20.15: 20.7a Nucleophilic Addition of Hydrazin - The Wolff-Kishner Reaction
- Page ID
- 143463
Objectives
After completing this section, you should be able to
- write an equation to illustrate the Wolff‑Kishner reduction of an aldehyde or ketone.
- identify the product formed from the Wolff‑Kishner reduction of a given aldehyde or ketone.
Key Terms
Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key term below.
- Wolff‑Kishner reduction
Study Notes
After studying this section, you can add yet another method of reducing organic compounds to your growing list of reduction reactions.
Aldehydes and ketones can be converted to a hydrazine derivative by reaction with hydrazine. These "hydrazones" can be further converted to the corresponding alkane by reaction with base and heat. These two steps can be combined into one reaction called the Wolff-Kishner Reduction which represents a general method for converting aldehydes and ketones into alkanes. Typically a high boiling point solvent, such as ethylene glycol, is used to provide the high temperatures needed for this reaction to occur. Note! Nitrogen gas is produced as part of this reaction.
Reaction of Aldehydes or Ketones with Hydrazine Produces a Hydrazone
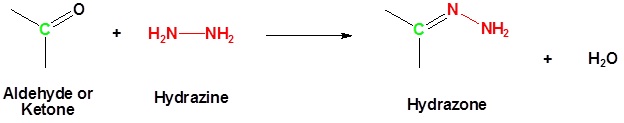
Reaction with a Base and Heat Converts a Hydrazone to an Alkane
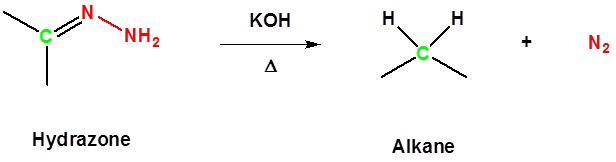
Both Reactions Together Produces the Wolff-Kishner Reduction
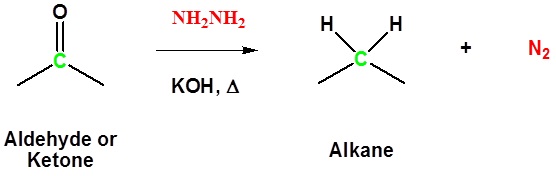
Example
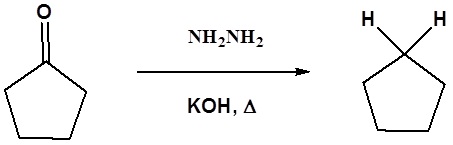
Mechanism of the Wolff-Kishner Reduction
1) Deprotonation of Nitrogen
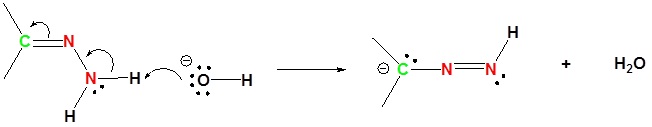
2) Protonation of the Carbon
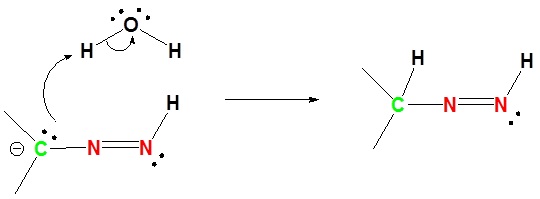
3) Deprotonation of Nitrogen
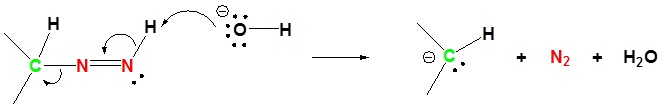
4) Protonation of Carbon
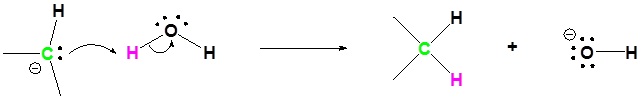
Problems
1) Please draw the products of the following reactions.
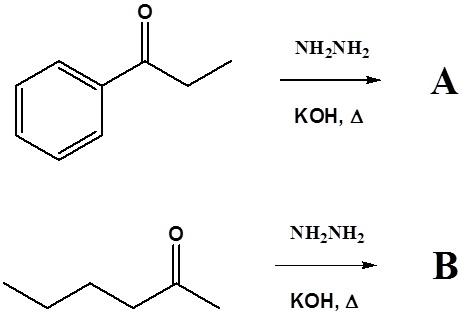
Answers
1)
Contributors
Dr. Dietmar Kennepohl FCIC (Professor of Chemistry, Athabasca University)
Prof. Steven Farmer (Sonoma State University)

