3.14: Quiz 2C Key
- Page ID
- 19095
- Clearly indicate true (T) or false (F) for the following statements (2 pts each):
| __F__ | A tert-butyl ethyl ether molecule has 5 carbon atoms. (False, It has 6!) |
| __T__ | The staggered conformation of ethane is more stable than the eclipsed form of ethane because there is less steric strain and electron repulsion. |
| __F__ | A molecule containing only C-H bonds has hydrogen-bonding interactions. (False, it has van der Waalʼs interactions!) |
| __T__ | A sigma bond is stronger than a hydrogen bond. |
- Multiple Choice: (2 pts each)
- Where are the two lone pairs of electrons of the oxygen atom in an alcohol molecule located?

- in two s orbitals
- in two p orbitals
- in two sp orbitals
- in two sp3 orbitals
- in two sp2 orbitals
- Which of the following conformations of butane is the most stable?
- Where are the two lone pairs of electrons of the oxygen atom in an alcohol molecule located?
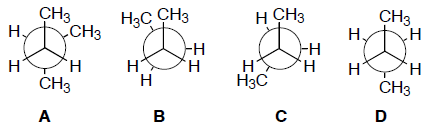

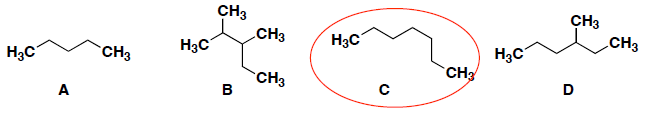
 Which of the following has the greatest van der Waal's interaction between molecules of the same kind?
Which of the following has the greatest van der Waal's interaction between molecules of the same kind?
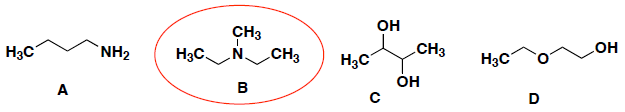
 Which of the following will NOT form hydrogen bonds between its molecules?
Which of the following will NOT form hydrogen bonds between its molecules?
- (6 pts) You have obtained a summer internship with a pharmaceutical company and they have a secret new sedative compound that can penetrate the non-polar membranes of cells better then current drugs on the market. Which of the following compounds will be more effective as a sedative? Circle your answer and provide a brief explanation for your answer.
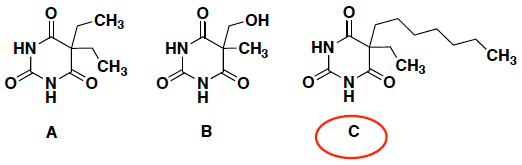
All three molecules have polar groups, but molecule C has a long chair of C and H atoms that is non-polar, and this makes the overall molecule less polar. This non-polar group will make the molecule penetrate (i.e. be soluble in) the non-polar membranes of cells because it has more surface area for van der Waalʼs interactions with the cell membrane molecules.
(Molecule B is the most polar since it has an extra OH group.)
Note: For this type of question, the size of the molecule is not related to the answer since it is more important to consider the type of interactions that the molecule can have to make it “soluble” in the membrane.
- (6 pts) Ethanol and butylamine have the same boiling point, even though they have different numbers of carbon atoms. Consider the molecular interactions for butylamine and ethanol and explain why they have the same boiling point.
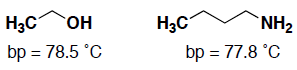
Both molecules have C-C and C-H for van der Waalʼs interactions and also OH and NH groups capable of hydrogen-bonding, so you have to consider/compare the strength of these interactions. The oxygen is more electronegative so that the O-H bond has a stronger dipole, which means that the hydrogen bonding will be stronger between molecules with the OH group compared to the hydrogen-bonding between molecules with the NH group. (see page 60-62) However, the butylamine has 2 more carbons, which means that it has more surface area for van der Waalʼs interactions. Overall, it balances out and they are about the same bp!
- (6 pts) Provide a brief explanation why a C-C single bond can freely rotate but a C=C double bond cannot. Please include any relevant orbital drawing in your explanation.
A C-C single bond can freely rotate because there is only a sigma bond with end-to-end overlap. A C=C double bond consists of a sigma bond and a pi bond. There are two p-orbitals that form the pi bond and these must have parallel overlap to form the pi bond. If you rotate a C=C double bond, then the p orbitals would not have parallel overlap and the pi bond would break. (see page 86)
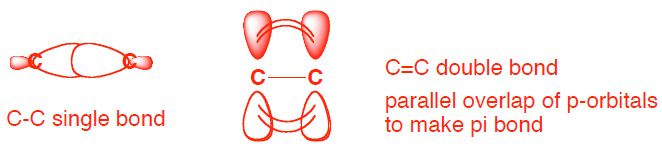
if you donʼt have parallel p-orbitals, then the π bond breaks
-
- (4 pts) Each of the following compounds has important nutrition and health benefits. Label whether the indicated alkene in each of the following is the cis or trans form.
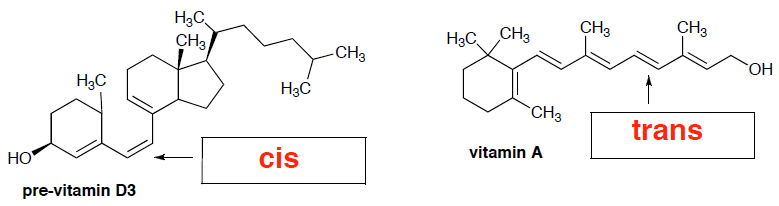
- (2 pts) Do you predict that these vitamins (from part 6a) are fat-soluble or water-soluble?
fat-soluble
- (4 pts) Provide a brief explanation for your answer in part 6b.
These vitamin molecules are almost exclusively C-C and C-H bonds, which makes them very non-polar molecules. They will have good surface area to be soluble in fat, which is also nonpolar. They will not be soluble in water… even though there is one OH group that can have hydrogen-bonding interactions with water, this is not enough. (Recall from our comparison of ethanol and butanol, that even butanol with 4 carbons and an OH group is not very miscible with water)

