Gas Chromatography Lecture
- Page ID
- 283889
Announcements
- Complete your course evaluation!
- Monday May 14th is a review session
- Wednesday May 16th is the last exam (normal class time and place)
Previously…
- We looked at the details of how analytes (solutes) generally behave during chromatography
- Retention time and order
- Resolution
- Band broadening
- The effects of different experimental conditions
Today…
Gas chromatography (GC)!
- Mini-lecture followed by problem solving
SLO1: Describe the basic components of a GC instrument and a flame ionization detector
SLO2: Name and explain the factors that affect analyte retention and resolution in GC experiments.
SLO3: Describe temperature programming and its benefits.
Ch 24 – GC video
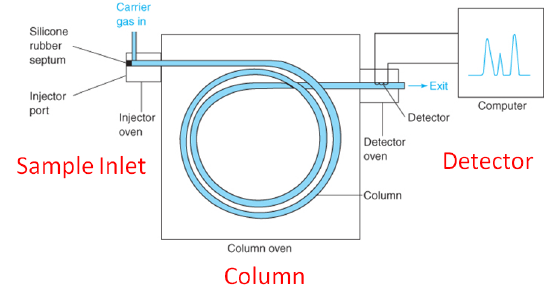
This is the general setup of a gas chromatograph:
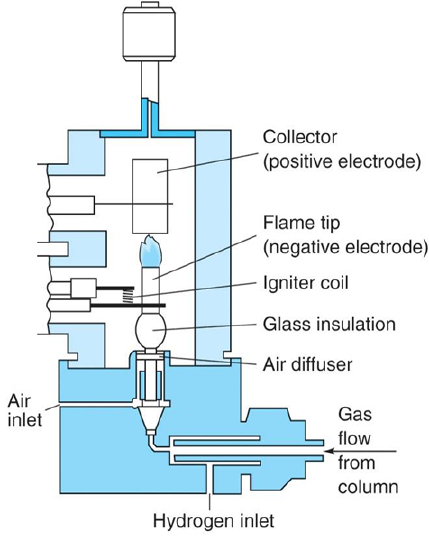
Flame Ionization Detector (FID):
- As organic analytes elute off the column and are combusted, CHO+ ions and electrons are generated and cause current flow between cathode and anode
- Responds to most organic compounds (but not NO, O2, N2, CO2)
- Sensitive (LODs in ng range)
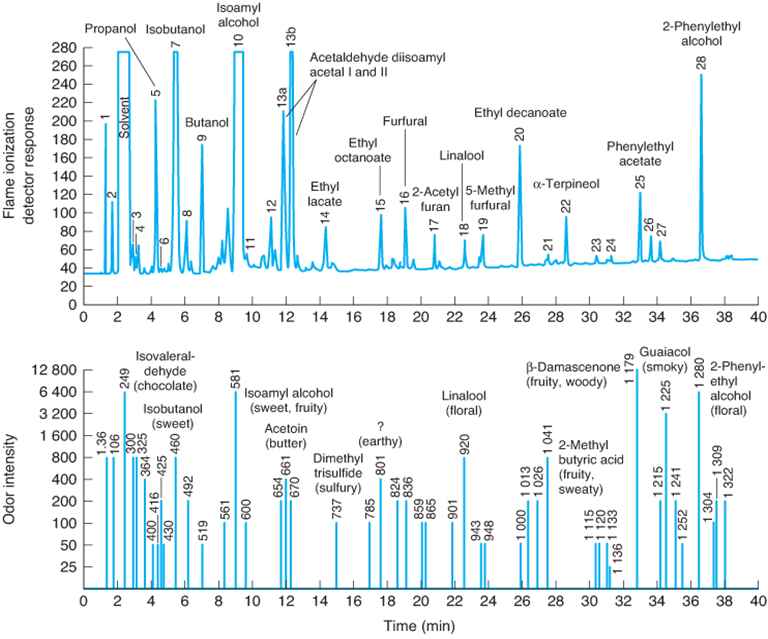
Tequila analyzed by GC using FID (top) and olfactory detection (bottom)
Worksheet
- Each student must fill in a worksheet.
- Must be handed in before you leave.
- It will be returned to you via Gradescope and will count as your clicker participation today.
- The Key for the worksheet will be placed online.
SLO1: Describe the basic components of a GC instrument and a flame ionization detector
SLO2: Name and explain the factors that affect analyte retention and resolution in GC experiments.
SLO3: Describe temperature programming and its benefits.
In summary, we discussed the main factors that influence retention time and resolution in GC experiments:
- Column temperature
- Boiling point of analyte
- Column composition
You should be able to explain how and why these factors influence the retention time and resolution of an analyte.
Conclusions / ToDo / Next Class
- Read Chapter 24 section 24-1, and Flame Ionization Detectors in section 24-3
Contributors and Attributions
- Krista Vikse, San Francisco State University (kristak@sfsu.edu)
- Sourced from the Analytical Sciences Digital Library


