8: Homework Solutions
- Page ID
- 43942
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
Hydrocarbons
(01) Answers may vary.
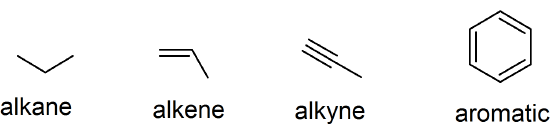
(02)
- F
- F
- T
- F
(03) Saturation: when an organic compound contains the maximum number of C to H bonds and they are all single bonds
- saturated
- unsaturated
- unsaturated
- saturated
- saturated
(04)
- Hydrophobic
- H-bond incapable
- Lipid-soluble
- Covalent bonding
- Many combinations
(05) The other compound most likely contains a structural feature that can H-bond with an O-H or N-H structural feature.
Saturated Hydrocarbons
(06)
- F
- T
- F
- F
- F
(07)
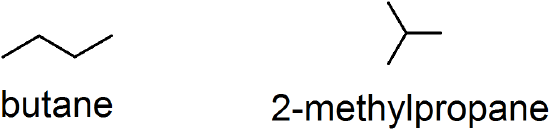
(08) alkyne: linear; alkene: trigonal planar; alkane: tetrahedral and considered ‘saturated’
(09)
- conformers
- completely different
- completely different
- identical
- identical
Writing Structures
(10)
- CH3CH(CH3)C(CH3)2CH3 or CH3CH(CH3)C(CH3)3
- CH3CH(CH3)CH(CH2CH3)CH(CH3)CH3
- CH3CH(CH3)C(CH3)2CH(CH3)2
- CH3C(CH3)2C(CH3)2C(CH3)2C(CH3)2CH3
- CH3CH(CH3)CH(CH3)2
(11)
- CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2CH3; 3,3-dimethylpentane
- CH2=CHCH(CH3)CH2CH3; 3-methyl-1-pentene
- CH3C=CC(CH3)3; 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentyne
- CH3CH(CH3)2C(CH3)2CH3 or CH3CH(CH3)2C(CH3)3;2,2,3,3-tetramethylbutane
- C6H5CH2CH3; ethylbenzene
(12)
- 3,4-diethyl-3-methylhexane
- 2,3,3,4-tetramethylhexane
- 2,3,4-trimethyl-2-pentene
- 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
- 3-ethyl-2,4-dimethylpentane
(13)
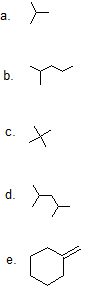
(14)
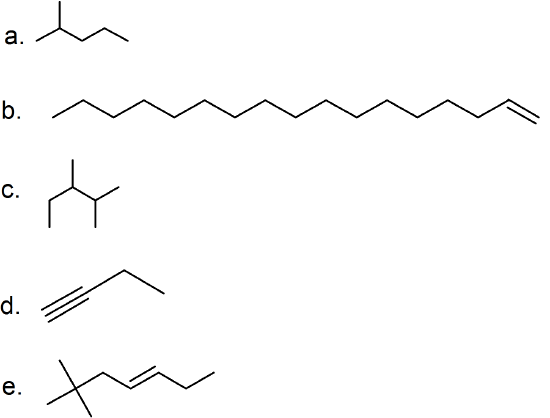
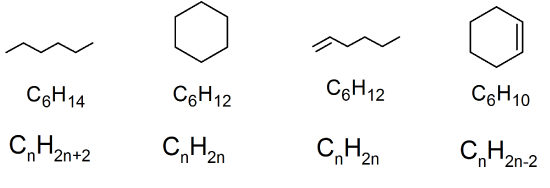
(15) unsaturated (CnH2n) vs saturated (CnH2n+2)
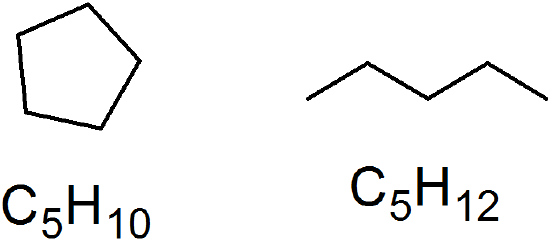
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Alkenes and Alkynes
(16)
- aromatic
- alkene
- alkene
- diene
- polyene
Naming Hydrocarbons
(17)
- heptane
- trans-2-pentene
- ethyne or acetylene (The common name is used more frequently than the IUPAC name.)
- nonane
- 1-butene
(18)
- 3-ethyl-2,2,3-trimethylhexane; C11H24
- 2,3,5-trimethylhexane; C10H22
- 3-ethyl-2,2,5-trimethylheptane; C12H26
- 1-ethyl-2-methylcyclohexane; C9H18
- 3,3-diethylpentane; C9H20
(19)
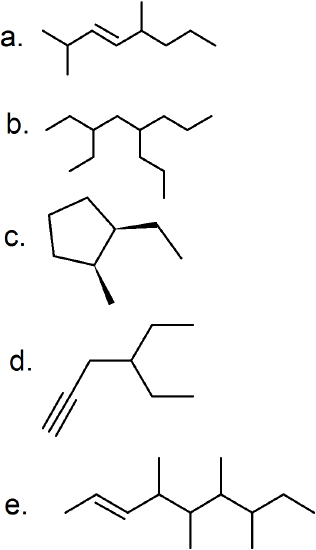
(20)
- 2,2-dimethylbutane
- 3,4,5-trimethylheptane
- 1-butyl-2-methylcyclopentane
- 2,3,3,4,4,5,6-heptamethylheptane
- 1,2,3,5-tetramethylcyclohexane
(21)
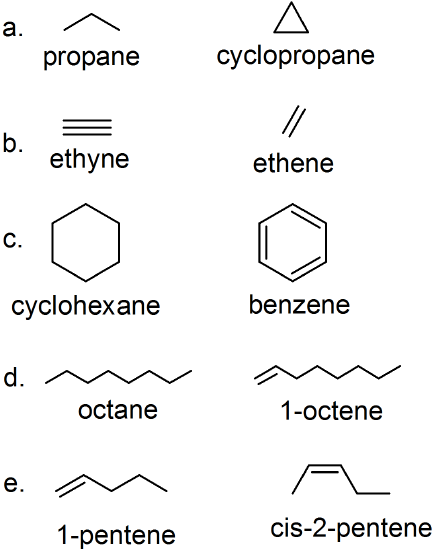
(22)
- 3-methylcyclobutene
- 3,4-dimethyl-2-pentene
- 5,6-dimethyl-1-heptene
- trans-2-octene
- 4-methyl-2-pentyne
(23)
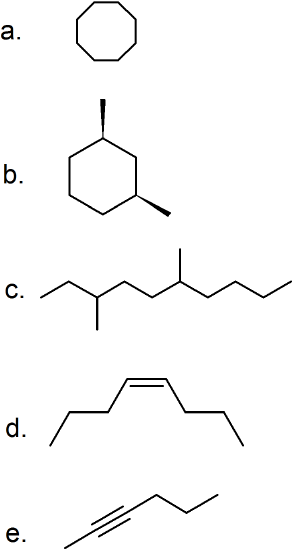
(24)
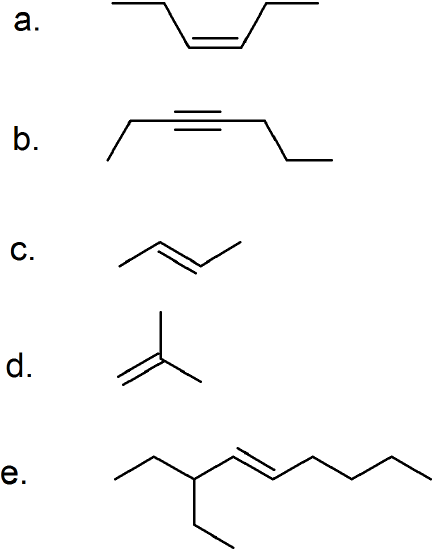
(25)
- 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne
- 4,4-dimethyl-2-pentyne
- 1-pentyne
- 3-ethyl-3,4-dimethyl-1-pentyne
- 2,2,5-trimethyl-3-hexyne
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
(26)
(27)
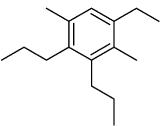
(28)
(29)
- Vitamin B2
- Vitamin B5 has 4 continuous C's and Vitamin B2has 5 continuous in the aromatic ring.
- Vitamin B5 C9H17NO5 and Vitamin B2 C17H20N4O6
- Water soluble because there are less than 4 non-polar carbons per polar group.
- Ye4s
(30) A
Additional Exercises
31. organic
32. Methylcyclopentane and cyclohexane both have the chemical formula of C6H12, so they are structural isomers.
33.
- Two numbers are needed to indicate two substituents; 2,2-dimethylpropane.
- The lowest possible numbers were not used; 2,2,3-trimethylbutane.
- An ethyl substituent is not possible on the second carbon atom; 3,5-dimethylheptane.
- A propyl substituent is not possible on the fifth carbon atom; 3,4,5-trimethyloctane.
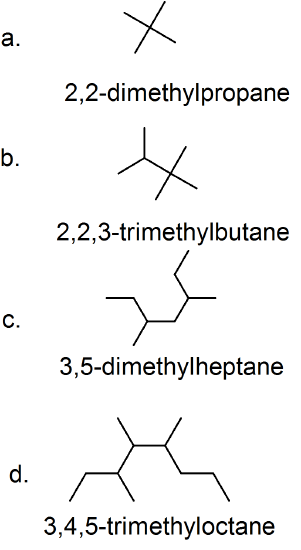
34.
- C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
- 2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O
35. 7.6 lb
36.
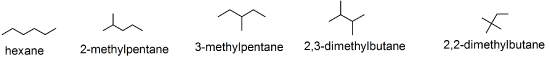
37.
- same
- structural isomers
- structural isomers
38.
- i & ii (C7H14) and iii & iv (C7H16)
- i & v

