6: Homework Solutions
- Page ID
- 43940
Molecular Mass, Formula Mass, and Molar Mass
(1) 1 mole = 6.02 x 1023
(2) What is the mass of each of the following quantities:
- 2.0 g
- 36 g
- 21 g
- 18 g
- 12 g
(3) Chlorine atoms because they contain more protons and neutrons.
(4) 32.05 amu/molecule; 32.05 g/mole
(5) For each of these different compounds, using the given masses, calculate how many moles each sample contains.
- 0.053 mole NaCl
- 0.14 mole H2O2
- 0.3 mole LiOH
- 0.33 mole O2
- 1.3 mole NH3
(6) Contrasting with the previous problem, this time find the mass of each sample by using the given number of moles.
- 190 g P
- 220 g Fe
- 198 g F2
- 47 g HCl
- 160 g Ne
(7) Combine the following ions into an ionic compound and calculate the molar mass.
- (NH4)2S; 68.16 g/mol
- Sr3N2; 290.88 g/mol
- AlF3; 83.98 g/mol
- CaI2; 293.88 g/mol
- Ag2O; 231.74 g/mol
Mole Questions
(8) 84.01 g/mol
(9) 0.50 mol NaHCO3
(10) 35 g NaHCO3
(11) 1.8 x 1023 formula units of NaHCO3
(12) 2.3 x 1022 Na+ ions
(13) 92.11 g/mol
(14) 0.46 mole glycerine
(15) 39 g glycerine
(16) 1.6 x 1023 molecules glycerine
(17) 6.3 x 1022 C atoms
(18) a) 194.22 g/mol caffeine and 163.94 g/mol for sodium phosphate
b) Caffeine is covalent because all the atoms are non-metals. Sodium phosphate is ionic because it contains a metal cation and polyatomic anion.
c) sodium phosphate because 0.014 mol sodium phosphate is greater than 0.012 mol caffeine
(19) CH2O because it has the smallest molar mass.
(20) a) NaHCO3
b) NaHCO3
Writing and Balancing a Chemical Equation
(21) Balance the following chemical equations.
- \(2 Al_{(s)} + 6 H_2O_{(l)} \rightarrow 2 AlOH_{(aq)} + 3 H_{2\;(g)}\)
- \(N_{2\;(g)} + 2 O_{2\; (g)} \rightarrow 2 NO_{2\; (g)}\)
- \(H_2CO_{3\;(aq)} \rightarrow H_2O_{(l)} + CO_{2\; (g)}\)
- \(2 P_2O_{5\;(s)} \rightarrow P_{4\;(s)} + 5 O_{2\; (g)}\)
- \(N_{2\;(g)} + 4 H_{2\;(g)} + Cl_{2\;(g)} \rightarrow 2 NH_4Cl_{(s)}\)
(22) Balance each of the given combustion reactions.
- \(2 C_6H_6(l) + 15 O_{2\; (g)} \rightarrow 12 CO_{2\; (g)} + 6 H_2O_{(g)}\)
- \(2 C_2H_2(g) + 5 O_{2\; (g)} \rightarrow 4 CO_{2\; (g)} + 2 H_2O_{(g)}\)
- \(2 C_8H_{18}(l) + 25 O_{2\; (g)} \rightarrow 16 CO_{2\; (g)} + 18 H_2O_{(g)}\)
- \(C_4H_9OH(l) + 6 O_{2\; (g)} \rightarrow 4 CO_{2\; (g)} + 5 H_2O_{(g)}\)
- 2 CH3(CH2)4OCH2CH3(l) + 21 O2(g) → 14 CO2(g) + 16 H2O(g)
(23) The next set of chemical equations are NOT properly balanced. Alter the coefficients as needed so that the equations are properly balanced.
- \(N_{2\;(g)} + 3 H_{2\;(g)} \rightarrow 2NH_{3\;(l)} \)
- \(Ba(OH)_2\;{(aq)} + H_2SO_{4\;(aq)} \rightarrow BaSO_{4\;(aq)} + 2 H_2O(l) \)
- \(CH_{4\; (g)} + N_{2\;(g)} \rightarrow 2 HCN(g) + H_{2\;(g)} \)
- \(4 Cl_{2\;(g)} + 4 H_2O(l) \rightarrow HClO_{4\;(aq)} + 7 HCl(aq) \)
- \(PH_3(aq) + 2O_{2\; (g)} \rightarrow H_3PO_{4\;(aq)} \)
Energy and Chemical Reactions
(24)
- 54 kcal; 2.3 x 105 J
- 36 kcal; 1.5 x 105 J
- 28 kcal; 1.2 x 105 J
- 104 kcal; 4.3 x 105 J
- 128 kcal; 5.4 x 105 J
(25)
- exothermic
- endothermic
- exothermic
- exothermic
- endothermic
(26) Perform the following unit conversions.
- 4.1 x 10-3 kcal
- 1.9 x 103 cal
- 3.77 x 103 J
- 837 kJ
- 1.3 kcal
(27) Proteins and carbohydrates both contain 4 Cal per gram. Fats contain the most energy at 9 Cal per gram.
(28) For each of the following characteristics, determine whether they are more common of anabolic reactions or catabolic reactions.
- catabolic
- anabolic
- anabolic
- catabolic
(29) catabolic
Kinetics: Reaction Rates
(30)
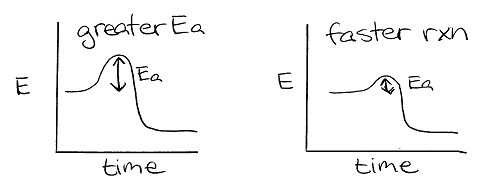
(31)
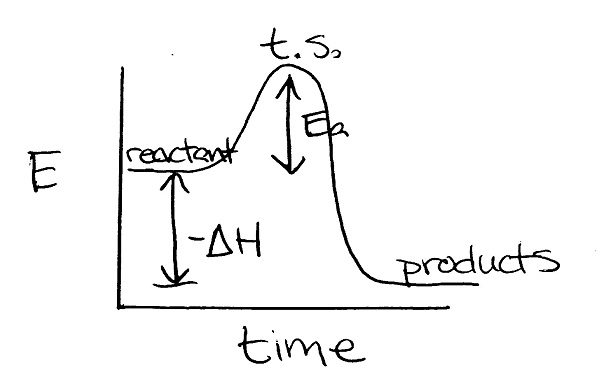
- exothermic because the products are lower in energy than the reactants.
- refer to graph
- refer to graph
- refer to graph
- refer to graph
- The transition state and activation energy decrease when a catalyst is added. The energy of the reactants, products, and enthalpy remain the same.
(32) Many things can affect the rate of a reaction. Determine what effect the following scenarios may have on a reaction.
- increases the reaction rate
- increases the reaction rate
- decreases the reaction rate
- decreases the reaction rate
- increases the reaction rate
(33) Answer the following true or false statements.
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
(34)
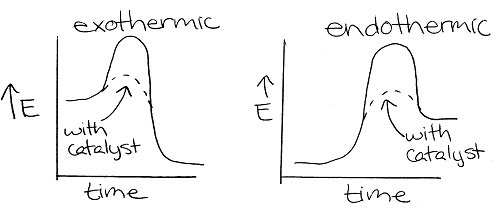
Equilibrium & Le Châtelier’s Principle
(35)
- equilibrium
- right
- left
- right
- left
- left
- right
(36)
- \( CO_{(g)} + 2H_{2\; (g)} \rightleftharpoons CH_3OH_{(g)}\)
- right
- left
- right
- left
Additional Exercises
(37) 480 kcal
(38) Protein: 700 kcal & 175 g; Carbohydrates: 900 kcal & 225 g; Fat: 400 kcal or 44 g
(39)
- endothermic
- exothermic
- the glass feels colder because the heat moves into the iodine crystals as they sublimate.
(40) C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + HEAT
(41) 2300 mol of water
(42) 0.0187 mol Fe
(43)
- 2.67 mol of Ca2+ and 5.34 mol of Cl-
- 5.34 mol of Na+, 2.67 mol of SO42-
- 2.67 mol of Al3+, 8.01 mol of NO3-
- 8.01 mol of Fe2+, and 5.34 mol of PO43-
(45) 324 g/mol
(46) 5.3 x 10-7 mol hemoglobin

