10: Organic Functional Groups Physical Properities and Intro to Acid Base Chemistry
- Page ID
- 43924
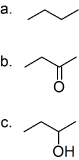
(01) From most to least, rank the following compounds in order of water solubility.
a. 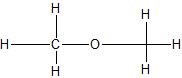
b. 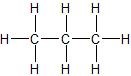
c. 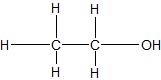
(02) Rank each of the following (with 1 being lowest, 3 being highest) in order of their respective boiling points.
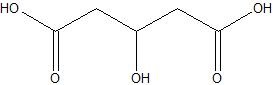
(03) Predict the water solubility of the molecule below and explain your reasoning using intermolecular forces.
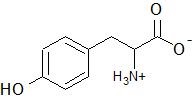
(04) Tyrosine, an amino acid, is shown below. Is the amino group in its neutral or ionic form? Is the carboxylic acids in its neutral form or its ionic form? Cite any other functional group(s) present.
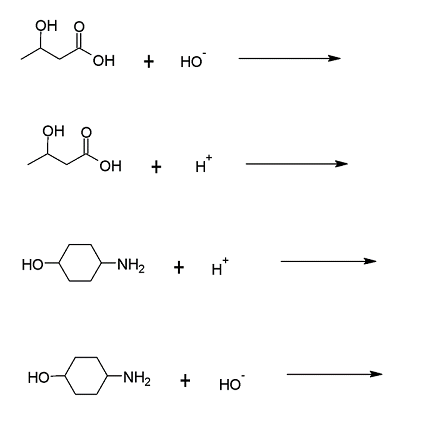
(05) If a reaction occurs, write the product(s) using skeletal-line structure for the organic products. If no reaction occurs, then write “no reaction” on the product side of the reaction arrow.
Additional Questions
(06) Acetic acid has the following structure:
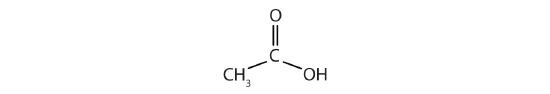
This molecule can lose a hydrogen ion (H+) and the resulting anion can combine with other cations, such as Na+:
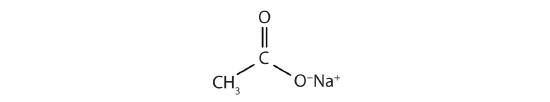
Name this ionic compound.
(07) Formic acid (HCOOH) loses a hydrogen ion to make the formate ion (HCOO−). Write the chemical formula for each ionic compound: potassium formate, calcium formate, and iron(III) formate.
(08) The molecular formula C3H6 represents not only propene, a compound with a carbon–carbon double bond, but also a molecule that has all single bonds. Draw the molecule with formula C3H6 that has all single bonds. What is the name that describes the relationship betweeen these two compounds?
(09) In addition to themselves, what other atom(s) can carbon atoms bond with and make covalent bonds that are nonpolar (or as nonpolar as possible)?
(10) Acetaminophen, a popular painkiller, has the following structure:
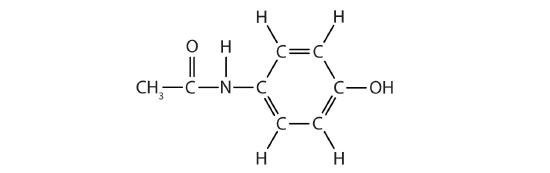
Draw the bond-line structure and then circle and name the functional groups.
(11) Glutamic acid is the parent compound of monosodium glutamate (known as MSG), which is used as a flavor enhancer. Glutamic acid has the following structure:
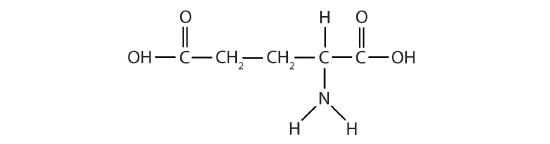
Circle the acidic functional group(s) and box the basic functional group(s).
There is a structural error in the compound above. Re-draw the structure correcting the error.

