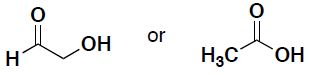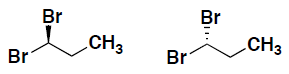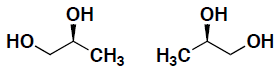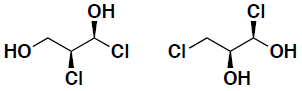3.1: Practice Final A
- Page ID
- 19403
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
NOTE: Parts of this exam are harder than the actual final exam, and part of it is easier. It is expected to be longer than the actual final exam will be. Most of the questions are a similar format to what you will see on the final exam.
- T/F and Multiple Choice:
- Which of the following is correct?
 Curved arrows are always drawn from an electron poor center to an electron rich center
Curved arrows are always drawn from an electron poor center to an electron rich center- Curved arrows are always drawn from an electron rich center to an electron poor center
- Curved arrows are used to show movement of protons
- A doubled headed curved arrow means that one electron has been moved
- Which of the following correctly describes intermediates and/or transition states?
 Transition states occur at minima on reaction coordinate diagrams
Transition states occur at minima on reaction coordinate diagrams- Both transition states and intermediates occur at maxima on reaction coordinate diagrams
- Transition states have partially formed bonds whereas intermediates have fully formed bonds
- none of the above
- Which of the following statements are correct concerning localized electrons?
 Electrons are restricted to a particular region
Electrons are restricted to a particular region- Electrons belong to a single atom
- Electrons are related to a bond between atoms
- A, B, and C
- A and C
- Which of the following statements are correct concerning delocalized electrons?
 Electrons do not belong to a single atom.
Electrons do not belong to a single atom.- Electrons are not confined to a bond between two atoms
- Electrons are shared by three or more atoms
- A and B
- A, B and C
- Where are the two lone pairs of electrons of the oxygen atom in an alcohol molecule located?
 in two s orbitals
in two s orbitals- in two p orbitals
- in two sp orbitals
- in two sp2 orbitals
- in two sp3 orbitals
- Which of the following is the strongest interaction between two different molecules?
 a covalent bond
a covalent bond- induced dipole-induced dipole interactions
- dipole-dipole interactions
- hydrogen bonding
- Van der Waals
- The compound methylamine, H3C-NH2, contains a C-N bond. In this C-N bond, which of the following best describes the charge on the nitrogen atom?
 +1
+1- partial positive (δ+)
- uncharged (neutral)
- partial negative (δ-)
- -1
- Which of the following is correct?
- Organic Molecules in Biology and Daily Life, part 1:
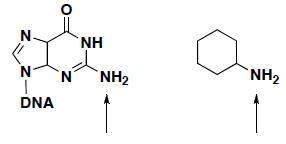
- Adenine and guanosine nucleosides of DNA have a nucleophile amine that can react with electrophiles, leading to DNA mutations. If you compare the primary amine in DNA to a primary amine in cyclohexamine, which amine is more nucleophilic? Explain your answer.
- Butanol is considered to be a better biofuel alternative compared to ethanol for several reasons. Draw the structure of each molecule:
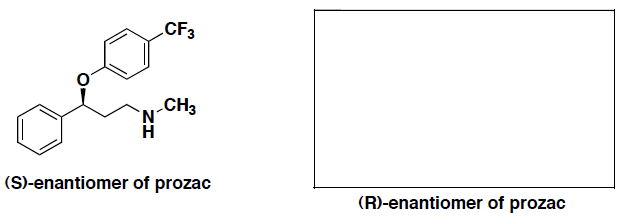
- The (S)-enantiomer of prozac shown below. Draw the perspective structure for the (R)-enantiomer (ie, the other enantiomer) in the box provided.
- Intermolecular forces:
- Circle which of the following compounds will form hydrogen bonds networks with itself (between its molecules).

- Which is stronger an OH covalent bond or an OH hydrogen bond? Explain your answer.
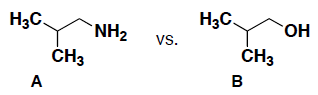
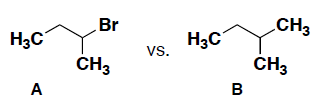
- Consider the following pairs of compounds (A and B) and circle which compound will have the highest boiling point. Briefly explain your answer, including the intermolecular forces for each.
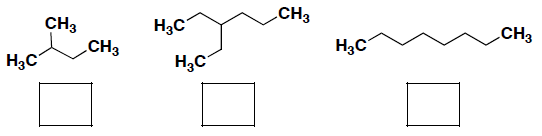
- Rank the boiling points for the following compounds, where 1 = highest boiling point.
- Organic Structure:
- Provide a drawing of benzene that shows what orbitals allow benzene to have a conjugated pi system with delocalized electrons shared by all six carbon atoms.
- Draw a structure of a molecule other than benzene that also has a conjugated pi system.
- Comparing the molecule you drew in part b with benzene, which molecule will absorb UV light at a higher wavelength (λmax, greater nm)?
- Resonance structures: where are the electrons?
- Draw two resonance structures for the following carbocation intermediate to explain why this carbocation is stabilized. (you should be able to show arrows to get to these structures!!)
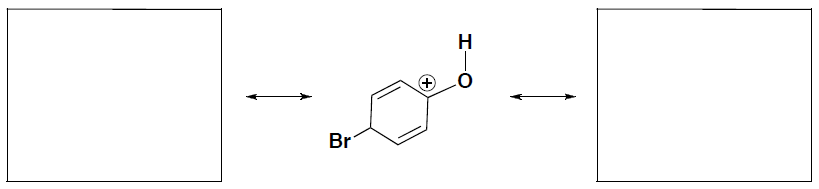
- In your answer above, which resonance structure makes a greater contribution to the resonance hybrid? Briefly explain your answer.
- Which of the following structures is the greatest contributor to the resonance hybrid? Briefly explain your answer.
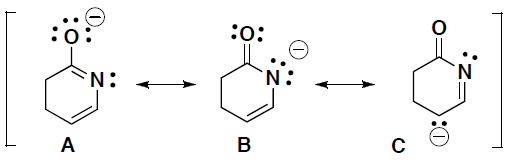
- For part d above, draw curved arrows for the formation of B from A. Then draw curved arrows for the formation of C from B.
- Acidity concepts:
For each pair of molecules below, complete the following steps and determine which is more acidic.
- draw the conjugate base (deprotonated form) of EACH molecule given
- circle the original acidic molecule that is more acidic (has the lowest pKa)
- provide a brief explanation for your choice
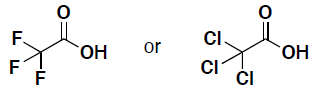
- (9 pts) Each of the following molecules has an acidic proton. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following molecules.
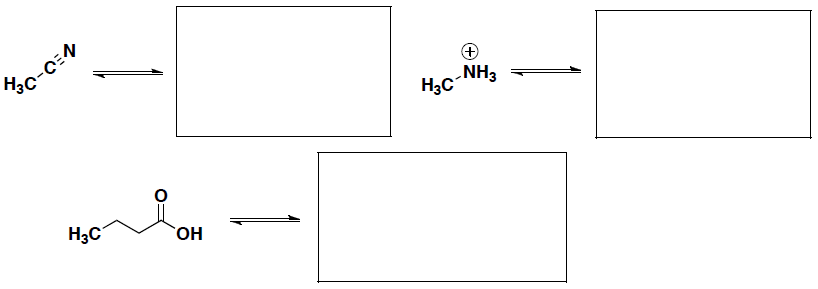
- Identifying electrophiles and nucleophiles for reaction mechanisms:
- Explain the different between a nucleophile and electrophile and give an example of each.
- Two possible products can be formed in the following reaction. Label the nucleophile and electrophile in this reaction and then draw the structure for each of the possible products.
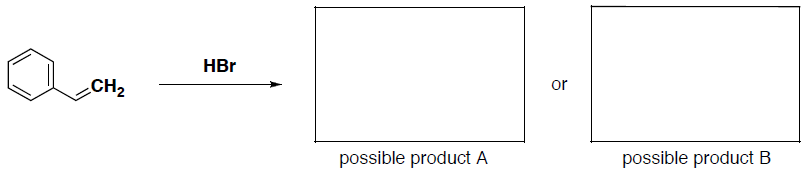
- Now indicate which product will be more likely to form (in part c) and provide an explanation for your answer that includes the structures of the intermediates for the reaction.
- For the following reaction, it has been shown that the rate of the reaction increases when the amount of nucleophile increases. Is this reaction an SN1 or an SN2 reaction? Draw the curved arrow mechanism for this reaction.
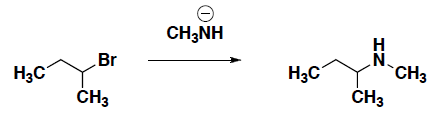
- Is the product in part d chiral? Yes or No
- Products of chemical and biological reactions:
- What is the product of the following substitution reaction? Identify the nucleophile and electrophile and then draw curved arrows showing how the react to give the product.
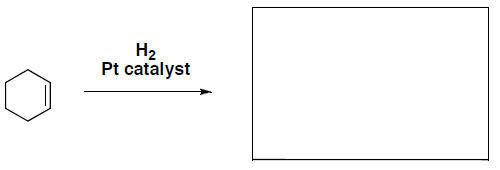
- What is the product of the following hydrogenation reaction?
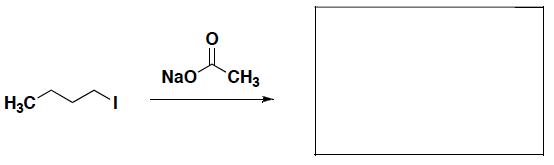
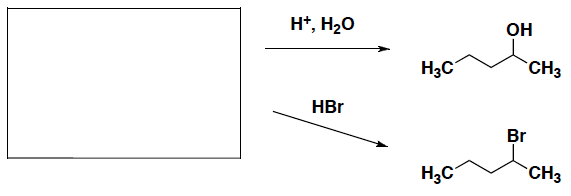
- What is the carbon building block that can be used to synthesize the following alcohol or alkyl bromide?
- What is the product of the following substitution reaction? Identify the nucleophile and electrophile and then draw curved arrows showing how the react to give the product.
(you should also be able to draw the mechanism for each of these reactions….)
- Reactivity and Stability of Molecules:
(although not specifically asked in each of these questions, you should also be able to provide an explanation for each of your answers…)- Rank the stability of the following carbocations (where 1 = most stable):
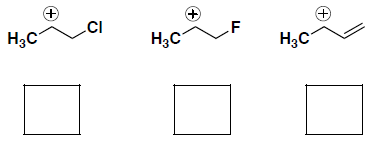
- Rank the nucleophilicity of the following molecules (where 1 = most nucleophilic):
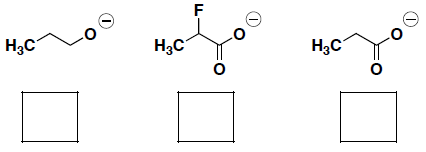
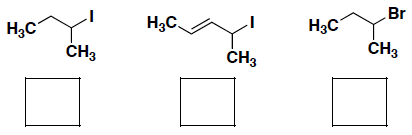
- An SN1 reaction rate depends on the stability of the carbocation that forms. Rank the reactivity of the following alkylhalides in an SN1 reaction (where 1 = most reactive):
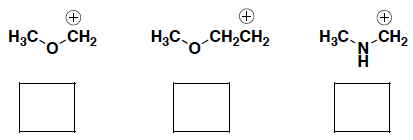
- Rank the electrophilicity of the following carbocations, where 1 = most electrophilic). Provide a brief explanation for your answer.
- Rank the stability of the following carbocations (where 1 = most stable):
- Stereochemistry:
- Vocabulary
- Stereoisomers with an asymmetric carbon center and non-superimposable mirror images are called:
- Equal amounts of two enantiomers is called a
- Isomers that differ in connections between atoms are called
- The interconversion of a single enantiomer into a racemic mixture is called:
- Explain the difference between constitutional isomers and stereoisomers.
- Stereoisomers with an asymmetric carbon center and non-superimposable mirror images are called:
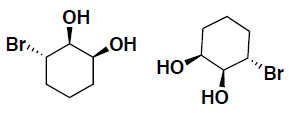
- Indicate for the following pairs of compounds whether they are identical, constitutional isomers, or enantiomers. (put your answer in the box provided)
-
- Metolachlor is a liquid herbicide used for many crops. In 1996, it generated sales of $450 million, making it one of the most popular pesticides on the market. Metolachlor kills weeds by preventing the plants from making a waxy coating on the leaves. This wax is produced with the help of an enzyme called fatty acid elongase. When the enzyme activity is inhibited, the wax is not produced and the weed dies. The following graph shows the amount of R- and S-metolachlor required to interfere with the enzyme.
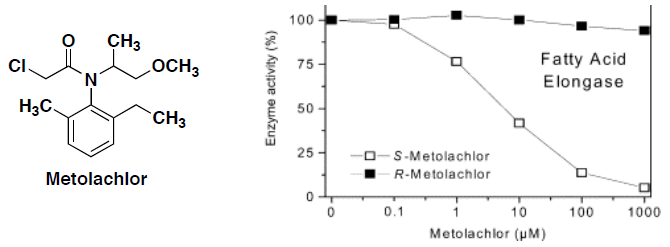
- Identify three functional groups in metolachlor.
- Identify the asymmetric carbon center in metolachlor and draw a perspective structure for each enantiomer of metolachlor.
- Based on the graph data, if you wanted to kill weeds which enantiomer would you use?
- Why do these enantiomers have different activities?
- Both the R- and S-enantiomers of metolachlor are degraded in the environment to produce a metabolite that kills fish. Metolachlor is currently sold as a racemic mixture. As a environmental policy maker, what legislation would you promote to reduce the levels of toxic metabolites by 50%?
- Identify three functional groups in metolachlor.
- Vocabulary
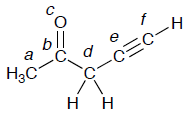
- Which of the atom(s) in the following molecule is (are) sp hybridized?
Which of the atom(s) in the following molecule is (are) sp2 hybridized?
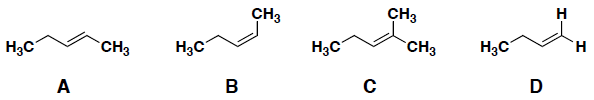
Which of the following molecules is considered a trans isomer?
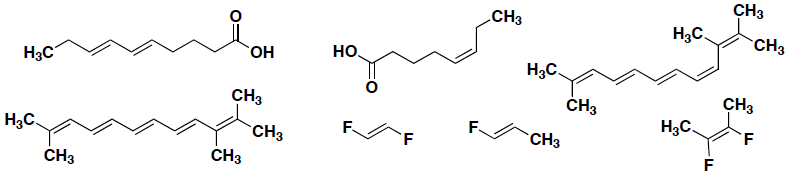
Circle any of the following structures that represent a cis isomer?
What is the appropriate formal charge for the following molecule?
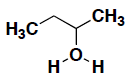

- +1
- –1
- 0
- +2
- –2