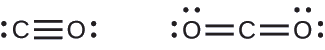4.3: Multiple Covalent Bonds
- Page ID
- 86204
- Identify when a multiple bond (double or triple) is needed to complete an octet.
The sharing of a pair of electrons represents a single covalent bond, usually just referred to as a single bond. However, in many molecules atoms attain complete octets by sharing more than one pair of electrons between them:
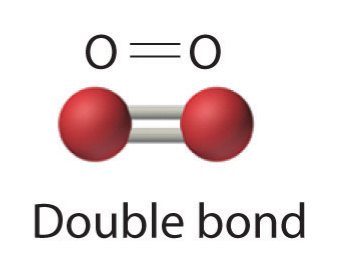
- Two electron pairs shared a double bond
- Three electron pairs shared a triple bond
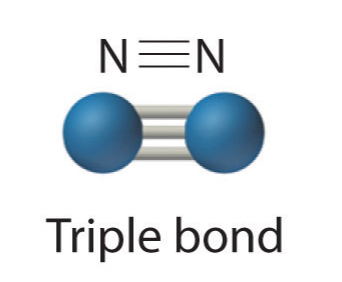
Because each nitrogen contains 5 valence electrons, they need to share 3 pairs to each achieve a valence octet. N2 is fairly inert, due to the strong triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms.
In addition to nitrogen and oxygen, carbon will also commonly form multiple bonds to complete valence octets. Additional examples involving these three atoms are shown below.
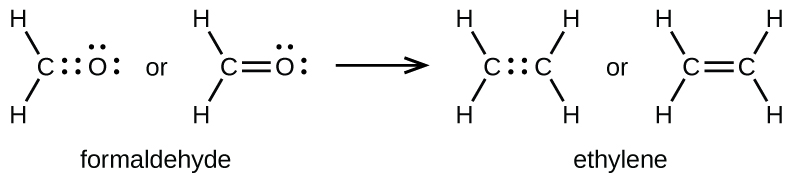
A double bond is formed between the carbon and oxygen atoms in CH2O (formaldehyde) and between the two carbon atoms in C2H4 (ethylene):
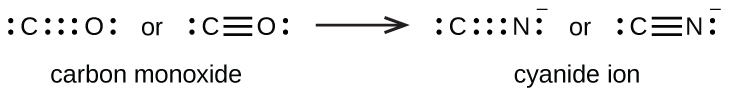
A triple bond is formed between carbon and oxygen in carbon monoxide (CO) and between carbon and nitrogen in the cyanide ion (CN–):
NASA’s Cassini-Huygens mission detected a large cloud of toxic hydrogen cyanide (HCN) on Titan, one of Saturn’s moons. Titan also contains ethane (H3CCH3), acetylene (HCCH), and ammonia (NH3). What are the Lewis structures of these molecules?
Solution
Calculate the number of valence electrons.
- HCN: (1 × 1) + (4 × 1) + (5 × 1) = 10
- H3CCH3: (1 × 3) + (2 × 4) + (1 × 3) = 14
- HCCH: (1 × 1) + (2 × 4) + (1 × 1) = 10
- NH3: (5 × 1) + (3 × 1) = 8
Draw a skeleton and connect the atoms with single bonds. Remember that H is never a central atom:
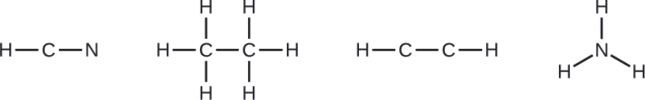
Where needed, distribute electrons to the terminal atoms:
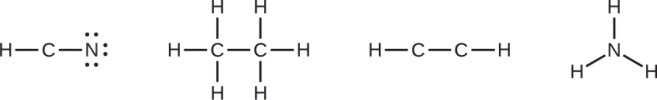
- HCN: six electrons placed on N
- H3CCH3: no electrons remain
- HCCH: no terminal atoms capable of accepting electrons
- NH3: no terminal atoms capable of accepting electrons
Where needed, place remaining electrons on the central atom:
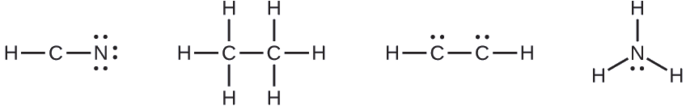
- HCN: no electrons remain
- H3CCH3: no electrons remain
- HCCH: four electrons placed on carbon
- NH3: two electrons placed on nitrogen
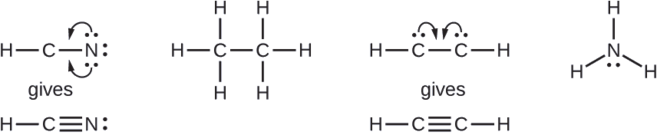
Where needed, rearrange electrons to form multiple bonds in order to obtain an octet on each atom:
- HCN: form two more C–N bonds
- H3CCH3: all atoms have the correct number of electrons
- HCCH: form a triple bond between the two carbon atoms
- NH3: all atoms have the correct number of electrons
Both carbon monoxide, CO, and carbon dioxide, CO2, are products of the combustion of fossil fuels. Both of these gases also cause problems: CO is toxic and CO2 has been implicated in global climate change. What are the Lewis structures of these two molecules?
- Answer
-