7.4: Colligative Properties
- Page ID
- 236764
Skills to Develop
- Describe the effect of solute concentration on various solution properties (vapor pressure, boiling point, freezing point, and osmotic pressure)
- Perform calculations using the mathematical equations that describe the various colligative effects
- Describe ion pairing and use the van't Hoff factor in calculations
Colligative Properties
The properties of a solution are different from those of either the pure solute(s) or solvent. Many solution properties are dependent upon the chemical identity of the solute. Compared to pure water, a solution of hydrogen chloride is more acidic, a solution of ammonia is more basic, a solution of sodium chloride is more dense, and a solution of sucrose is more viscous. There are a few solution properties, however, that depend only upon the total concentration of solute species, regardless of their identities. These colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. This small set of properties is of central importance to many natural phenomena and technological applications, as will be described in this module.
Vapor Pressure Lowering
The equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by its gaseous phase when vaporization and condensation are occurring at equal rates:
\[ \text{liquid} \rightleftharpoons \text{gas} \label{11.5.4}\]
Dissolving a nonvolatile substance in a volatile liquid results in a lowering of the liquid’s vapor pressure. This phenomenon can be rationalized by considering the effect of added solute molecules on the liquid's vaporization and condensation processes. To vaporize, solvent molecules must be present at the surface of the solution. The presence of solute decreases the surface area available to solvent molecules and thereby reduces the rate of solvent vaporization. Since the rate of condensation is unaffected by the presence of solute, the net result is that the vaporization-condensation equilibrium is achieved with fewer solvent molecules in the vapor phase (i.e., at a lower vapor pressure) (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). While this kinetic interpretation is useful, it does not account for several important aspects of the colligative nature of vapor pressure lowering. A more rigorous explanation involves the property of entropy, a topic of discussion in a later text chapter on thermodynamics. For purposes of understanding the lowering of a liquid's vapor pressure, it is adequate to note that the greater entropy of a solution in comparison to its separate solvent and solute serves to effectively stabilize the solvent molecules and hinder their vaporization. A lower vapor pressure results, and a correspondingly higher boiling point as described in the next section of this module.
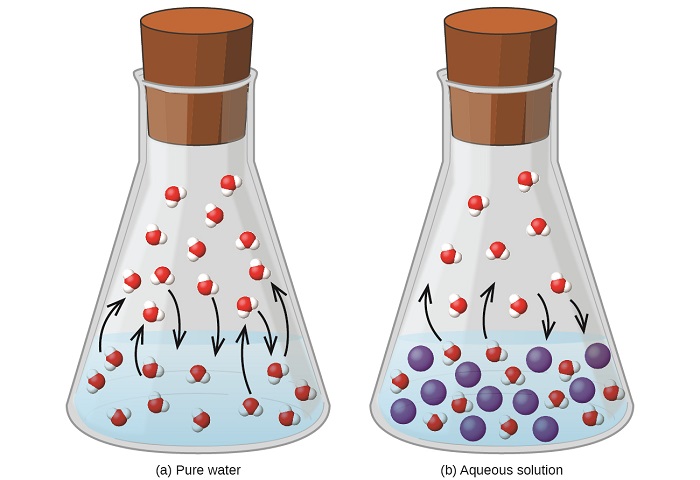
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): The presence of nonvolatile solutes lowers the vapor pressure of a solution by impeding the evaporation of solvent molecules.
The relationship between the vapor pressures of solution components and the concentrations of those components is described by Raoult’s law: The partial pressure exerted by any component of an ideal solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.
\[P_\ce{A}=X_\ce{A}P^\circ_\ce{A} \label{11.5.5}\]
where PA is the partial pressure exerted by component A in the solution,
Elevation of the Boiling Point of a Solvent
As described in the chapter on liquids and solids, the boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure is equal to ambient atmospheric pressure. Since the vapor pressure of a solution is lowered due to the presence of nonvolatile solutes, it stands to reason that the solution’s boiling point will subsequently be increased. Compared to pure solvent, a solution, therefore, will require a higher temperature to achieve any given vapor pressure, including one equivalent to that of the surrounding atmosphere. The increase in boiling point observed when nonvolatile solute is dissolved in a solvent, \(ΔT_b\), is called boiling point elevation and is directly proportional to the molal concentration of solute species:
\[ΔT_b=K_bm \label{11.5.8}\]
where
- \(K_\ce{b}\) is the boiling point elevation constant, or the ebullioscopic constant and
- \(m\) is the molal concentration (molality) of all solute species.
Boiling point elevation constants are characteristic properties that depend on the identity of the solvent. Values of Kb for several solvents are listed in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
| Solvent | Boiling Point (°C at 1 atm) | Kb (Cm−1) | Freezing Point (°C at 1 atm) | Kf (Cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| water | 100.0 | 0.512 | 0.0 | 1.86 |
| hydrogen acetate | 118.1 | 3.07 | 16.6 | 3.9 |
| benzene | 80.1 | 2.53 | 5.5 | 5.12 |
| chloroform | 61.26 | 3.63 | −63.5 | 4.68 |
| nitrobenzene | 210.9 | 5.24 | 5.67 | 8.1 |
The extent to which the vapor pressure of a solvent is lowered and the boiling point is elevated depends on the total number of solute particles present in a given amount of solvent, not on the mass or size or chemical identities of the particles. A 1 m aqueous solution of sucrose (342 g/mol) and a 1 m aqueous solution of ethylene glycol (62 g/mol) will exhibit the same boiling point because each solution has one mole of solute particles (molecules) per kilogram of solvent.
Example \(\PageIndex{7}\): Calculating the Boiling Point of a Solution
What is the boiling point of a 0.33 m solution of a nonvolatile solute in benzene?
Solution
Use the equation relating boiling point elevation to solute molality to solve this problem in two steps.

- Calculate the change in boiling point.
- Add the boiling point elevation to the pure solvent’s boiling point.
\(\mathrm{Boiling\: temperature=80.1\:°C+0.83\:°C=80.9\:°C}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\)
What is the boiling point of the antifreeze described in Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)?
- Answer
-
109.2 °C
Example \(\PageIndex{8}\): The Boiling Point of an Iodine Solution
Find the boiling point of a solution of 92.1 g of iodine, I2, in 800.0 g of chloroform, CHCl3, assuming that the iodine is nonvolatile and that the solution is ideal.
Solution
We can solve this problem using four steps.
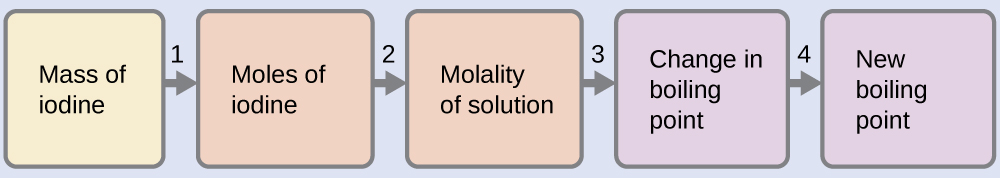
- Convert from grams to moles of I2 using the molar mass of I2 in the unit conversion factor.
Result: 0.363 mol - Determine the molality of the solution from the number of moles of solute and the mass of solvent, in kilograms.
Result: 0.454 m - Use the direct proportionality between the change in boiling point and molal concentration to determine how much the boiling point changes.
Result: 1.65 °C - Determine the new boiling point from the boiling point of the pure solvent and the change.
Result: 62.91 °C
Check each result as a self-assessment.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\)
What is the boiling point of a solution of 1.0 g of glycerin, C3H5(OH)3, in 47.8 g of water? Assume an ideal solution.
- Answer
-
100.12 °C
Distillation of Solutions
Distillation is a technique for separating the components of mixtures that is widely applied in both in the laboratory and in industrial settings. It is used to refine petroleum, to isolate fermentation products, and to purify water. This separation technique involves the controlled heating of a sample mixture to selectively vaporize, condense, and collect one or more components of interest. A typical apparatus for laboratory-scale distillations is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\).
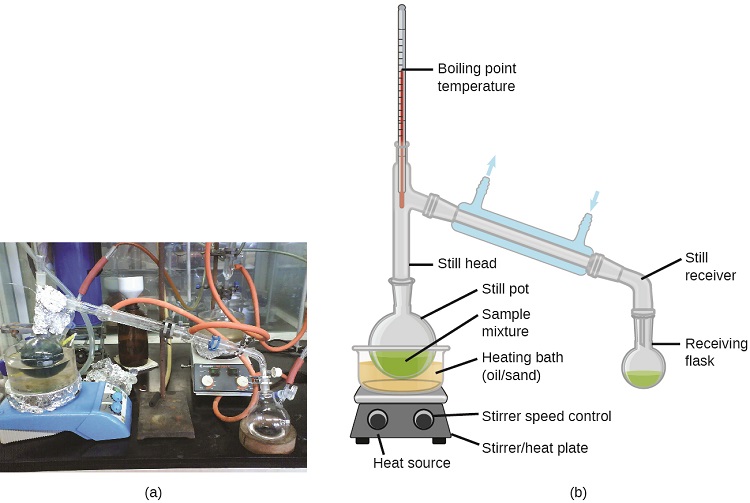
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): A typical laboratory distillation unit is shown in (a) a photograph and (b) a schematic diagram of the components. (credit a: modification of work by “Rifleman82”/Wikimedia commons; credit b: modification of work by “Slashme”/Wikimedia Commons)
Oil refineries use large-scale fractional distillation to separate the components of crude oil. The crude oil is heated to high temperatures at the base of a tall fractionating column, vaporizing many of the components that rise within the column. As vaporized components reach adequately cool zones during their ascent, they condense and are collected. The collected liquids are simpler mixtures of hydrocarbons and other petroleum compounds that are of appropriate composition for various applications (e.g., diesel fuel, kerosene, gasoline), as depicted in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\).
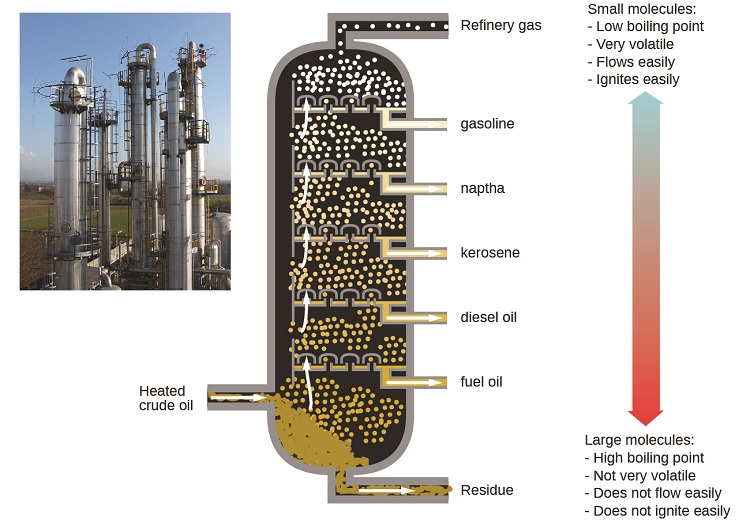
Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\): Crude oil is a complex mixture that is separated by large-scale fractional distillation to isolate various simpler mixtures.
Depression of the Freezing Point of a Solvent
Solutions freeze at lower temperatures than pure liquids. This phenomenon is exploited in “de-icing” schemes that use salt (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)), calcium chloride, or urea to melt ice on roads and sidewalks, and in the use of ethylene glycol as an “antifreeze” in automobile radiators. Seawater freezes at a lower temperature than fresh water, and so the Arctic and Antarctic oceans remain unfrozen even at temperatures below 0 °C (as do the body fluids of fish and other cold-blooded sea animals that live in these oceans).

Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): Rock salt (NaCl), calcium chloride (CaCl2), or a mixture of the two are used to melt ice. (credit: modification of work by Eddie Welker)
The decrease in freezing point of a dilute solution compared to that of the pure solvent, ΔTf, is called the freezing point depression and is directly proportional to the molal concentration of the solute
\[ΔT_\ce{f}=K_\ce{f}m \label{11.5.9}\]
where
- \(m\) is the molal concentration of the solute in the solvent and
- \(K_f\) is called the freezing point depression constant (or cryoscopic constant).
Just as for boiling point elevation constants, these are characteristic properties whose values depend on the chemical identity of the solvent. Values of Kf for several solvents are listed in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
Example \(\PageIndex{9}\): Calculation of the Freezing Point of a Solution
What is the freezing point of the 0.33 m solution of a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte solute in benzene described in Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)?
Solution
Use the equation relating freezing point depression to solute molality to solve this problem in two steps.

- Calculate the change in freezing point. \[ΔT_\ce{f}=K_\ce{f}m=5.12\:°\ce C\:m^{−1}×0.33\:m=1.7\:°\ce C\]
- Subtract the freezing point change observed from the pure solvent’s freezing point. [\mathrm{Freezing\: Temperature=5.5\:°C−1.7\:°C=3.8\:°C}\]
Exercise \(\PageIndex{9}\)
What is the freezing point of a 1.85 m solution of a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte solute in nitrobenzene?
- Answer
-
−9.3 °C
Colligative Properties and De-Icing
Sodium chloride and its group 2 analogs calcium and magnesium chloride are often used to de-ice roadways and sidewalks, due to the fact that a solution of any one of these salts will have a freezing point lower than 0 °C, the freezing point of pure water. The group 2 metal salts are frequently mixed with the cheaper and more readily available sodium chloride (“rock salt”) for use on roads, since they tend to be somewhat less corrosive than the NaCl, and they provide a larger depression of the freezing point, since they dissociate to yield three particles per formula unit, rather than two particles like the sodium chloride.
Because these ionic compounds tend to hasten the corrosion of metal, they would not be a wise choice to use in antifreeze for the radiator in your car or to de-ice a plane prior to takeoff. For these applications, covalent compounds, such as ethylene or propylene glycol, are often used. The glycols used in radiator fluid not only lower the freezing point of the liquid, but they elevate the boiling point, making the fluid useful in both winter and summer. Heated glycols are often sprayed onto the surface of airplanes prior to takeoff in inclement weather in the winter to remove ice that has already formed and prevent the formation of more ice, which would be particularly dangerous if formed on the control surfaces of the aircraft (Video \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
Video \(\PageIndex{1}\): Freezing point depression is exploited to remove ice from the control surfaces of aircraft.
Phase Diagram for an Aqueous Solution of a Nonelectrolyte
The colligative effects on vapor pressure, boiling point, and freezing point described in the previous section are conveniently summarized by comparing the phase diagrams for a pure liquid and a solution derived from that liquid. Phase diagrams for water and an aqueous solution are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\).
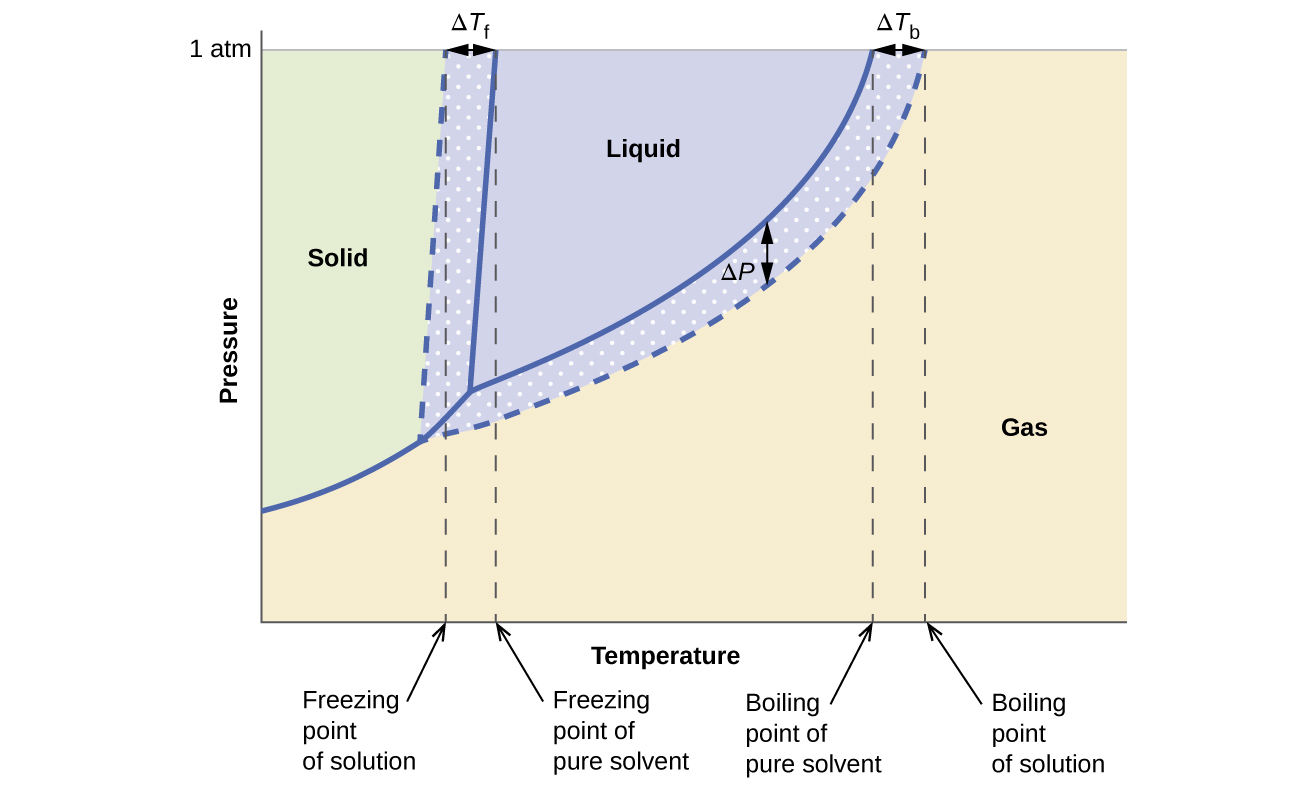
Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\): These phase diagrams show water (solid curves) and an aqueous solution of nonelectrolyte (dashed curves).
The liquid-vapor curve for the solution is located beneath the corresponding curve for the solvent, depicting the vapor pressure lowering, ΔP, that results from the dissolution of nonvolatile solute. Consequently, at any given pressure, the solution’s boiling point is observed at a higher temperature than that for the pure solvent, reflecting the boiling point elevation, ΔTb, associated with the presence of nonvolatile solute. The solid-liquid curve for the solution is displaced left of that for the pure solvent, representing the freezing point depression, ΔTf, that accompanies solution formation. Finally, notice that the solid-gas curves for the solvent and its solution are identical. This is the case for many solutions comprising liquid solvents and nonvolatile solutes. Just as for vaporization, when a solution of this sort is frozen, it is actually just the solvent molecules that undergo the liquid-to-solid transition, forming pure solid solvent that excludes solute species. The solid and gaseous phases, therefore, are composed solvent only, and so transitions between these phases are not subject to colligative effects.
Determination of Molar Masses
Changes in freezing point, boiling point, and vapor pressure are directly proportional to the concentration of solute present. Consequently, we can use a measurement of one of these properties to determine the molar mass of the solute from the measurements.
Example \(\PageIndex{10}\): Determining Molar Mass from Freezing Point Depression
A solution of 4.00 g of a nonelectrolyte dissolved in 55.0 g of benzene is found to freeze at 2.32 °C. What is the molar mass of this compound?
Solution
We can solve this problem using the following steps.
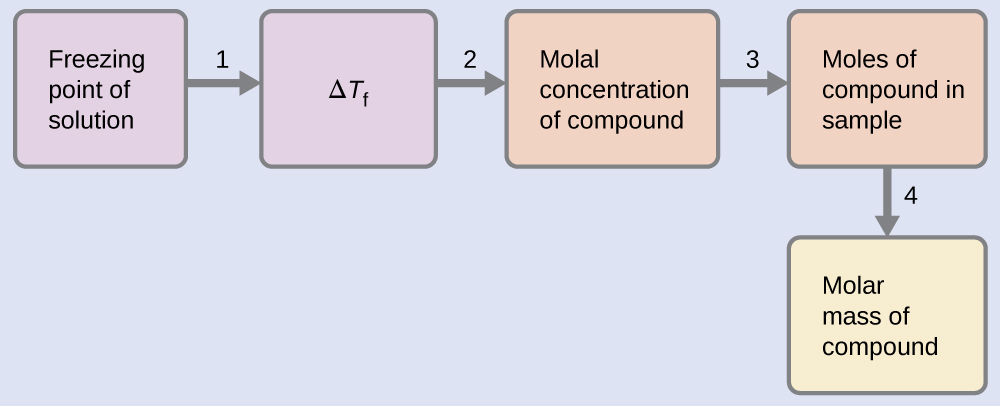
- Determine the change in freezing point from the observed freezing point and the freezing point of pure benzene (Table 11.5.1).
\(ΔT_\ce{f}=\mathrm{5.5\:°C−2.32\:°C=3.2\:°C}\) - Determine the molal concentration from Kf, the freezing point depression constant for benzene (Table 11.5.1), and ΔTf.
\(ΔT_\ce{f}=K_\ce{f}m\)
\(m=\dfrac{ΔT_\ce{f}}{K_\ce{f}}=\dfrac{3.2\:°\ce C}{5.12\:°\ce C m^{−1}}=0.63\:m\) - Determine the number of moles of compound in the solution from the molal concentration and the mass of solvent used to make the solution.
\(\mathrm{Moles\: of\: solute=\dfrac{0.62\:mol\: solute}{1.00\cancel{kg\: solvent}}×0.0550\cancel{kg\: solvent}=0.035\:mol}\) - Determine the molar mass from the mass of the solute and the number of moles in that mass.
\(\mathrm{Molar\: mass=\dfrac{4.00\:g}{0.034\:mol}=1.2×10^2\:g/mol}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{10}\)
A solution of 35.7 g of a nonelectrolyte in 220.0 g of chloroform has a boiling point of 64.5 °C. What is the molar mass of this compound?
- Answer
-
1.8 × 102 g/mol
Example \(\PageIndex{11}\): Determination of a Molar Mass from Osmotic Pressure
A 0.500 L sample of an aqueous solution containing 10.0 g of hemoglobin has an osmotic pressure of 5.9 torr at 22 °C. What is the molar mass of hemoglobin?
Solution
Here is one set of steps that can be used to solve the problem:
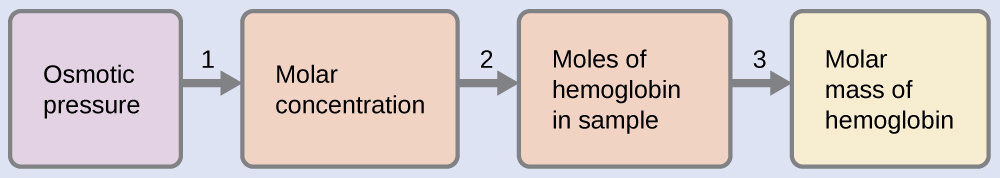
- Convert the osmotic pressure to atmospheres, then determine the molar concentration from the osmotic pressure.
\[\Pi=\mathrm{\dfrac{5.9\:torr×1\:atm}{760\:torr}=7.8×10^{−3}\:atm}\]
\[\Pi=MRT\]
\(M=\dfrac{Π}{RT}=\mathrm{\dfrac{7.8×10^{−3}\:atm}{(0.08206\:L\: atm/mol\: K)(295\:K)}=3.2×10^{−4}\:M}\) - Determine the number of moles of hemoglobin in the solution from the concentration and the volume of the solution.
\(\mathrm{moles\: of\: hemoglobin=\dfrac{3.2×10^{−4}\:mol}{1\cancel{L\: solution}}×0.500\cancel{L\: solution}=1.6×10^{−4}\:mol}\) - Determine the molar mass from the mass of hemoglobin and the number of moles in that mass.
\(\mathrm{molar\: mass=\dfrac{10.0\:g}{1.6×10^{−4}\:mol}=6.2×10^4\:g/mol}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{11}\)
What is the molar mass of a protein if a solution of 0.02 g of the protein in 25.0 mL of solution has an osmotic pressure of 0.56 torr at 25 °C?
- Answer
-
2.7 × 104 g/mol
Colligative Properties of Electrolytes
As noted previously in this module, the colligative properties of a solution depend only on the number, not on the kind, of solute species dissolved. For example, 1 mole of any nonelectrolyte dissolved in 1 kilogram of solvent produces the same lowering of the freezing point as does 1 mole of any other nonelectrolyte. However, 1 mole of sodium chloride (an electrolyte) forms 2 moles of ions when dissolved in solution. Each individual ion produces the same effect on the freezing point as a single molecule does.
Example \(\PageIndex{13}\): The Freezing Point of a Solution of an Electrolyte
The concentration of ions in seawater is approximately the same as that in a solution containing 4.2 g of NaCl dissolved in 125 g of water. Assume that each of the ions in the NaCl solution has the same effect on the freezing point of water as a nonelectrolyte molecule, and determine the freezing temperature the solution (which is approximately equal to the freezing temperature of seawater).
Solution
We can solve this problem using the following series of steps.
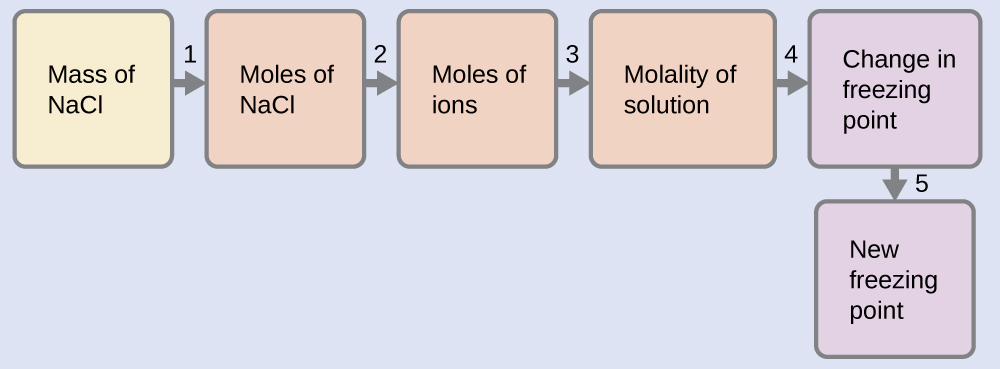
- Convert from grams to moles of NaCl using the molar mass of NaCl in the unit conversion factor. Result: 0.072 mol NaCl
- Determine the number of moles of ions present in the solution using the number of moles of ions in 1 mole of NaCl as the conversion factor (2 mol ions/1 mol NaCl). Result: 0.14 mol ions
- Determine the molality of the ions in the solution from the number of moles of ions and the mass of solvent, in kilograms. Result: 1.1 m
- Use the direct proportionality between the change in freezing point and molal concentration to determine how much the freezing point changes. Result: 2.0 °C
- Determine the new freezing point from the freezing point of the pure solvent and the change. Result: −2.0 °C
Check each result as a self-assessment.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Assume that each of the ions in calcium chloride, CaCl2, has the same effect on the freezing point of water as a nonelectrolyte molecule. Calculate the freezing point of a solution of 0.724 g of CaCl2 in 175 g of water.
- Answer
-
−0.208 °C
Assuming complete dissociation, a 1.0 m aqueous solution of NaCl contains 2.0 mole of ions (1.0 mol Na+ and 1.0 mol Cl−) per each kilogram of water, and its freezing point depression is expected to be
\[ΔT_\ce{f}=\mathrm{2.0\:mol\: ions/kg\: water×1.86\:°C\: kg\: water/mol\: ion=3.7\:°C.} \label{11.5.11}\]
When this solution is actually prepared and its freezing point depression measured, however, a value of 3.4 °C is obtained. Similar discrepancies are observed for other ionic compounds, and the differences between the measured and expected colligative property values typically become more significant as solute concentrations increase. These observations suggest that the ions of sodium chloride (and other strong electrolytes) are not completely dissociated in solution.
To account for this and avoid the errors accompanying the assumption of total dissociation, an experimentally measured parameter named in honor of Nobel Prize-winning German chemist Jacobus Henricus van’t Hoff is used. The van’t Hoff factor (i) is defined as the ratio of solute particles in solution to the number of formula units dissolved:
\[i=\dfrac{\textrm{moles of particles in solution}}{\textrm{moles of formula units dissolved}} \label{11.5.12}\]
Values for measured van’t Hoff factors for several solutes, along with predicted values assuming complete dissociation, are shown in Table \(\PageIndex{2}\).
| Electrolyte | Particles in Solution | i (Predicted) | i (Measured) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCl | H+, Cl− | 2 | 1.9 |
| NaCl | Na+, Cl− | 2 | 1.9 |
| MgSO4 | Mg2+, \(\ce{SO4^2-}\) | 2 | 1.3 |
| MgCl2 | Mg2+, 2Cl− | 3 | 2.7 |
| FeCl3 | Fe3+, 3Cl− | 4 | 3.4 |
| glucose (a non-electrolyte) | C12H22O11 | 1 | 1.0 |
In 1923, the chemists Peter Debye and Erich Hückel proposed a theory to explain the apparent incomplete ionization of strong electrolytes. They suggested that although interionic attraction in an aqueous solution is very greatly reduced by solvation of the ions and the insulating action of the polar solvent, it is not completely nullified. The residual attractions prevent the ions from behaving as totally independent particles (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)). In some cases, a positive and negative ion may actually touch, giving a solvated unit called an ion pair. Thus, the activity, or the effective concentration, of any particular kind of ion is less than that indicated by the actual concentration. Ions become more and more widely separated the more dilute the solution, and the residual interionic attractions become less and less. Thus, in extremely dilute solutions, the effective concentrations of the ions (their activities) are essentially equal to the actual concentrations. Note that the van’t Hoff factors for the electrolytes in Table \(\PageIndex{2}\) are for 0.05 m solutions, at which concentration the value of i for NaCl is 1.9, as opposed to an ideal value of 2.
>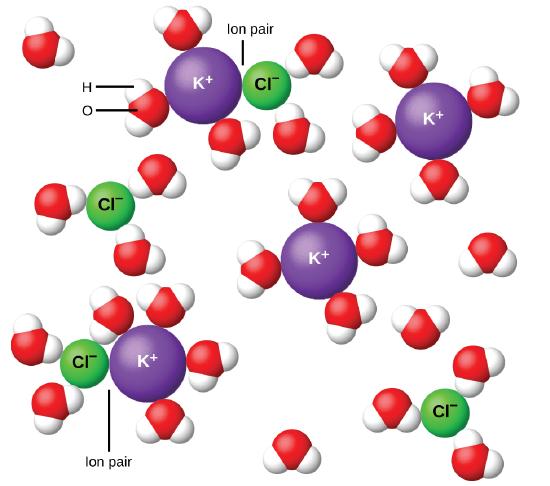
Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\): Ions become more and more widely separated the more dilute the solution, and the residual interionic attractions become less.
Summary
Video \(\PageIndex{2}\): An overview of concentration units for solutions.
In addition to molarity, a number of other solution concentration units are used in various applications. Percentage concentrations based on the solution components’ masses, volumes, or both are useful for expressing relatively high concentrations, whereas lower concentrations are conveniently expressed using ppm or ppb units. These units are popular in environmental, medical, and other fields where mole-based units such as molarity are not as commonly used.
Properties of a solution that depend only on the concentration of solute particles are called colligative properties. They include changes in the vapor pressure, boiling point, and freezing point of the solvent in the solution. The magnitudes of these properties depend only on the total concentration of solute particles in solution, not on the type of particles. Ionic compounds may not completely dissociate in solution due to activity effects, in which case observed colligative effects may be less than predicted.
Key Equations
- ΔTb = Kbm
- ΔTf = Kfm
- Π = MRT
Footnotes
- A nonelectrolyte shown for comparison.
Glossary
- mass percentage
- ratio of solute-to-solution mass expressed as a percentage
- mass-volume percent
- ratio of solute mass to solution volume, expressed as a percentage
- parts per billion (ppb)
- ratio of solute-to-solution mass multiplied by 109
- parts per million (ppm)
- ratio of solute-to-solution mass multiplied by 106
- volume percentage
- ratio of solute-to-solution volume expressed as a percentage
- boiling point elevation
- elevation of the boiling point of a liquid by addition of a solute
- boiling point elevation constant
- the proportionality constant in the equation relating boiling point elevation to solute molality; also known as the ebullioscopic constant
- colligative property
- property of a solution that depends only on the concentration of a solute species
- freezing point depression
- lowering of the freezing point of a liquid by addition of a solute
- freezing point depression constant
- (also, cryoscopic constant) proportionality constant in the equation relating freezing point depression to solute molality
- ion pair
- solvated anion/cation pair held together by moderate electrostatic attraction
- molality (m)
- a concentration unit defined as the ratio of the numbers of moles of solute to the mass of the solvent in kilograms
- van’t Hoff factor (i)
- the ratio of the number of moles of particles in a solution to the number of moles of formula units dissolved in the solution
Contributors
Paul Flowers (University of North Carolina - Pembroke), Klaus Theopold (University of Delaware) and Richard Langley (Stephen F. Austin State University) with contributing authors. Textbook content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/85abf193-2bd...a7ac8df6@9.110).
- Adelaide Clark, Oregon Institute of Technology
- Crash Course Chemistry: Crash Course is a division of Complexly and videos are free to stream for educational purposes.

