Digging Deeper: Cellular Respiration
- Page ID
- 184255
Let's dig a little deeper into the process of cellular respiration.
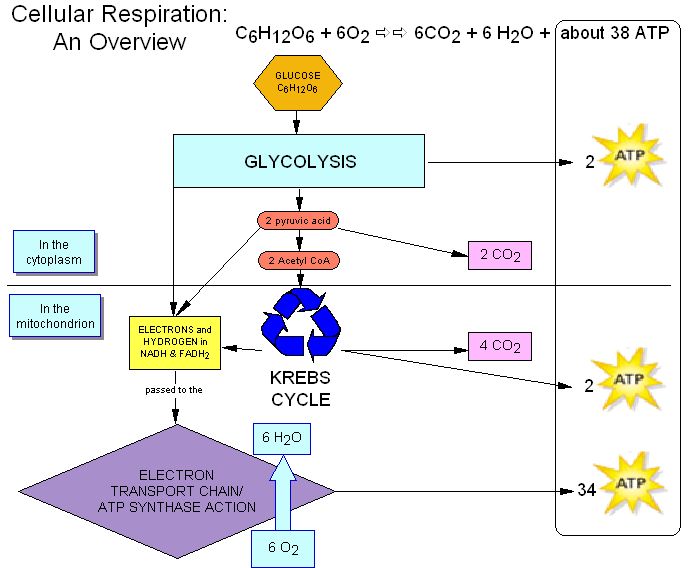
Cellular respiration has two main stages, and is an aerobic process.
Glycolysis - is needed for cellular respiration to occur, and the products of glycolysis enter cellular respiration when oxygen is available.
Glycolysis summary:
- 2 ATP molecules are used to split glucose
- 4 ATP molecules are produced
- 2 molecules of NADH are produced
- 2 molecules of pyruvate are produced
The Krebs cycle is the first main stage of cellular respiration - the Krebs cycle produces energy carrying molecules.
Krebs cycle summary:
- NADH and FADH2 are made
- citric acid (6-carbon molecule is formed)
- citric acid is broken down
- CO2 is released
- 5-carbon molecule is borken down, CO2 is released
- ATP is made
- 4-carbon molecule is rearranged.
The elecrton transport chain is the second main part of cellular respiration. The electron transport chain uses NADH and FADH2 to make ATP. The breakdown of one glucose moledule produces up to 38 molecules of ATP, and water is released as a waste product.