5.3: Determining the Sensitivity
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 219813
To standardize an analytical method we also must determine the analyte’s sensitivity, kA, in Equation 5.3.1 or Equation 5.3.2 .
\[S_{total} = k_A n_A + S_{reag} \label{5.1}\]
\[S_{total} = k_A C_A + S_{reag} \label{5.2}\]
In principle, it is possible to derive the value of kA for any analytical method if we understand fully all the chemical reactions and physical processes responsible for the signal. Unfortunately, such calculations are not feasible if we lack a sufficiently developed theoretical model of the physical processes or if the chemical reaction’s evince non-ideal behavior. In such situations we must determine the value of kA by analyzing one or more standard solutions, each of which contains a known amount of analyte. In this section we consider several approaches for determining the value of kA. For simplicity we assume that Sreag is accounted for by a proper reagent blank, allowing us to replace Stotal in Equation \ref{5.1} and Equation \ref{5.2} with the analyte’s signal, SA.
Equation \ref{5.3} and Equation \ref{5.4} essentially are identical, differing only in whether we choose to express the amount of analyte in moles or as a concentration. For the remainder of this chapter we will limit our treatment to Equation \ref{5.4}. You can extend this treatment to Equation \ref{5.3} by replacing CA with nA.
Single-Point versus Multiple-Point Standardizations
The simplest way to determine the value of kA in Equation \ref{5.4} is to use a single-point standardization in which we measure the signal for a standard, Sstd, that contains a known concentration of analyte, Cstd. Substituting these values into Equation \ref{5.4}
\[k_A = \frac {S_{std}} {C_{std}} \label{5.5}\]
gives us the value for kA. Having determined kA, we can calculate the concentration of analyte in a sample by measuring its signal, Ssamp, and calculating CA using Equation \ref{5.6}.
\[C_A = \frac {S_{samp}} {k_A} \label{5.6}\]
A single-point standardization is the least desirable method for standardizing a method. There are two reasons for this. First, any error in our determination of kA carries over into our calculation of CA. Second, our experimental value for kA is based on a single concentration of analyte. To extend this value of kA to other concentrations of analyte requires that we assume a linear relationship between the signal and the analyte’s concentration, an assumption that often is not true [Cardone, M. J.; Palmero, P. J.; Sybrandt, L. B. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 1187–1191]. Figure 5.3.1 shows how assuming a constant value of kA leads to a determinate error in CA if kA becomes smaller at higher concentrations of analyte. Despite these limitations, single-point standardizations find routine use when the expected range for the analyte’s concentrations is small. Under these conditions it often is safe to assume that kA is constant (although you should verify this assumption experimentally). This is the case, for example, in clinical labs where many automated analyzers use only a single standard.
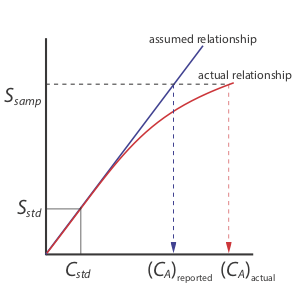
The better way to standardize a method is to prepare a series of standards, each of which contains a different concentration of analyte. Standards are chosen such that they bracket the expected range for the analyte’s concentration. A multiple-point standardization should include at least three standards, although more are preferable. A plot of Sstd versus Cstd is called a calibration curve. The exact standardization, or calibration relationship, is determined by an appropriate curve-fitting algorithm.
Linear regression, which also is known as the method of least squares, is one such algorithm. Its use is covered in Section 5.4.
There are two advantages to a multiple-point standardization. First, although a determinate error in one standard introduces a determinate error, its effect is minimized by the remaining standards. Second, because we measure the signal for several concentrations of analyte, we no longer must assume kA is independent of the analyte’s concentration. Instead, we can construct a calibration curve similar to the “actual relationship” in Figure 5.3.1 .
External Standards
The most common method of standardization uses one or more external standards, each of which contains a known concentration of analyte. We call these standards “external” because they are prepared and analyzed separate from the samples.
Appending the adjective “external” to the noun “standard” might strike you as odd at this point, as it seems reasonable to assume that standards and samples are analyzed separately. As we will soon learn, however, we can add standards to our samples and analyze both simultaneously.
Single External Standard
With a single external standard we determine kA using EEquation \ref{5.5} and then calculate the concentration of analyte, CA, using Equation \ref{5.6}.
Example 5.3.1
A spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood yields an Sstd of 0.474 for a single standard for which the concentration of lead is 1.75 ppb. What is the concentration of Pb2+ in a sample of blood for which Ssamp is 0.361?
Solution
Equation \ref{5.5} allows us to calculate the value of kA using the data for the single external standard.
\[k_A = \frac {S_{std}} {C_{std}} = \frac {0.474} {1.75 \text{ ppb}} = 0.2709 \text{ ppb}^{-1} \nonumber\]
Having determined the value of kA, we calculate the concentration of Pb2+ in the sample of blood is calculated using Equation \ref{5.6}.
\[C_A = \frac {S_{samp}} {k_A} = \frac {0.361} {0.2709 \text{ ppb}^{-1}} = 1.33 \text{ ppb} \nonumber\]
Multiple External Standards
Figure 5.3.2 shows a typical multiple-point external standardization. The volumetric flask on the left contains a reagent blank and the remaining volumetric flasks contain increasing concentrations of Cu2+. Shown below the volumetric flasks is the resulting calibration curve. Because this is the most common method of standardization, the resulting relationship is called a normal calibration curve.
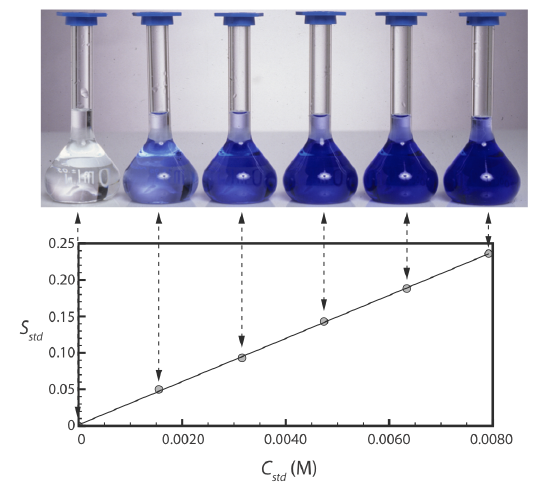
When a calibration curve is a straight-line, as it is in Figure 5.3.2 , the slope of the line gives the value of kA. This is the most desirable situation because the method’s sensitivity remains constant throughout the analyte’s concentration range. When the calibration curve is not a straight-line, the method’s sensitivity is a function of the analyte’s concentration. In Figure 5.3.1 , for example, the value of kA is greatest when the analyte’s concentration is small and it decreases continuously for higher concentrations of analyte. The value of kA at any point along the calibration curve in Figure 5.3.1 is the slope at that point. In either case, a calibration curve allows to relate Ssamp to the analyte’s concentration.
Example 5.3.2
A second spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood has a normal calibration curve for which
\[S_{std} = (0.296 \text{ ppb}^{-1} \times C_{std}) + 0.003 \nonumber\]
What is the concentration of Pb2+ in a sample of blood if Ssamp is 0.397?
Solution
To determine the concentration of Pb2+ in the sample of blood, we replace Sstd in the calibration equation with Ssamp and solve for CA.
\[C_A = \frac {S_{samp} - 0.003} {0.296 \text{ ppb}^{-1}} = \frac {0.397 - 0.003} {0.296 \text{ ppb}^{-1}} = 1.33 \text{ ppb} \nonumber\]
It is worth noting that the calibration equation in this problem includes an extra term that does not appear in Equation \ref{5.6}. Ideally we expect our calibration curve to have a signal of zero when CA is zero. This is the purpose of using a reagent blank to correct the measured signal. The extra term of +0.003 in our calibration equation results from the uncertainty in measuring the signal for the reagent blank and the standards.
Exercise 5.3.1
Figure 5.3.2 shows a normal calibration curve for the quantitative analysis of Cu2+. The equation for the calibration curve is
\[S_{std} = 29.59 \text{ M}^{-1} \times C_{std} + 0.015 \nonumber\]
What is the concentration of Cu2+ in a sample whose absorbance, Ssamp, is 0.114? Compare your answer to a one-point standardization where a standard of \(3.16 \times 10^{-3} \text{ M}\) Cu2+ gives a signal of 0.0931.
- Answer
-
Substituting the sample’s absorbance into the calibration equation and solving for CA give
\[S_{samp} = 0.114 = 29.59 \text{ M}^{-1} \times C_{A} + 0.015 \nonumber\]
\[C_A = 3.35 \times 10^{-3} \text{ M} \nonumber\]
For the one-point standardization, we first solve for kA
\[k_A = \frac {S_{std}} {C_{std}} = \frac {0.0931} {3.16 \times 10^{-3} \text{ M}} = 29.46 \text{ M}^{-1} \nonumber\]
and then use this value of kA to solve for CA.
\[C_A = \frac {S_{samp}} {k_A} = \frac {0.114} {29.46 \text{ M}^{-1}} = 3.87 \times 10^{-3} \text{ M} \nonumber\]
When using multiple standards, the indeterminate errors that affect the signal for one standard are partially compensated for by the indeterminate errors that affect the other standards. The standard selected for the one-point standardization has a signal that is smaller than that predicted by the regression equation, which underestimates kA and overestimates CA.
An external standardization allows us to analyze a series of samples using a single calibration curve. This is an important advantage when we have many samples to analyze. Not surprisingly, many of the most common quantitative analytical methods use an external standardization.
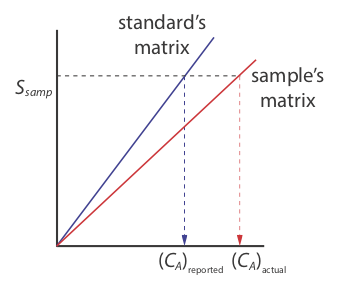
There is a serious limitation, however, to an external standardization. When we determine the value of kA using Equation \ref{5.5}, the analyte is present in the external standard’s matrix, which usually is a much simpler matrix than that of our samples. When we use an external standardization we assume the matrix does not affect the value of kA. If this is not true, then we introduce a proportional determinate error into our analysis. This is not the case in Figure 5.3.3 , for instance, where we show calibration curves for an analyte in the sample’s matrix and in the standard’s matrix. In this case, using the calibration curve for the external standards leads to a negative determinate error in analyte’s reported concentration. If we expect that matrix effects are important, then we try to match the standard’s matrix to that of the sample, a process known as matrix matching. If we are unsure of the sample’s matrix, then we must show that matrix effects are negligible or use an alternative method of standardization. Both approaches are discussed in the following section.
The matrix for the external standards in Figure 5.3.2 , for example, is dilute ammonia. Because the \(\ce{Cu(NH3)4^{2+}}\) complex absorbs more strongly than Cu2+, adding ammonia increases the signal’s magnitude. If we fail to add the same amount of ammonia to our samples, then we will introduce a proportional determinate error into our analysis.
Standard Additions
We can avoid the complication of matching the matrix of the standards to the matrix of the sample if we carry out the standardization in the sample. This is known as the method of standard additions.
Single Standard Addition
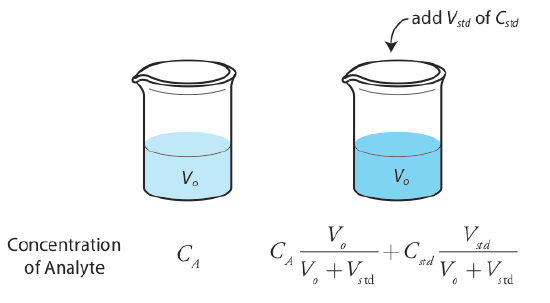
The simplest version of a standard addition is shown in Figure 5.3.4 . First we add a portion of the sample, Vo, to a volumetric flask, dilute it to volume, Vf, and measure its signal, Ssamp. Next, we add a second identical portion of sample to an equivalent volumetric flask along with a spike, Vstd, of an external standard whose concentration is Cstd. After we dilute the spiked sample to the same final volume, we measure its signal, Sspike.
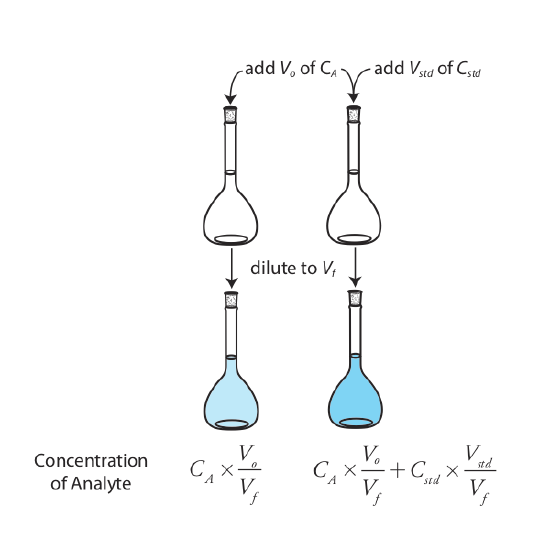
The following two equations relate Ssamp and Sspike to the concentration of analyte, CA, in the original sample.
\[S_{samp} = k_A C_A \frac {V_o} {V_f} \label{5.7}\]
\[S_{spike} = k_A \left( C_A \frac {V_o} {V_f} + C_{std} \frac {V_{std}} {V_f} \right) \label{5.8}\]
As long as Vstd is small relative to Vo, the effect of the standard’s matrix on the sample’s matrix is insignificant. Under these conditions the value of kA is the same in Equation \ref{5.7} and Equation \ref{5.8}. Solving both equations for kA and equating gives
\[\frac {S_{samp}} {C_A \frac {V_o} {V_f}} = \frac {S_{spike}} {C_A \frac {V_o} {V_f} + C_{std} \frac {V_{std}} {V_f}} \label{5.9}\]
which we can solve for the concentration of analyte, CA, in the original sample.
Example 5.3.3
A third spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood yields an Ssamp of 0.193 when a 1.00 mL sample of blood is diluted to 5.00 mL. A second 1.00 mL sample of blood is spiked with 1.00 mL of a 1560-ppb Pb2+ external standard and diluted to 5.00 mL, yielding an Sspike of 0.419. What is the concentration of Pb2+ in the original sample of blood?
Solution
We begin by making appropriate substitutions into Equation \ref{5.9} and solving for CA. Note that all volumes must be in the same units; thus, we first convert Vstd from 1.00 mL to \(1.00 \times 10^{-3} \text{ mL}\).
\[\frac {0.193} {C_A \frac {1.00 \text{ mL}} {5.00 \text{ mL}}} = \frac {0.419} {C_A \frac {1.00 \text{ mL}} {5.00 \text{ mL}} + 1560 \text{ ppb} \frac {1.00 \times 10^{-3} \text{ mL}} {5.00 \text{ mL}}} \nonumber\]
\[\frac {0.193} {0.200C_A} = \frac {0.419} {0.200C_A + 0.3120 \text{ ppb}} \nonumber\]
\[0.0386C_A + 0.0602 \text{ ppb} = 0.0838 C_A \nonumber\]
\[0.0452 C_A = 0.0602 \text{ ppb} \nonumber\]
\[C_A = 1.33 \text{ ppb} \nonumber\]
The concentration of Pb2+ in the original sample of blood is 1.33 ppb.
It also is possible to add the standard addition directly to the sample, measuring the signal both before and after the spike (Figure 5.3.5 ). In this case the final volume after the standard addition is Vo + Vstd and Equation \ref{5.7}, Equation \ref{5.8}, and Equation \ref{5.9} become
\[S_{samp} = k_A C_A \nonumber\]
\[S_{spike} = k_A \left( C_A \frac {V_o} {V_o + V_{std}} + C_{std} \frac {V_{std}} {V_o + V_{std}} \right) \label{5.10}\]
\[\frac {S_{samp}} {C_A} = \frac {S_{spike}} {C_A \frac {V_o} {V_o + V_{std}} + C_{std} \frac {V_{std}} {V_o + V_{std}}} \label{5.11}\]
Example 5.3.4
A fourth spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood yields an Ssamp of 0.712 for a 5.00 mL sample of blood. After spiking the blood sample with 5.00 mL of a 1560-ppb Pb2+ external standard, an Sspike of 1.546 is measured. What is the concentration of Pb2+ in the original sample of blood?
Solution
\[\frac {0.712} {C_A} = \frac {1.546} {C_A \frac {5.00 \text{ mL}} {5.005 \text{ mL}} + 1560 \text{ ppb} \frac {5.00 \times 10^{-3} \text{ mL}} {5.005 \text{ mL}}} \nonumber\]
\[\frac {0.712} {C_A} = \frac {1.546} {0.9990C_A + 1.558 \text{ ppb}} \nonumber\]
\[0.7113C_A + 1.109 \text{ ppb} = 1.546C_A \nonumber\]
\[C_A = 1.33 \text{ ppb} \nonumber\]
The concentration of Pb2+ in the original sample of blood is 1.33 ppb.
Multiple Standard Additions
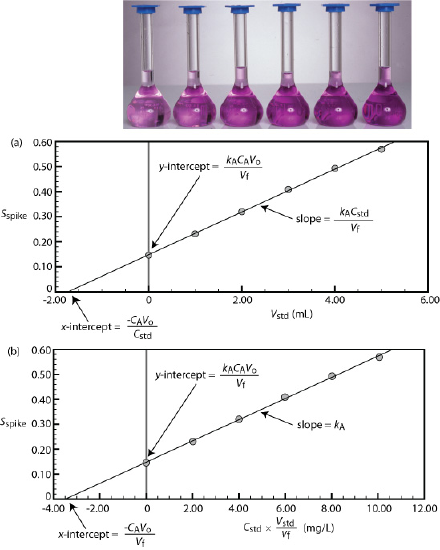
We can adapt a single-point standard addition into a multiple-point standard addition by preparing a series of samples that contain increasing amounts of the external standard. Figure 5.3.6 shows two ways to plot a standard addition calibration curve based on Equation \ref{5.8}. In Figure 5.3.6 a we plot Sspike against the volume of the spikes, Vstd. If kA is constant, then the calibration curve is a straight-line. It is easy to show that the x-intercept is equivalent to –CAVo/Cstd.
Example 5.3.5
Beginning with Equation \ref{5.8} show that the equations in Figure 5.3.6 a for the slope, the y-intercept, and the x-intercept are correct.
Solution
We begin by rewriting Equation \ref{5.8} as
\[S_{spike} = \frac {k_A C_A V_o} {V_f} + \frac {k_A C_{std}} {V_f} \times V_{std} \nonumber\]
which is in the form of the equation for a straight-line
\[y = y\text{-intercept} + \text{slope} \times x\text{-intercept} \nonumber\]
where y is Sspike and x is Vstd. The slope of the line, therefore, is kACstd/Vf and the y-intercept is kACAVo/Vf. The x-intercept is the value of x when y is zero, or
\[0 = \frac {k_A C_A V_o} {V_f} + \frac {k_A C_{std}} {V_f} \times x\text{-intercept} \nonumber\]
\[x\text{-intercept} = - \frac {k_A C_A V_o / V_f} {K_A C_{std} / V_f} = - \frac {C_A V_o} {C_{std}} \nonumber\]
Exercise 5.3.2
Beginning with Equation \ref{5.8} show that the Equations in Figure 5.3.6 b for the slope, the y-intercept, and the x-intercept are correct.
- Answer
-
We begin with Equation \ref{5.8}
\[S_{spike} = k_A \left( C_A \frac {V_o} {V_f} + C_{std} \frac {V_{std}} {V_f} \right) \nonumber\]
rewriting it as
\[S_{spike} = \frac {k_A C_A V_o} {V_f} + k_A \left( C_{std} \frac {V_{std}} {V_f} \right) \nonumber\]
which is in the form of the linear equation
\[y = y\text{-intercept} + \text{slope} \times x\text{-intercept} \nonumber\]
where y is Sspike and x is Cstd \(\times\) Vstd/Vf. The slope of the line, therefore, is kA, and the y-intercept is kACAVo/Vf. The x-intercept is the value of x when y is zero, or
\[x\text{-intercept} = - \frac {k_A C_A V_o/V_F} {k_A} = - \frac {C_A V_o} {V_f} \nonumber\]
Because we know the volume of the original sample, Vo, and the concentration of the external standard, Cstd, we can calculate the analyte’s concentrations from the x-intercept of a multiple-point standard additions.
Example 5.3.6
A fifth spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood uses a multiple-point standard addition based on Equation \ref{5.8}. The original blood sample has a volume of 1.00 mL and the standard used for spiking the sample has a concentration of 1560 ppb Pb2+. All samples were diluted to 5.00 mL before measuring the signal. A calibration curve of Sspike versus Vstd has the following equation
\[S_{spike} = 0.266 + 312 \text{ mL}^{-1} \times V_{std} \nonumber\]
What is the concentration of Pb2+ in the original sample of blood?
Solution
To find the x-intercept we set Sspike equal to zero.
\[S_{spike} = 0.266 + 312 \text{ mL}^{-1} \times V_{std} \nonumber\]
Solving for Vstd, we obtain a value of \(-8.526 \times 10^{-4} \text{ mL}\) for the x-intercept. Substituting the x-intercept’s value into the equation from Figure 5.3.6 a
\[-8.526 \times 10^{-4} \text{ mL} = - \frac {C_A V_o} {C_{std}} = - \frac {C_A \times 1.00 \text{ mL}} {1560 \text{ ppb}} \nonumber\]
and solving for CA gives the concentration of Pb2+ in the blood sample as 1.33 ppb.
Exercise 5.3.3
Figure 5.3.6 shows a standard additions calibration curve for the quantitative analysis of Mn2+. Each solution contains 25.00 mL of the original sample and either 0, 1.00, 2.00, 3.00, 4.00, or 5.00 mL of a 100.6 mg/L external standard of Mn2+. All standard addition samples were diluted to 50.00 mL with water before reading the absorbance. The equation for the calibration curve in Figure 5.3.6 a is
\[S_{std} = 0.0854 \times V_{std} + 0.1478 \nonumber\]
What is the concentration of Mn2+ in this sample? Compare your answer to the data in Figure 5.3.6 b, for which the calibration curve is
\[S_{std} = 0.425 \times C_{std}(V_{std}/V_f) + 0.1478 \nonumber\]
- Answer
-
Using the calibration equation from Figure 5.3.6 a, we find that the x-intercept is
\[x\text{-intercept} = - \frac {0.1478} {0.0854 \text{ mL}^{-1}} = - 1.731 \text{ mL} \nonumber\]
If we plug this result into the equation for the x-intercept and solve for CA, we find that the concentration of Mn2+ is
\[C_A = - \frac {x\text{-intercept} \times C_{std}} {V_o} = - \frac {-1.731 \text{ mL} \times 100.6 \text{ mg/L}} {25.00 \text{ mL}} = 6.96 \text{ mg/L} \nonumber\]
For Figure 5.3.6 b, the x-intercept is
\[x\text{-intercept} = - \frac {0.1478} {0.0425 \text{ mL/mg}} = - 3.478 \text{ mg/mL} \nonumber\]
and the concentration of Mn2+ is
\[C_A = - \frac {x\text{-intercept} \times V_f} {V_o} = - \frac {-3.478 \text{ mg/mL} \times 50.00 \text{ mL}} {25.00 \text{ mL}} = 6.96 \text{ mg/L} \nonumber\]
Since we construct a standard additions calibration curve in the sample, we can not use the calibration equation for other samples. Each sample, therefore, requires its own standard additions calibration curve. This is a serious drawback if you have many samples. For example, suppose you need to analyze 10 samples using a five-point calibration curve. For a normal calibration curve you need to analyze only 15 solutions (five standards and ten samples). If you use the method of standard additions, however, you must analyze 50 solutions (each of the ten samples is analyzed five times, once before spiking and after each of four spikes).
Using a Standard Addition to Identify Matrix Effects
We can use the method of standard additions to validate an external standardization when matrix matching is not feasible. First, we prepare a normal calibration curve of Sstd versus Cstd and determine the value of kA from its slope. Next, we prepare a standard additions calibration curve using Equation \ref{5.8}, plotting the data as shown in Figure 5.3.6 b. The slope of this standard additions calibration curve provides an independent determination of kA. If there is no significant difference between the two values of kA, then we can ignore the difference between the sample’s matrix and that of the external standards. When the values of kA are significantly different, then using a normal calibration curve introduces a proportional determinate error.
Internal Standards
To use an external standardization or the method of standard additions, we must be able to treat identically all samples and standards. When this is not possible, the accuracy and precision of our standardization may suffer. For example, if our analyte is in a volatile solvent, then its concentration will increase if we lose solvent to evaporation. Suppose we have a sample and a standard with identical concentrations of analyte and identical signals. If both experience the same proportional loss of solvent, then their respective concentrations of analyte and signals remain identical. In effect, we can ignore evaporation if the samples and the standards experience an equivalent loss of solvent. If an identical standard and sample lose different amounts of solvent, however, then their respective concentrations and signals are no longer equal. In this case a simple external standardization or standard addition is not possible.
We can still complete a standardization if we reference the analyte’s signal to a signal from another species that we add to all samples and standards. The species, which we call an internal standard, must be different than the analyte.
Because the analyte and the internal standard receive the same treatment, the ratio of their signals is unaffected by any lack of reproducibility in the procedure. If a solution contains an analyte of concentration CA and an internal standard of concentration CIS, then the signals due to the analyte, SA, and the internal standard, SIS, are
\[S_A = k_A C_A \nonumber\]
\[S_{IS} = k_{SI} C_{IS} \nonumber\]
where \(k_A\) and \(k_{IS}\) are the sensitivities for the analyte and the internal standard, respectively. Taking the ratio of the two signals gives the fundamental equation for an internal standardization.
\[\frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} = \frac {k_A C_A} {k_{IS} C_{IS}} = K \times \frac {C_A} {C_{IS}} \label{5.12}\]
Because K is a ratio of the analyte’s sensitivity and the internal standard’s sensitivity, it is not necessary to determine independently values for either kA or kIS.
Single Internal Standard
In a single-point internal standardization, we prepare a single standard that contains the analyte and the internal standard, and use it to determine the value of K in Equation \ref{5.12}.
\[K = \left( \frac {C_{IS}} {C_A} \right)_{std} \times \left( \frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} \right)_{std} \label{5.13}\]
Having standardized the method, the analyte’s concentration is given by
\[C_A = \frac {C_{IS}} {K} \times \left( \frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} \right)_{samp} \nonumber\]
Example 5.3.7
A sixth spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood uses Cu2+ as an internal standard. A standard that is 1.75 ppb Pb2+ and 2.25 ppb Cu2+ yields a ratio of (SA/SIS)std of 2.37. A sample of blood spiked with the same concentration of Cu2+ gives a signal ratio, (SA/SIS)samp, of 1.80. What is the concentration of Pb2+ in the sample of blood?
Solution
Equation \ref{5.13} allows us to calculate the value of K using the data for the standard
\[K = \left( \frac {C_{IS}} {C_A} \right)_{std} \times \left( \frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} \right)_{std} = \frac {2.25 \text{ ppb } \ce{Cu^{2+}}} {1.75 \text{ ppb } \ce{Pb^{2+}}} \times 2.37 = 3.05 \frac {\text{ppb } \ce{Cu^{2+}}} {\text{ppb } \ce{Pb^{2+}}} \nonumber\]
The concentration of Pb2+, therefore, is
\[C_A = \frac {C_{IS}} {K} \times \left( \frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} \right)_{samp} = \frac {2.25 \text{ ppb } \ce{Cu^{2+}}} {3.05 \frac {\text{ppb } \ce{Cu^{2+}}} {\text{ppb } \ce{Pb^{2+}}}} \times 1.80 = 1.33 \text{ ppb } \ce{Pb^{2+}} \nonumber\]
Multiple Internal Standards
A single-point internal standardization has the same limitations as a single-point normal calibration. To construct an internal standard calibration curve we prepare a series of standards, each of which contains the same concentration of internal standard and a different concentrations of analyte. Under these conditions a calibration curve of (SA/SIS)std versus CA is linear with a slope of K/CIS.
Although the usual practice is to prepare the standards so that each contains an identical amount of the internal standard, this is not a requirement.
Example 5.3.8
A seventh spectrophotometric method for the quantitative analysis of Pb2+ in blood gives a linear internal standards calibration curve for which
\[\left( \frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} \right)_{std} = (2.11 \text{ ppb}^{-1} \times C_A) - 0.006 \nonumber\]
What is the ppb Pb2+ in a sample of blood if (SA/SIS)samp is 2.80?
Solution
To determine the concentration of Pb2+ in the sample of blood we replace (SA/SIS)std in the calibration equation with (SA/SIS)samp and solve for CA.
\[C_A = \frac {\left( \frac {S_A} {S_{IS}} \right)_{samp} + 0.006} {2.11 \text{ ppb}^{-1}} = \frac {2.80 + 0.006} {2.11 \text{ ppb}^{-1}} = 1.33 \text{ ppb } \ce{Pb^{2+}} \nonumber\]
The concentration of Pb2+ in the sample of blood is 1.33 ppb.
In some circumstances it is not possible to prepare the standards so that each contains the same concentration of internal standard. This is the case, for example, when we prepare samples by mass instead of volume. We can still prepare a calibration curve, however, by plotting \((S_A / S_{IS})_{std}\) versus CA/CIS, giving a linear calibration curve with a slope of K.
You might wonder if it is possible to include an internal standard in the method of standard additions to correct for both matrix effects and uncontrolled variations between samples; well, the answer is yes as described in the paper “Standard Dilution Analysis,” the full reference for which is Jones, W. B.; Donati, G. L.; Calloway, C. P.; Jones, B. T. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2321-2327.


