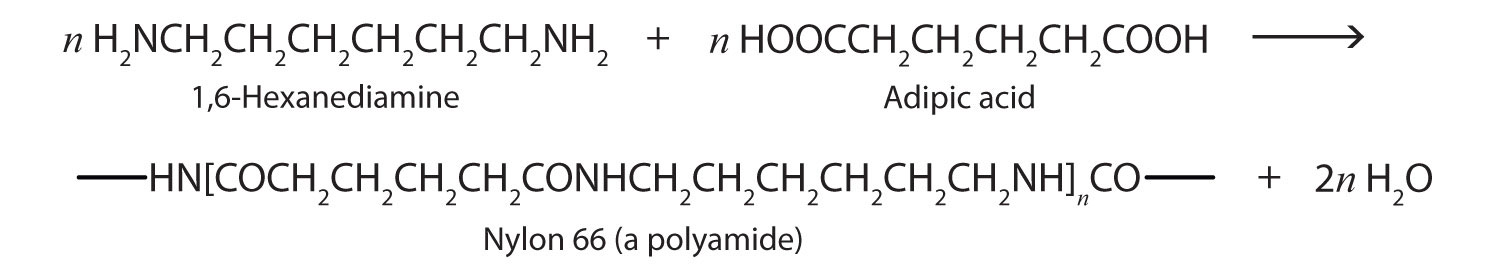Polyamides
Just as the reaction of a diol and a diacid forms a polyester, the reaction of a diacid and a diamine yields a polyamide. The two difunctional monomers often employed are adipic acid and 1,6-hexanediamine. The monomers condense by splitting out water to form a new product, which is still difunctional and thus can react further to yield a polyamide polymer.
Some polyamides are known as nylons. Nylons are among the most widely used synthetic fibers—for example, they are used in ropes, sails, carpets, clothing, tires, brushes, and parachutes. They also can be molded into blocks for use in electrical equipment, gears, bearings, and valves.
Polyesters
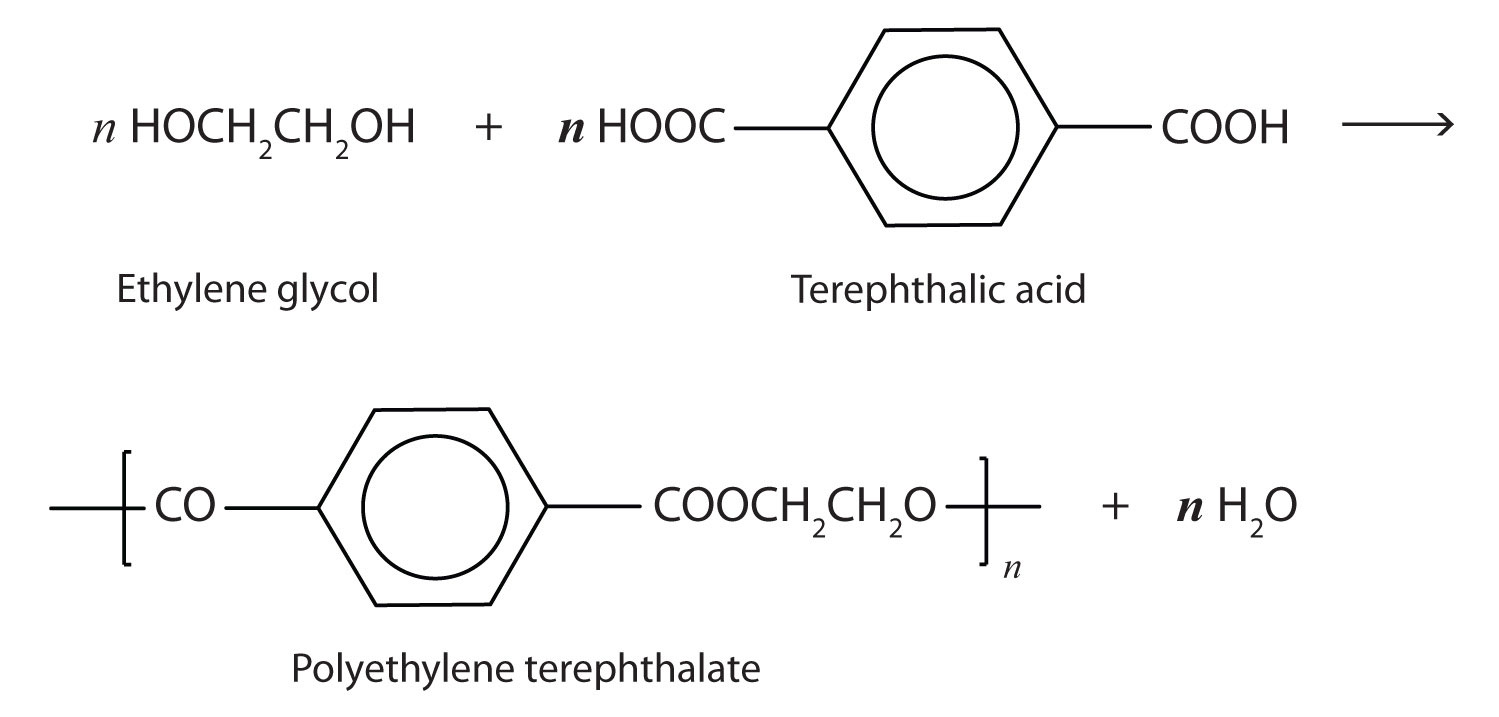
A commercially important esterification reaction is condensation polymerization, in which a reaction occurs between a dicarboxylic acid and a dihydric alcohol (diol), with the elimination of water. Such a reaction yields an ester that contains a free (unreacted) carboxyl group at one end and a free alcohol group at the other end. Further condensation reactions then occur, producing polyester polymers.
The most important polyester, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is made from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol monomers:
Polyester molecules make excellent fibers and are used in many fabrics. A knitted polyester tube, which is biologically inert, can be used in surgery to repair or replace diseased sections of blood vessels. PET is used to make bottles for soda pop and other beverages. It is also formed into films called Mylar. When magnetically coated, Mylar tape is used in audio- and videocassettes. Synthetic arteries can be made from PET, polytetrafluoroethylene, and other polymers.
Condensation Polymers
A large number of important and useful polymeric materials are not formed by chain-growth processes involving reactive species such as radicals, but proceed instead by conventional functional group transformations of polyfunctional reactants. These polymerizations often (but not always) occur with loss of a small byproduct, such as water, and generally (but not always) combine two different components in an alternating structure. The polyester Dacron and the polyamide Nylon 66, shown here, are two examples of synthetic condensation polymers, also known as step-growth polymers. In contrast to chain-growth polymers, most of which grow by carbon-carbon bond formation, step-growth polymers generally grow by carbon-heteroatom bond formation (C-O & C-N in Dacron & Nylon respectively). Although polymers of this kind might be considered to be alternating copolymers, the repeating monomeric unit is usually defined as a combined moiety.
Examples of naturally occurring condensation polymers are cellulose, the polypeptide chains of proteins, and poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid), a polyester synthesized in large quantity by certain soil and water bacteria. Formulas for these will be displayed below by clicking on the diagram.
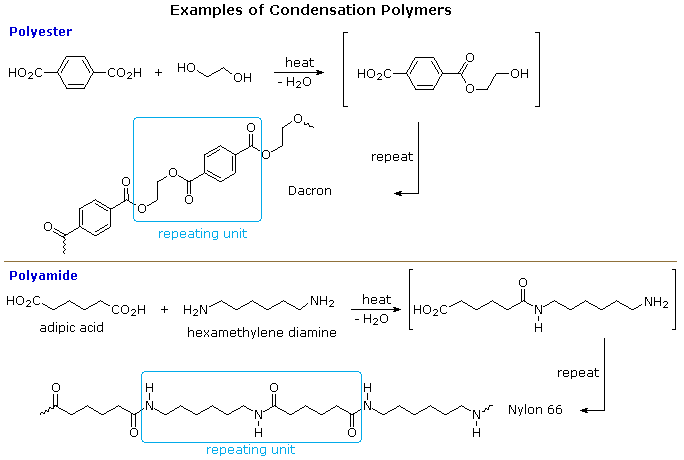
Characteristics of Condensation Polymers
Condensation polymers form more slowly than addition polymers, often requiring heat, and they are generally lower in molecular weight. The terminal functional groups on a chain remain active, so that groups of shorter chains combine into longer chains in the late stages of polymerization. The presence of polar functional groups on the chains often enhances chain-chain attractions, particularly if these involve hydrogen bonding, and thereby crystallinity and tensile strength. The following examples of condensation polymers are illustrative.
Note that for commercial synthesis the carboxylic acid components may actually be employed in the form of derivatives such as simple esters. Also, the polymerization reactions for Nylon 6 and Spandex do not proceed by elimination of water or other small molecules. Nevertheless, the polymer clearly forms by a step-growth process. Some Condensation Polymers

Contributors and Attributions
John D. Robert and Marjorie C. Caserio (1977) Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, second edition. W. A. Benjamin, Inc. , Menlo Park, CA. ISBN 0-8053-8329-8. This content is copyrighted under the following conditions, "You are granted permission for individual, educational, research and non-commercial reproduction, distribution, display and performance of this work in any format."