7: Solids, Liquids and Gases: Questions
- Page ID
- 43921
States of Matter
(01) The three states of matter differ primarily in terms of shape and volume. Describe solids, liquids and gases in these terms.
(02) Is a solar panel at night an example of potential energy or kinetic energy? Explain your answer.
(03) The following situations are examples of kinetic or potential energy. Determine which ones are kinetic and which ones are potential.
- A waterwheel on a rushing river
- A bouncing basketball
- Sand in an hourglass falling
- Water sitting in a glass
- A book about to fall off a shelf
(04) In each of the following pairs, which object has the most kinetic energy?
- A car traveling at 65 mph or 75 mph
- A match burning at 100 degrees Celsuis or 110 degrees Celsuis
- Digesting a 200 Calorie snack or a 300 Calorie snack
- An engine burning a 20 gallon tank or an engine burning a 10 gallon tank
- A 20-lb lead weight falling from a cliff or a 15-lb lead weight falling from a cliff
(05) Of the three physical states of matter, rank them in order of kinetic energy from least to greatest; then, do the same for potential energy.
(06) Rank the following substances by kinetic energy, from lowest to highest: ice, nitrogen gas, liquid mercury
(07) Temperature can be measured in a variety of units. Convert 25◦C (average room temperature) into Fahrenheit. Then, convert 98.6◦F (average human body temperature) into Celsius.
(08) Kelvin is a temperature directly related to Celsius. Convert a temperature of 350K to Celsius. Then convert that Celsius temperature to Fahrenheit.
(09) In previous chapters you’ve learned that solid H2O floats in liquid H2O. Would you expect something like solid mercury to float in liquid mercury the way water does? Why or why not?
Changes of State
(10) Between the solid and liquid states, is there a change that occurs in the bonds and/or intermolecular forces?
(11) In general, what happens with energy (adding/removing) to cause the progression of phase change from solid to liquid, and liquid to gas (and for solid to gas in the case of sublimation)? What about the progression of phase changes in the opposite direction?
(12) Explain the difference between being burned by boiling water and being burned by steam vapor. Which one is able to cause more harm?
(13) Two substances, propane (CH3CH2CH3) and propanol (CH3CH2CH2OH), have similar structures. However, at room temperature propane is a gas and propanol is a liquid. What is the key difference between them that causes their phases to be different at the same temperature?
Pressure
(14) Name at least three different units of measurement for pressure and relate them using conversion factors.
(15) Perform the following conversions of pressure from one unit to another.
- 120 psi into Torr
- 6.0 atmospheres into pascals
- 2800 mmHg into atmospheres
(16) Examine these three substances shown below. Their names are butane, isopropyl alcohol and formaldehyde, respectively.
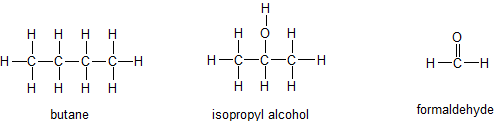
Arrange them in order from lowest vapor pressure to highest, according to what you know about intermolecular forces.
Arrange them in order from lowest boiling point to highest, according to what you know about intermolecular forces.
Gases
(17) A helium tank has a volume of 4.0 Liters. The pressure on the tank is 5.0 atmospheres. To save room the helium is transferred directly into a tank with a volume of 1.5 liters. What will the new pressure be in the new tank?
(18) If an athlete is training in a high altitude area where the atmospheric pressure is 0.90 atmospheres and their healthy lung capacity is 3.2 liters, what would the pressure be if they developed a respiratory disease that decreased their lung capacity to 2.5 liters?
(19) Answer the following True or False questions.
- As pressure increases, volume increases.
- As pressure decreases, volume increases
- As volume decreases, pressure increases
(20) Normal air contains a mixture of mostly nitrogen, with oxygen, carbon dioxide and argon gases. If the partial pressure of nitrogen is 70% of the total pressure, oxygen is 18% of the total pressure, and carbon dioxide is 10% of the total pressure, what is the partial pressure of Argon if the total pressure is 760 mmHg?
(22) A mixture of the halogen gases has four partial pressures that compose the total pressure. If chlorine gas has a partial pressure of 2.00 atmospheres, bromine gas has a partial pressure of 13.0 psi, fluorine gas has a partial pressure of 800 mmHg and iodine gas has a partial pressure of 900 Torr, what is the total pressure in mmHg? What is the percent composition for each of the gases in the mixture?

