3.20: Quiz 3C Key
- Page ID
- 19273
- Clearly indicate true (T) or false (F) for the following statements (2 pts each):
| __F__ | A chair conformer with substituents in the equatorial position is less stable. |
| __T__ | The stronger the acid, the more stable the conjugate base. |
| __T__ | Cyclopropane has more ring strain than cyclohexane, which is why molecules containing cyclopropane are often used for rocket fuel or explosives. |
- Give the best answer for the following multiple choice questions: (2 pts each)
Indicate which of the following molecules has a conjugated pi system.
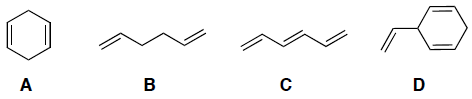

pi-bonds must be directly connected so p-orbitals overlap, sp3 carbons blocking…
Rank the following in order of deceasing λmax (i.e. decrease in nm):
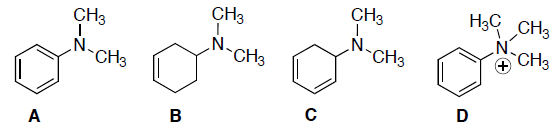

- A>B>C>D
- D>A>B>C
- A>D>C>B
- B>C>D>A
- D>B>A>C
If we are decreasing nm, then we rank with decreasing conjugation… A has a lone pair on N that adds to the 3 conjugated pi-bonds, but D has no lone pair and only 3 pi-bonds, C only has 2 pi bonds.
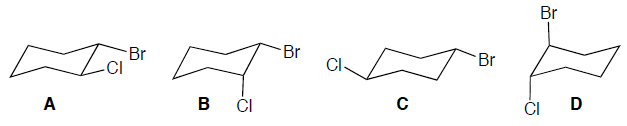
Which of the following represents a cis isomer of cyclohexane?

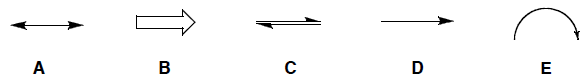
Which arrow is used to represent the movement or delocalization of electrons?

- (8 pts) Benzene and cyclohexane are both important 6-membered ring carbon structure that are predominant in pharmaceutical molecules and other molecules of biological interest. Draw the structure for each and then provide 3 chemical facts (i.e. orbitals, hybridization, conformation, etc) for each molecule that indicates the important differences in their structures.
| benzene | cyclohexane |
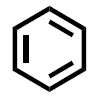 | 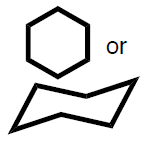 |
examples of possible chemical facts (others might also be acceptable):
|
|
- (6 pts) Which compound (A or B) is a stronger acid? In each case, circle your answer and provide a very brief explanation for your answer. (In this case, a simple correct phrase is sufficient for your answer…)
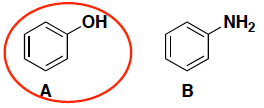
The oxygen on compound A is more electronegative and stabilizes the anion of the conjugate base better. (You will notice that both anions also have resonance stabilization.)
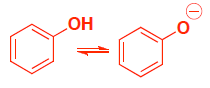
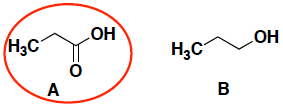
Compound A has resonance stabilization because the anion of the conjugate base is delocalized, and thus more stable. (both also have stabilization from the electronegative oxygen)

anion on electronegative oxygen, but no resonance stabilization
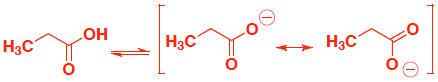
anion on electronegative oxygen, now also has resonance stabilization
(note: you didn’t have to show the conjugate base or draw resonance contributors for this question, but you possibly will have to in future questions)
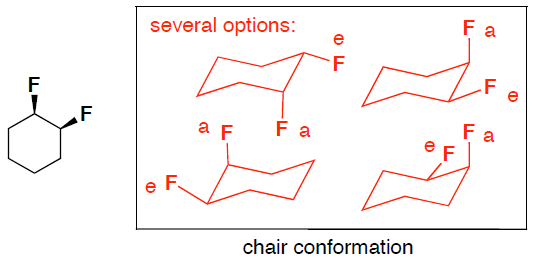
- (6 pts) Convert the flat difluorocyclohexane structure shown below to a drawing of a chair conformer. Clearly label if the fluoro groups are axial or equitorial in your chair structure.
- Delocalized electrons and resonance (10 pts total)
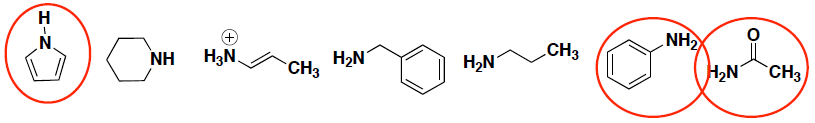
- Circle any of the following compounds that have a nitrogen atom with delocalized electrons.
- For each pair of resonance structures shown below (A and B), circle which resonance contributor makes a greater contribution to the resonance hybrid. Briefly explain your answer.
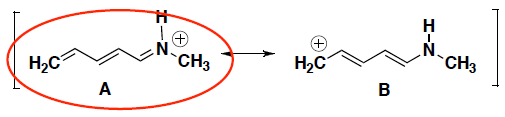
Structure A is the greater resonance contributor because it has all atoms with a full octet. Structure B has a carbocation, which means it does not have a full octet. (Note: We donʼt look at what electronegativity that atom with the charge has unless we are comparing all atoms with full octets)
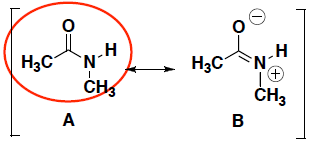
Structure A is a greater resonance contributor because it has fewer (i.e. no) formal charges. (But even with charges, structure B is a super important resonance contributor for amides like this and has a big influence on the structures of peptides and proteins, which are made of many amide bonds – more about this in 8B!)

