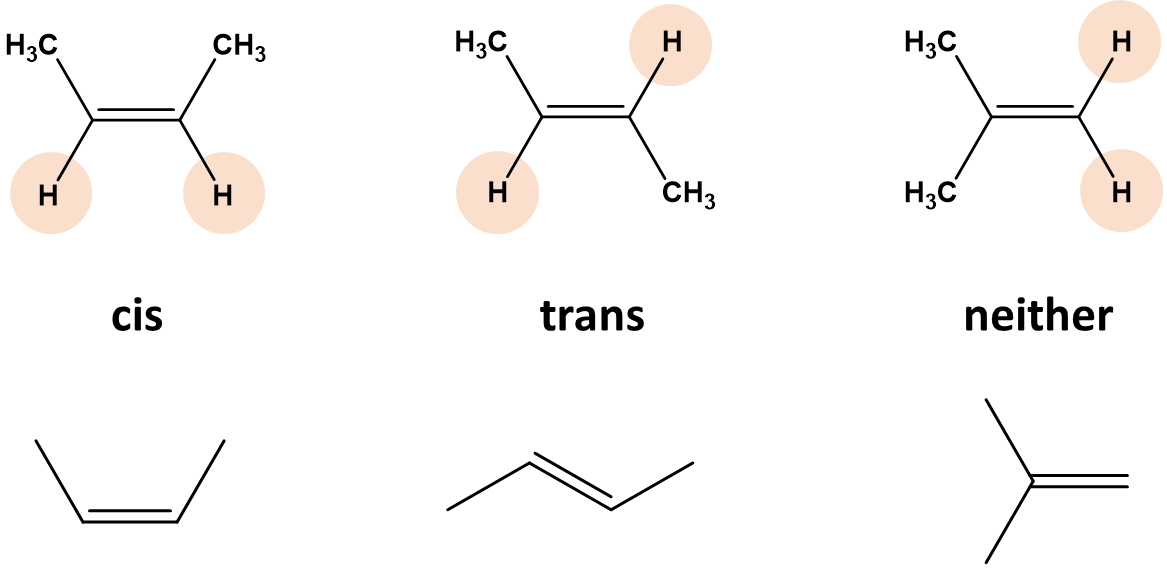 |
|||
| alkynes | Molecules that contain a carbon-carbon triple bond (C≡C) and general molecular formula: CnH2n-2 | ||||
| aromatic |
class of cyclic compounds that contain a benzene ring |
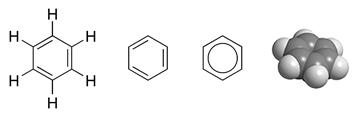 |
Cacycle, Benzene Structure, CC BY-SA 3.0, via WikiMedia Commons |
||
| functional group | atoms bonded in a specific way that represents a specific class of organic compounds | ||||
| alcohols | molecules that contain the hydroxyl (–OH) functional group | 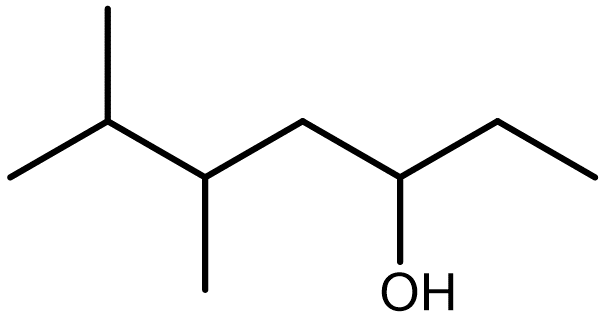 |
|||
| primary (1o) alcohol | alcohols that have one alkyl group attached to the carbon where the functional group is bonded | 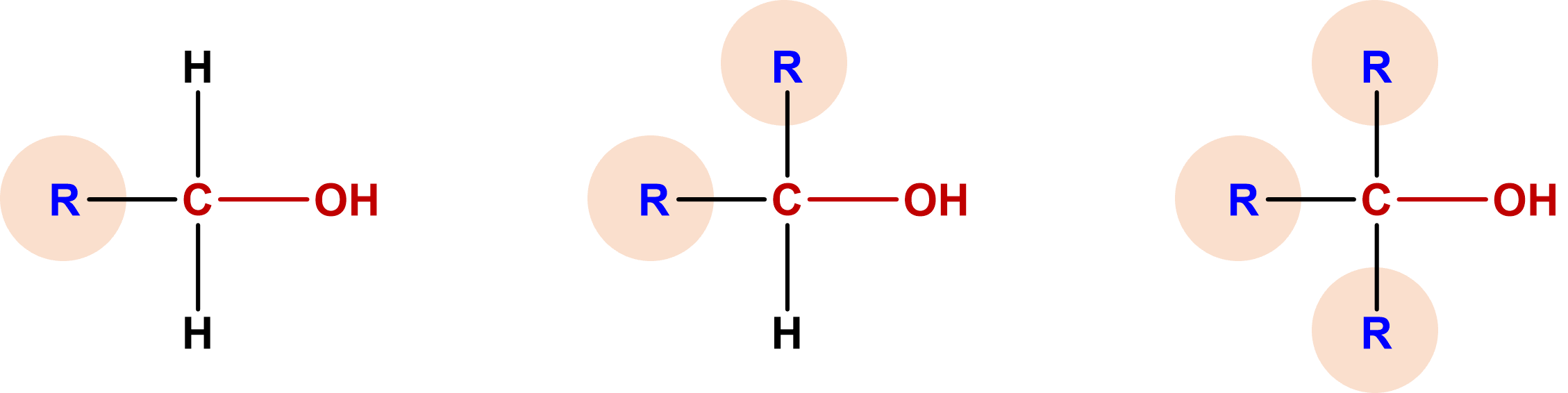 |
|||
| secondary (2o) alcohol | alcohols that have two alkyl groups attached to the carbon where the functional group is bonded |  |
|||
| tertiary (3o) alcohol | alcohols that have three alkyl groups attached to the carbon where the functional group is bonded |  |
|||
| diol | molecules that contain two hydroxyl (–OH) functional groups | ||||
| triol | molecules that contain three hydroxyl (–OH) functional groups | ||||
| polyol | molecules that contain many hydroxyl (–OH) functional groups | ||||
| phenol | molecules that contain the hydroxyl (–OH) functional group directly attached to a benzene ring | 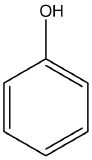 |
|||
| thiol | molecules that contain the sulfhydryl (–SH) functional group | 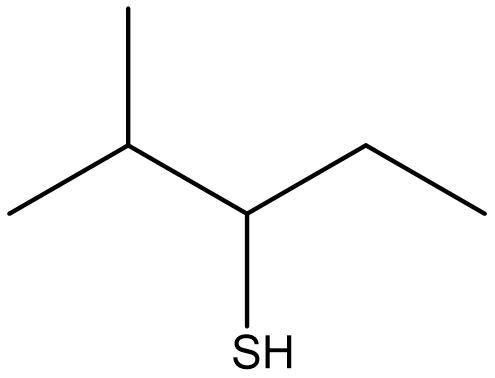 |
|||
| ether | molecules contain the R–O–R’ functional group | 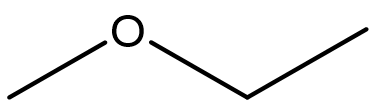 |
|||
| amine | Molecules derived from ammonia (NH3), where one or more hydrogen is replaced with a carbon | 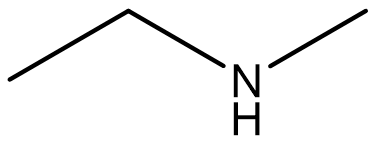 |
|||
| primary (1o) amine | amine that has one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen of the functional group | 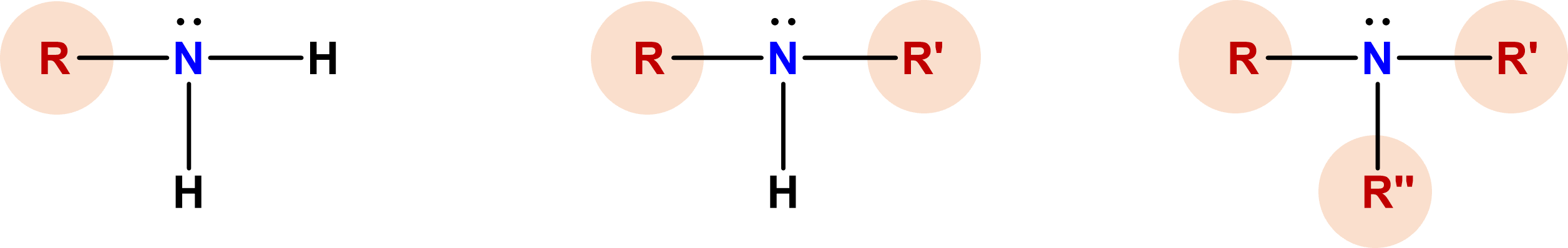 |
|||
| secondary (2o) amine | amine that has two alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen of the functional group |  |
|||
| tertiary (3o) amine | amine that has three alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen of the functional group |  |
|||
| carbonyl group | represents a carbon-oxygen double bond (C=O) | ||||
| aldehyde |
molecules that contain a hydrogen directly bonded to the carbon of a carbonyl group; condensed notation: R–CHO |
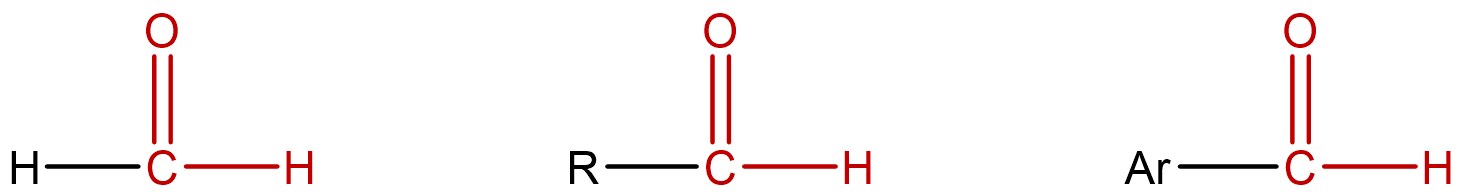 |
|||
| ketone | molecules that contain two carbon groups directly bonded to the carbon of the carbonyl group; condensed notation: R–CO–R' | 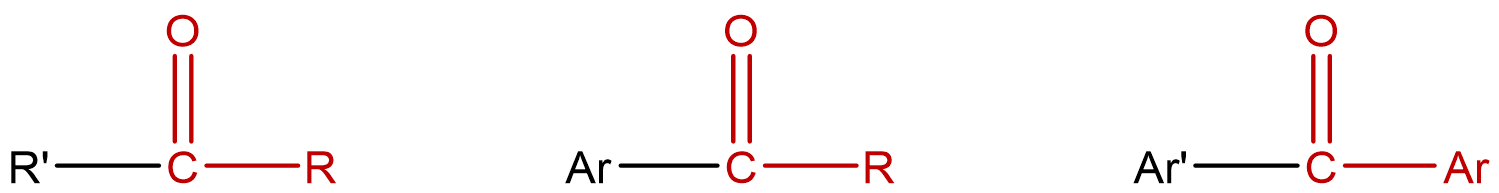 |
|||
| carboxylic acid | molecules that contain a hydroxyl (–OH) directly bonded to the carbon of a carbonyl group; condensed notation: R–COOH | 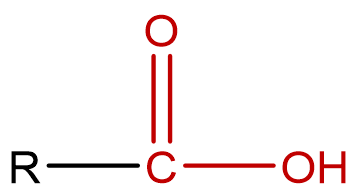 |
|||
| esters | molecules that are derivatives of carboxylic acids, formed by replacing the H of the carboxyl group with an alkyl (carbon) group; condensed notation: R–COOR' | 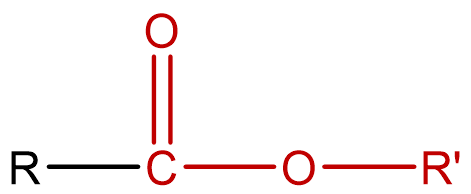 |
|||
| amide | molecules that are derivatives of carboxylic acids, formed by replacing the OH of the carboxyl group with ammonia or an amine; condensed notation: R–CONH2' | 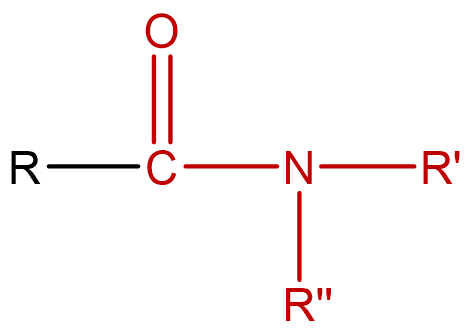 |
|||
|
Redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction |
reactions involving a transfer of electrons | ||||
| oxidation | loss of electrons; or in organic compounds, involves an increase in oxygen and/or decrease in hydrogen | ||||
| reduction | gain of electrons; or in organic compounds, involves an decrease in oxygen and/or increase in hydrogen | ||||
| reducing agent | undergoes oxidation; responsible for something else getting reduced | ||||
| oxidizing agent | undergoes reduction; responsible for something else getting oxidized | ||||
| addition reaction | reaction in which an atom or molecule is added to an unsaturated molecule, making a single product | ||||
| hydrogenation reaction |
addition of H2 to an alkene in the presence of a metal catalyst to produce an alkane |
 |
|||
| halogenation reaction |
addition of a halogen to an alkene to produce a di-substituted alkyl halide |
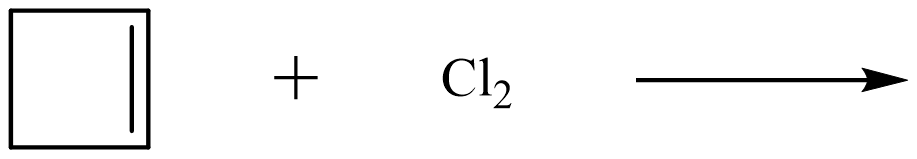 |
|||
| hydrohalogenation reaction | addition of a hydrogen halide to an alkene to produce a mono-substituted alkyl halide | 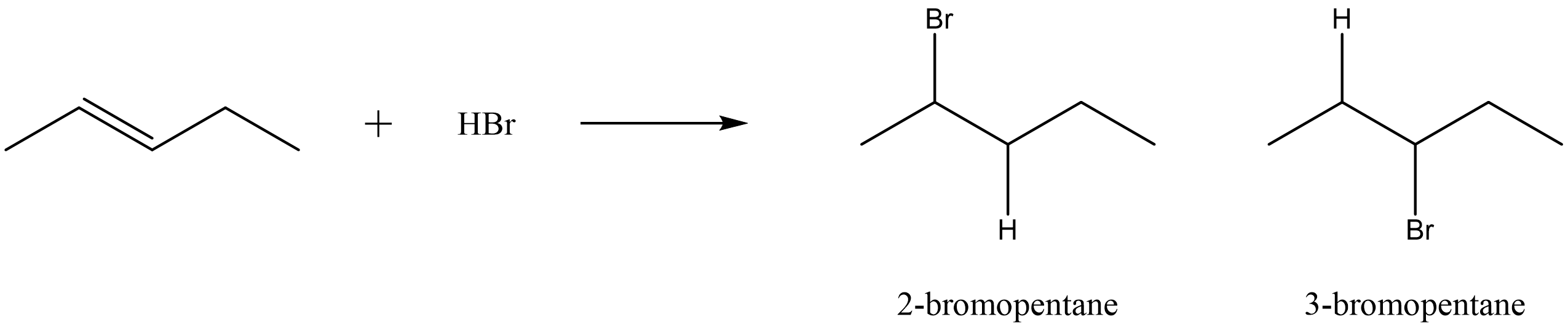 |
|||
| hydration reaction |
addition of water to an alkene in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an alcohol |
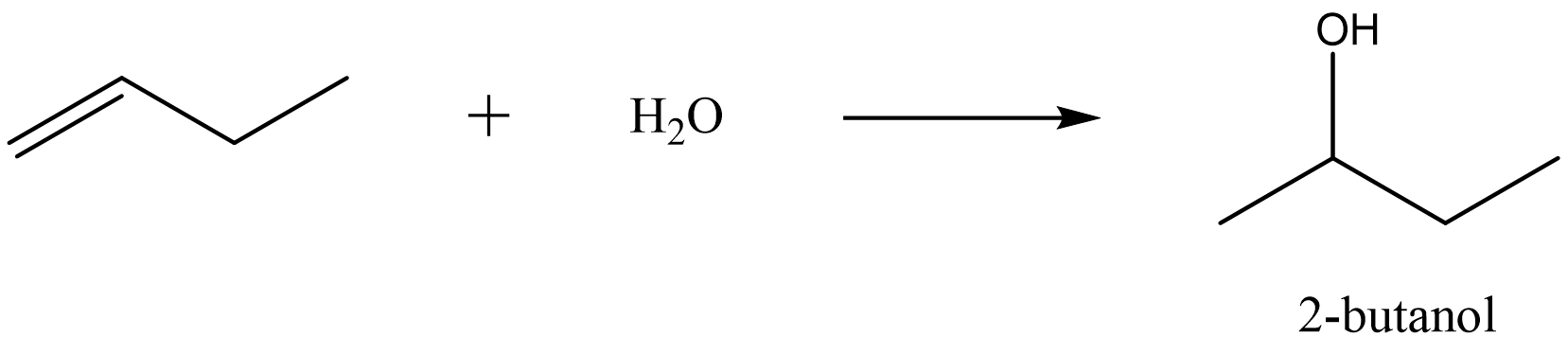 |
|||
| elimination reaction | reaction that involves the removal of adjacent atoms from a molecule to form an alkene | ||||
| dehydration reaction | elimination reaction where water is removed from the molecule to form an alkene | ||||
| dehydrogenation reaction | elimination reaction where molecular hydrogen is removed from the molecule to form an alkene | ||||
| dehalogenation reaction | elimination reaction where a halogen is removed from the molecule to form an alkene | ||||
| polymer | large molecule formed of repeating smaller units that are covalently bonded to one another in a repeating pattern | ||||
| monomer | smaller units that make up a polymer | ||||
| condensation reaction | reaction that involves two molecules combining to form one larger organic molecule and water. | ||||
| esterification | condensation reaction that occurs when a carboxylic acid and alcohol combine to form an ester and water | 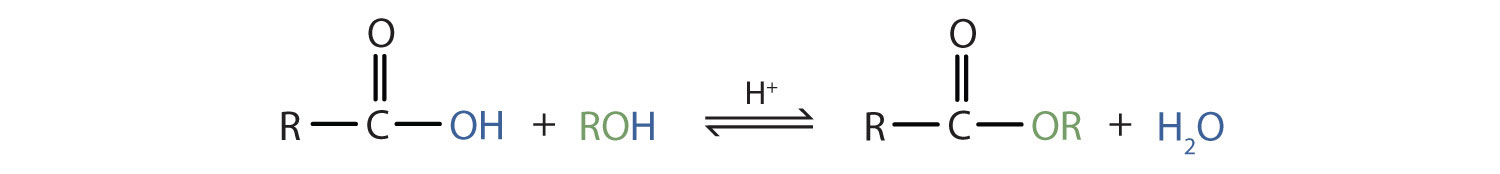 |
" Condensation Reactions" by LibreTexts is licensed under CC BY-NC . | ||
| amidation | condensation reaction that occurs when a carboxylic acid and amine (or ammonia) combine to form an amide and water | 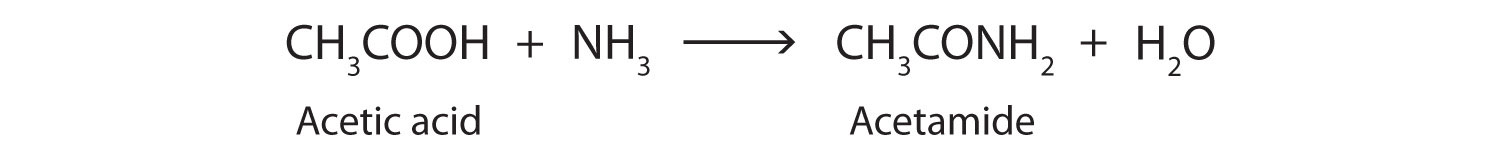 |
" Condensation Reactions" by LibreTexts is licensed under CC BY-NC . | ||
| hydrolysis reaction |
reaction that involves water reacting with an organic molecule to break it down to form two or more smaller organic molecules; opposite of condensation |
 |
FrozenMan, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| saponification | alkaline hydrolysis of an ester resulting in an alcohol and fatty acid salt (ionic compound of the conjugate base) | The original uploader was Rhadamante at French Wikipedia., CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| carbohydrates |
Sugars composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen that provide energy when consumed. |
||||
| monosaccharides | simplest carbohydrates that cannot be broken down to smaller carbohydrates; general formula: Cn(H2O)n | ||||
| disaccharides | carbohydrate consisting of two monosaccharide units chemical combined through a condensation reaction | ||||
| oligosaccharide | carbohydrate consisting of 3-9 monosaccharide units chemical combined through a condensation reaction | ||||
| polysaccharide | carbohydrate consisting of 10 or more monosaccharide units chemical combined through a condensation reaction | ||||
| chiral | objects/molecules that have nonsuperimposable (not identical) mirror images | ||||
| chiral center | tetrahedral carbon bonded to four different atoms or group of atoms. | 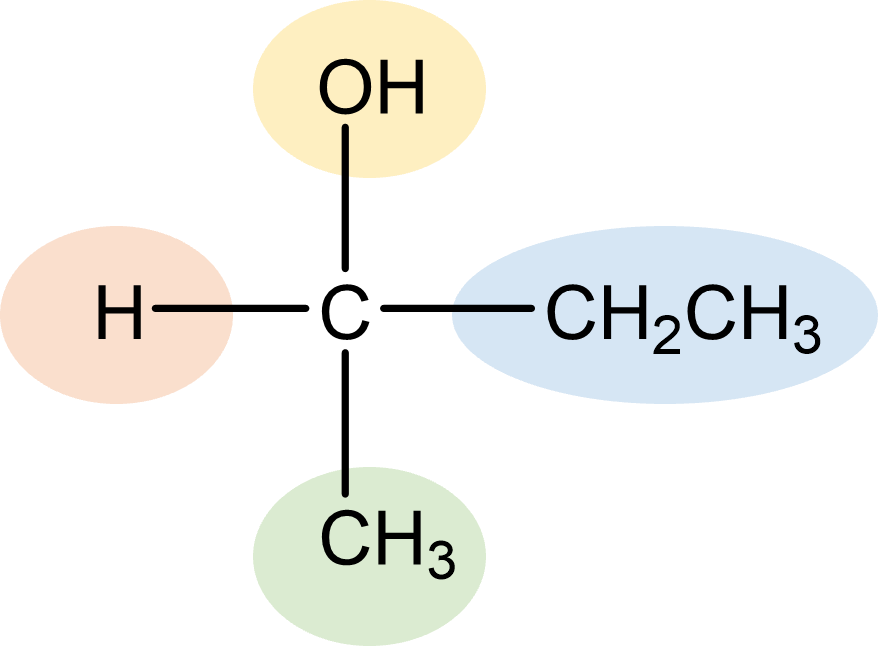 |
|||
| achiral | objects/molecules have superimposable (identical) mirror images | ||||
| stereoisomers | molecules that have the same molecular formula and same connectivity/bonding between the atoms. | ||||
| enantiomers | stereoisomers with nonsuperimposable mirror images. |  |
FlyScienceGuy, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| diastereomers | stereoisomers that are not enantiomers (not exact mirror images) |  |
FlyScienceGuy, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| aldose | monosaccharide that contains an aldehyde group | ||||
| ketose | monosaccharide that contains a ketone group | ||||
| sugar acid | product of the oxidation of a monosaccharide | ||||
| sugar alcohol | product of the reduction of a monosaccharide | ||||
| pyranose | six-membered ring (five carbon atoms and an oxygen) formed from aldoses | .png?revision=1) |
|||
| furanose | five-membered ring (four carbon atoms and an oxygen) formed from ketoses | .png?revision=1) |
|||
| epimers | diastereomers that differ only at one chiral carbon | 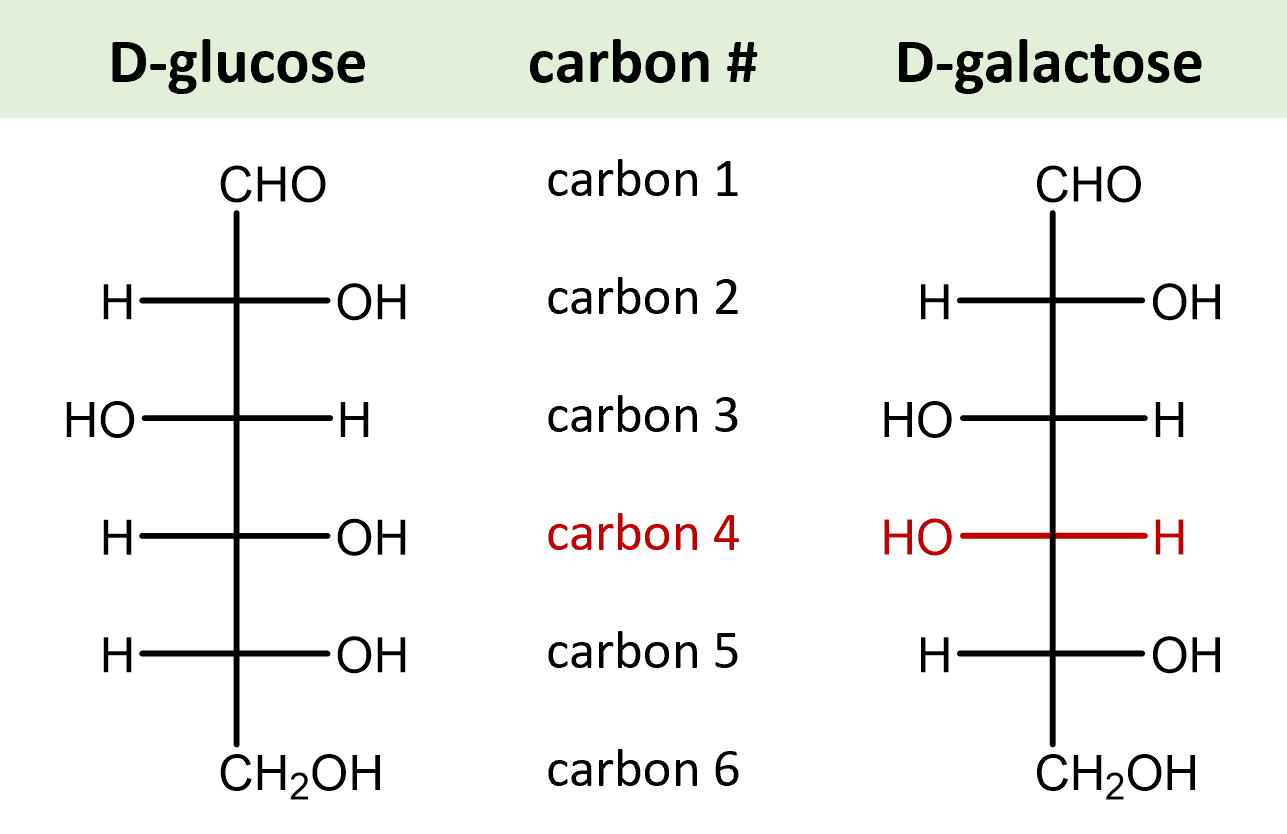 |
|||
| anomeric carbon | carbon of the carbonyl group | ||||
| anomers | diastereomers that differ only at the anomeric carbon | 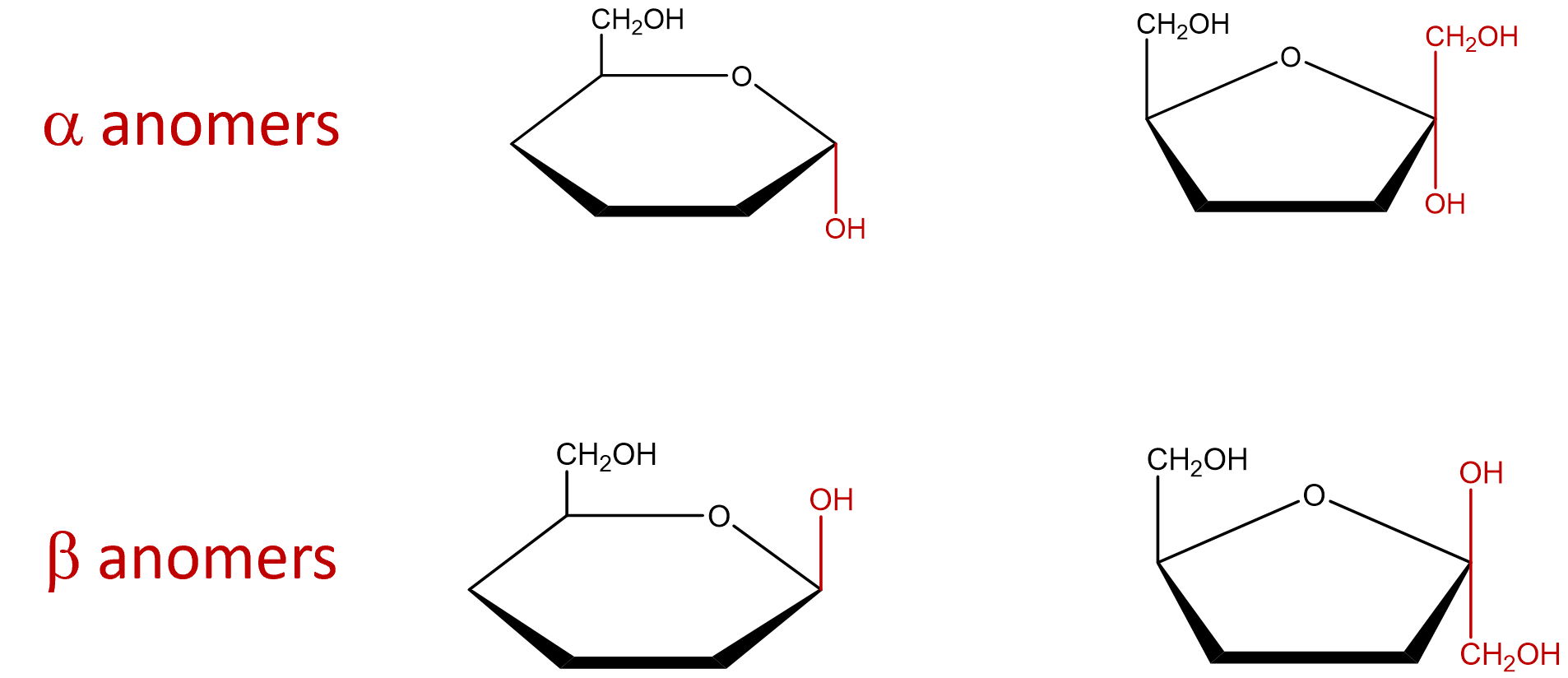 |
|||
| glycosidic bond | connects two molecules to one another through a condensation reaction | ||||
| lipid | class of biomolecules defined by low solubility in water and high solubility in nonpolar, organic solvents | ||||
| fatty acids | long-chained carboxylic acids with properties similar to alkanes. | 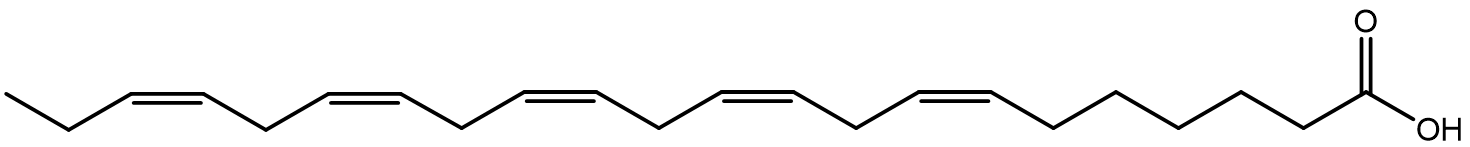 |
|||
| amphipathetic | contain both polar and nonpolar parts | ||||
| monounsaturated fatty acid | fatty acids that contain only one carbon–carbon double bond | 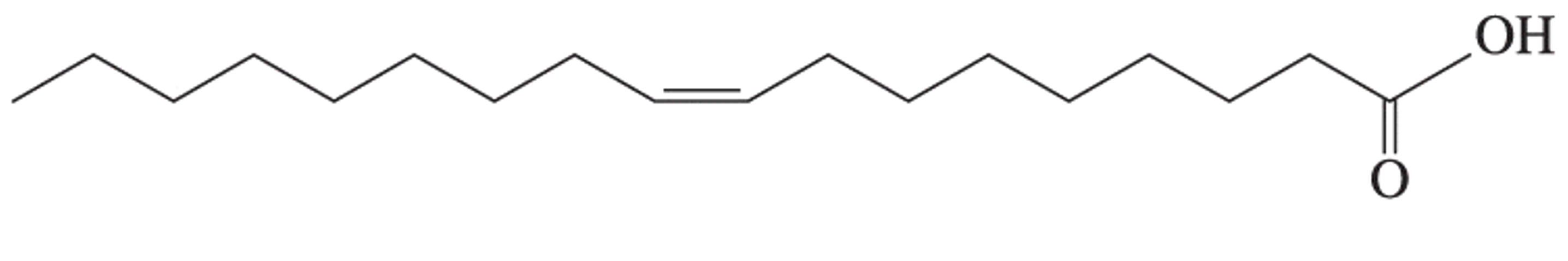 |
|||
| polyunsaturated fatty acid | fatty acids that contain more than one carbon–carbon double bond |  |
|||
| saturated fatty acid | fatty acids that contain only carbon–carbon single bonds | ||||
| triacylglycerol (triglyceride) | fats or oils; produced by the esterification of the hydroxyl groups of glycerol and the carboxyl groups of three fatty acids | Hbf878, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| wax | lipid produced by the esterification of one fatty acid and a long-chain alcohol each containing 14 to 30 carbons | ||||
| glycerophospholipids (or phospholipids) | lipids that have a glycerol backbone with two fatty acids linked to it through an ester bond and a third group which forms a phosphoester bond with an amino alcohol. | 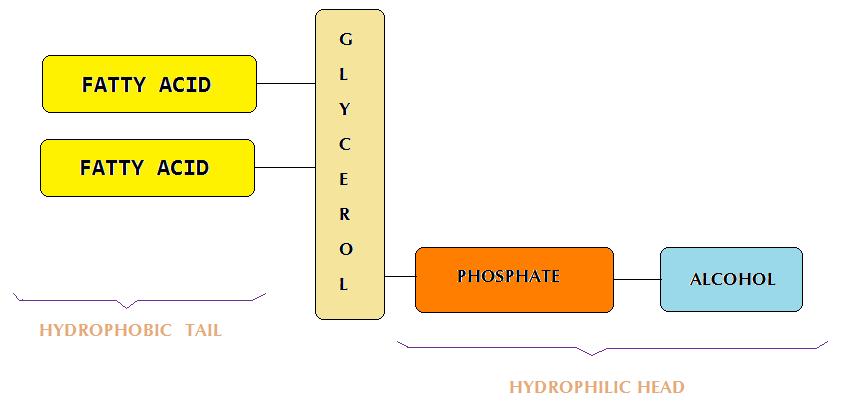 |
Clbt88 at English Wikibooks, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| sphingolipid | phospholipids that contain an 18-carbon unsaturated amino alcohol called sphingosine, instead of glycerol. |  |
Karol Langner at en.wikipedia, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| sphingosine | an amino alcohol found in all sphingolipids | Ed (Edgar181), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| glycolipids |
lipids that contain a carbohydrate. |
||||
| cerebrosides | glycolipids with a monosaccharide. | Epithelyann, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| steroids |
lipids that do not contain fatty acids; contain a steroid nucleus with four fused rings |
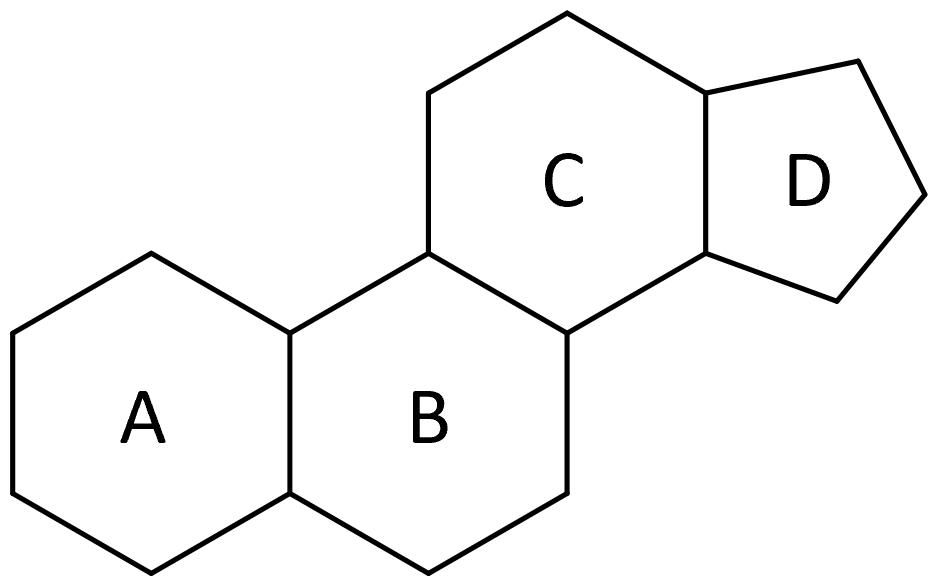 |
|||
| fat |
consist of triglycerides made up of mostly saturated fatty acids; exist as a solid or semisolid at room temperature. |
||||
| oil | consist of triglycerides made up of mostly unsaturated fatty acids; exist as a liquid at room temperature | ||||
| osmosis | occurs when water travels across the cell membrane (from a lower to a higher solution concentration) to equalize solute concentrations inside and outside of a cell | ||||
| isotonic solutions | solute concentration inside and outside of the cell are equal | ||||
| hypotonic solutions | solute concentration outside of the cell is lower than that inside of the cell | ||||
| hemolysis (or lysis) | swelling; water flows into the cell to dilute the concentration until they are equalized | ||||
| hypertonic solution | solute concentration outside of the cell is higher than that inside of the cell | ||||
| crenation | shrinking/shriveling; water flows out of the cell to dilute the concentration until they are equalize | ||||
| diffusion | movement of solute molecules from an area of high solute concentration to a low concentration | ||||
| passive (or simple) diffusion | small molecules and nonpolar molecules use this process to move across the semipermeable membrane; no energy required | ||||
| semipermeable | meaning that some things can enter, and some things cannot | ||||
| facilitated transport | occurs when small polar molecules and ions pass through a channel formed by integral membrane proteins; no energy required | ||||
| active transport | occurs when ions and small polar molecules move across the membrane in the opposite direction of diffusion (from low to high concentration); energy is required | ||||
| essential amino acids | must be consumed because the body cannot make them. | ||||
| amino acids | protein building blocks that contain an amino and carboxylic acid group |  |
Benjah-bmm27, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| zwitterion | form of an amino acid that contains the protonated amine and carboxylat e; typically occurs at neutral pH | 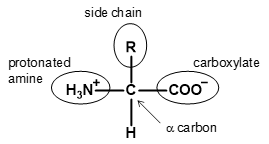 |
|||
| protein | biologically active polypeptide containing 50 or more amino acids | ||||
| peptide | compound containing amino acids joined by a peptide bond | ||||
| denaturation | process that disrupts the stabilizing attractive forces in the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures | ||||
| dipeptide | peptide containing only two amino acids | ||||
| polypeptide | peptide containing many amino acids | ||||
| enzyme | biological catalyst;biologically active globular proteins that accelerate chemical reactions. | ||||
| substrate | reactant in a chemical reaction (typically refers to enzyme-catalyzed reactions) | ||||
| cofactor | inorganic substances that serve as non-protein helpers | ||||
| conenzyme | organic substances , derived from vitamins, that serve as non-protein helper | ||||
| enzyme–substrate (ES) complex | interaction of the enzyme with the substrate; intermediate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction | ||||
|
lock-and-key model |
active site that has a rigid, inflexible shape that is an exact complement to the substrate | ||||
| induced-fit model | active site that is flexible and undergoes a conformational change, adjusting to the shape of the substrate when the substrate interacts with the enzyme. | ||||
| inhibitor | Molecules that cause enzymes to lose activity by preventing the active site from interacting with substrate to form the ES complex | ||||
| reversible inhibition |
occurs when the inhibitor causes a temporary loss of activity |
||||
| competitive inhibitors |
reversible inhibitors that have structures similar to that of the substrate that compete with a substrate for the active site |
||||
| noncompetitive inhibitors | reversible inhibitors that do no have structures similar to that of the substrate and do not compete with a substrate for the active site | ||||
| irreversible inhibition | occurs when the inhibitor causes a permanent loss of activity; forms a covalent bond with an amino acid side chain in the enzyme’s active site | ||||
| nucleic acids | biomolecules composed of nucleotides | ||||
| nucleoside | sugar/base combination between a pentose and a nitrogen containing purine or pyrimidine base | 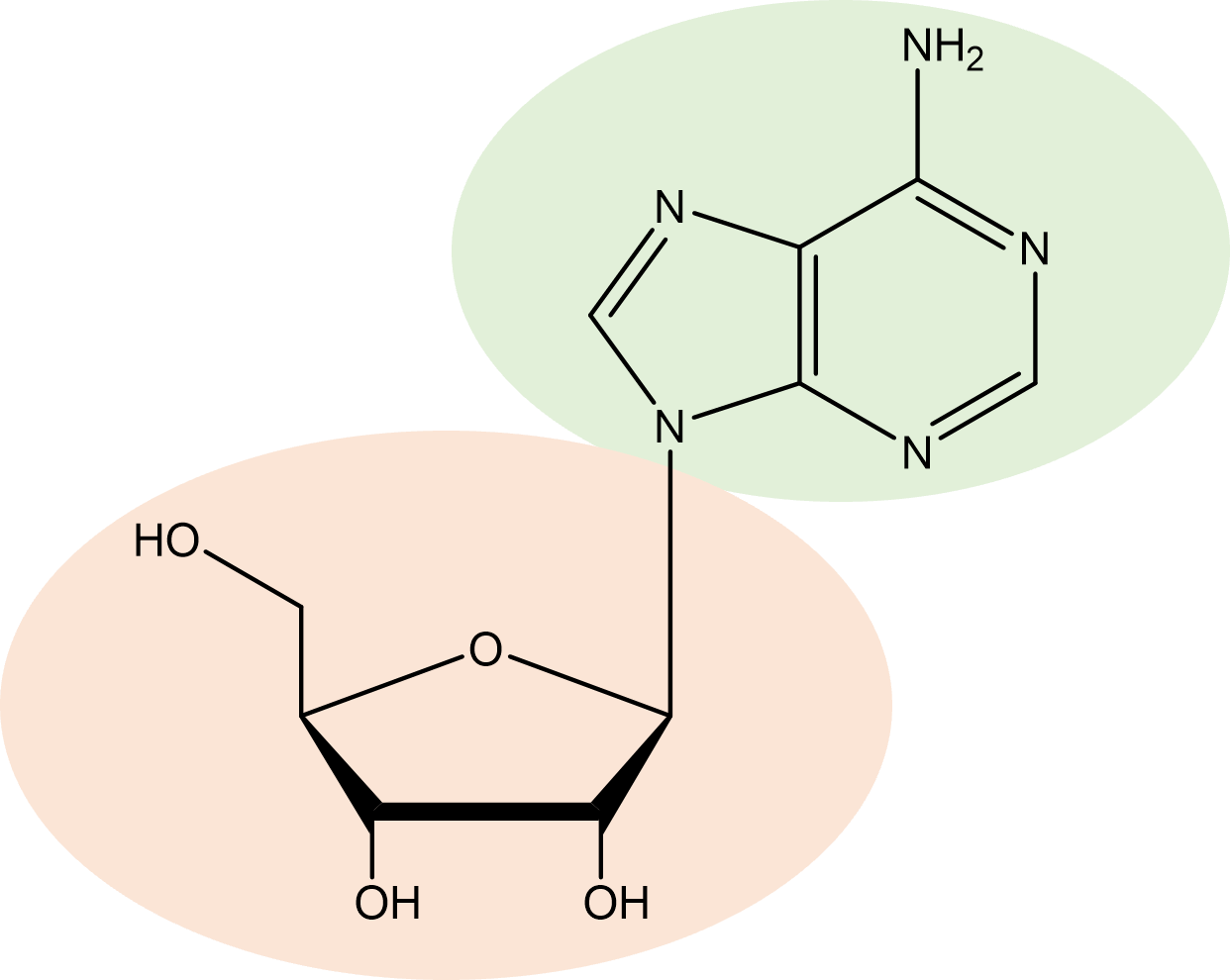 |
|||
| nucleotide | combination between a pentose, a nitrogen containing purine or pyrimidine base, and phosphate; building blocks of nucleic acids | 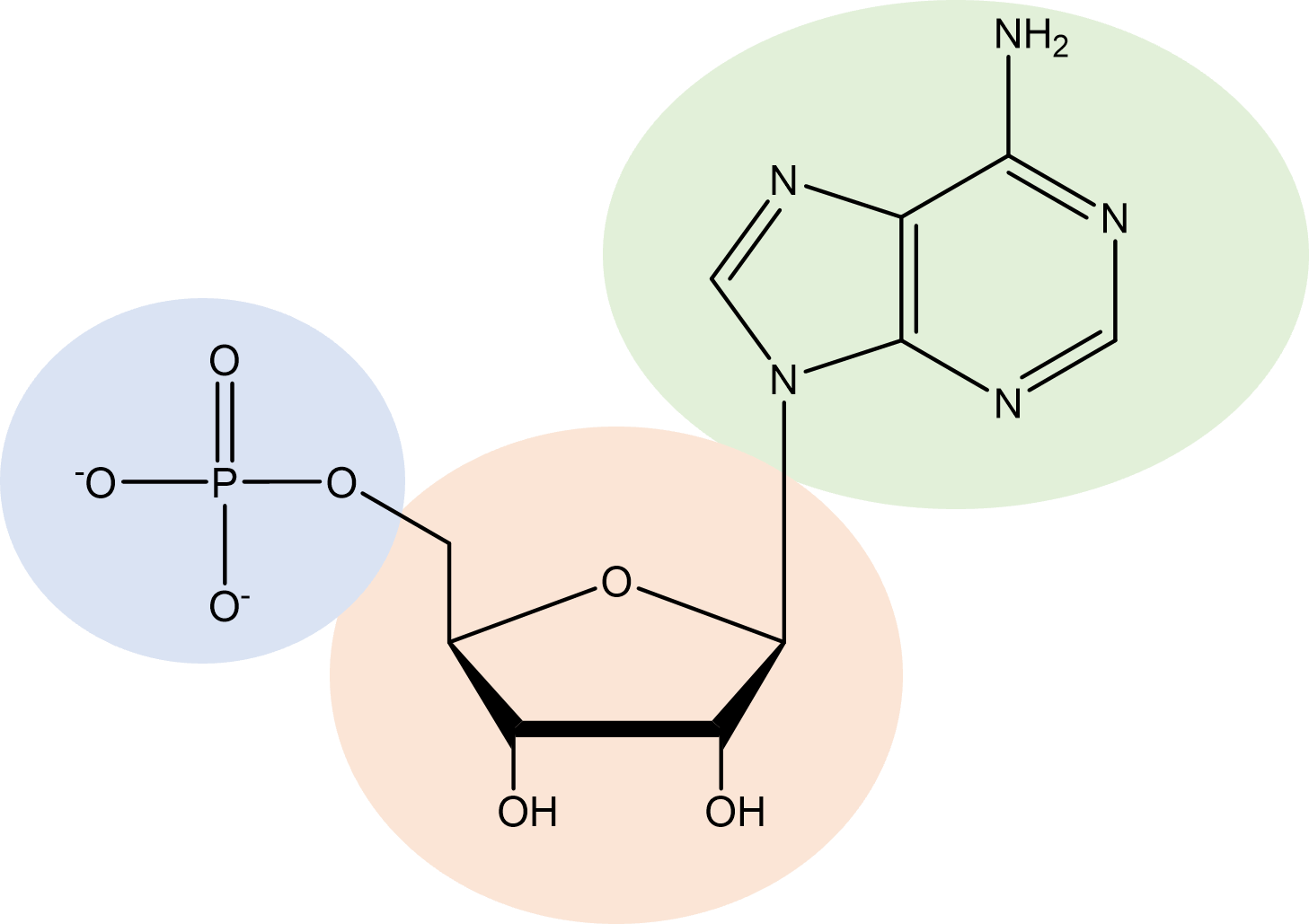 |
|||
| transcription | a segment of DNA is used to produce RNA; first step of making a protein from DNA is to make a copy of the gene from the DNA | ||||
| messenger RNA (mRNA) | codes for proteins | ||||
| ribosomal RNA (rRNA) | component of ribosomes | ||||
| transfer RNA (tRNA) | adapter molecule that brings the amino acid to the ribosome | ||||
| replication | process of making new copies of DNA | ||||
| template strand | DNA sequence that is transcribed to make RNA | ||||
| translation | process in which information in RNA is translated into a protein sequence | ||||
| codon | triplets sequence of nucleotides in mRNA; transcribed from DNA contains a sequence of bases specifying the protein to be made | Thomas Splettstoesser (www.scistyle.com), CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| genetic code | assigns all 20 amino acids to codons of mRNA | 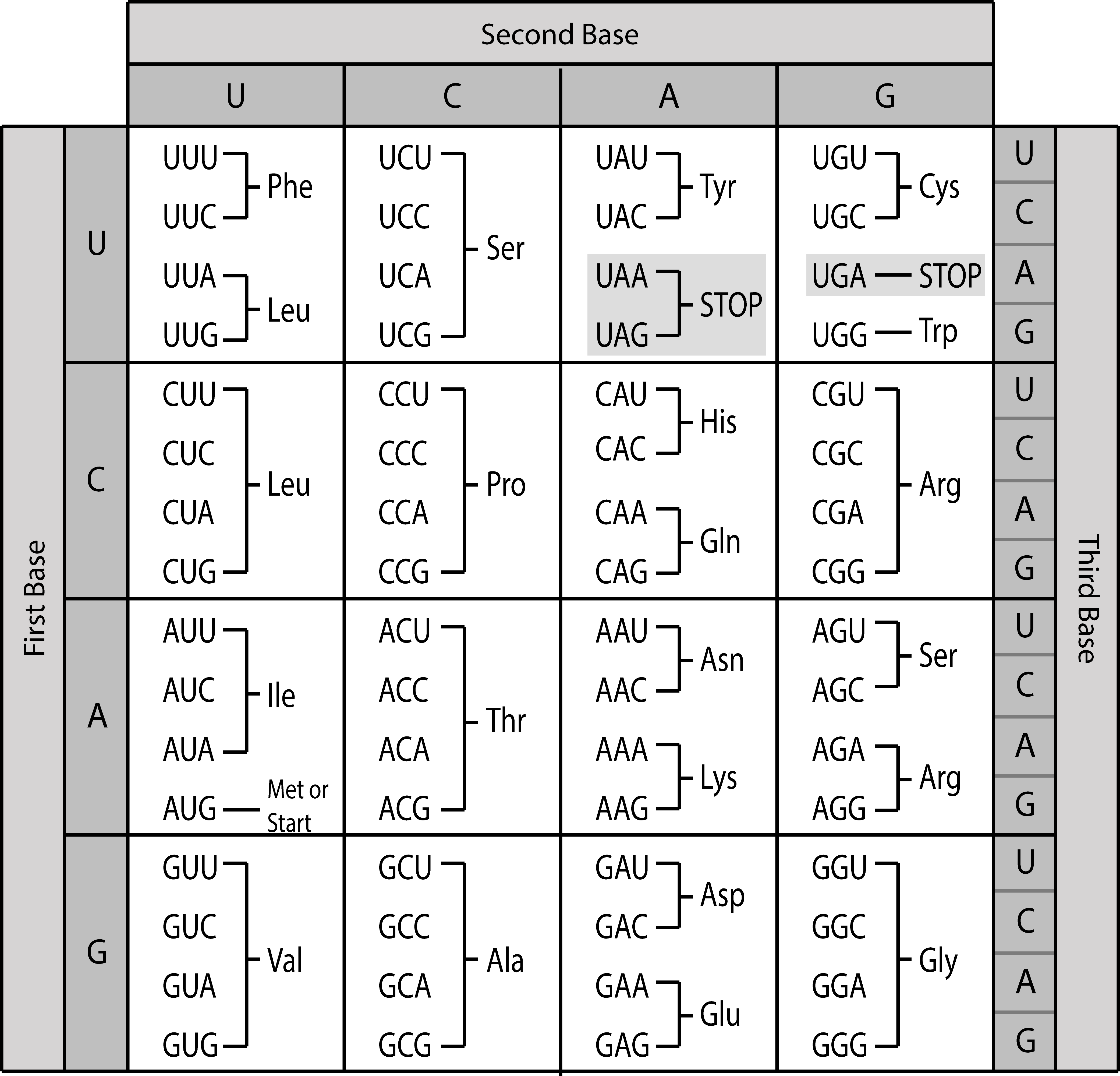 |
Sarah Greenwood, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| mutation | change in a DNA nucleotide sequence | ||||
| substitution (mutation) | a different nucleotide is substituted |  |
Hullo97, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| insertion (mutation) | a different nucleotide is substituted |  |
Hullo97, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| substitution (mutation) | the addition of a new nucloetide |  |
Hullo97, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| deletion (mutation) | the loss/removal of a nucloetide |  |
Hullo97, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| mutagen | chemical or physical agents that cause mutations | ||||
| metabolism | chemical reactions occurring in the body during the break down or building up of molecules | ||||
| metabolic pathway | series of steps in the chemical reactions in biological systems | ||||
| catabolic pathway |
chemical reactions that convert larger molecules into smaller molecules;energy is released |
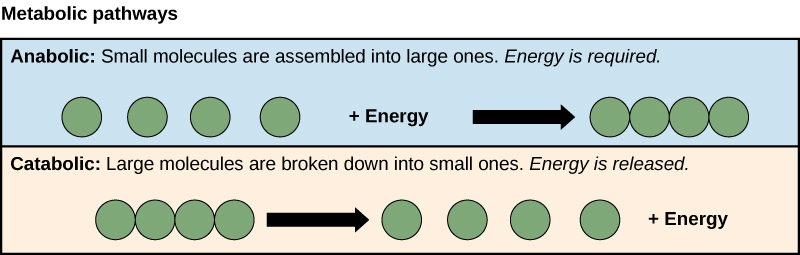 |
CNX OpenStax, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| anabolic pathway |
chemical reactions that convert smaller molecules into larrger molecules;energy is absorbed |
 |
CNX OpenStax, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| cellular respiration | biochemical process in which energy is transferred from carbohydrates and fats (high potential energy molecules) to ATP | ||||
| adenoside triphosphate (ATP) | energy currency of the cell; nucleotide; undergoes hydrolysis to ADP (low energy) during which energy is released. | NEUROtiker, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| digestion | stage I of catabolism where food molecules are broken down by hydrolysis reactions into the individual monomer units; occurs in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine | ||||
| glycolysis | catabolic process in which glucose is converted into pyruvate via ten enzymatic steps | Thomas Shafee, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| aerobic conditions | with oxygen | ||||
| anaerobic | without oxygen | ||||
| citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle) | series of reactions that degrade the two-carbon acetyl groups from acetyl CoA into carbon dioxide while generating the high-energy molecules NADH and FADH2. | Narayanese, WikiUserPedia, YassineMrabet, TotoBaggins, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons | |||
| beta-oxidation (ß-oxidation) | stage II of catabolism where fatty acids are converted to acetyl CoA | ||||
| reducing sugar | carbohydrate that can act as a reducing agent | ||||
| Benedict's test | qualitative test to determine whether a carbohydrate is a reducing sugar | ||||
| pyruvate | result of the breakdown of glucose during glycolysis | Pyruvic-acid-2D-skeletal.png: Benjah-bmm27derivative work: Kpengboy (talk)further derivative work GKFXtalk, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons |

This glossary content and images were created by Tanesha Osborne (except where noted otherwise). This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (except where noted otherwise).

