Hybridization
2-1 For each of the following compounds, identify the hybridization of each carbon or nitrogen atom with an arrow pointed at it. 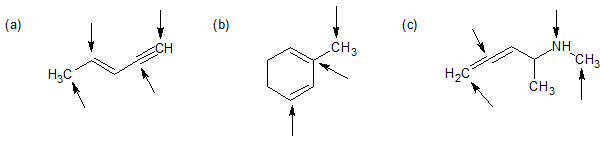
2-2 Rank the following bonds in order of decreasing bond length. Then rank the bonds in order from strongest to weakest.
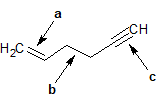
2-3 How many sigma and pi bonds are in a molecule of ethane (C2H6)?
2-4 How many sigma and pi bonds are in a molecule of ethylene (C2H4)?
2-5 How many sigma and pi bonds are in a molecule of acetylene (C2H2)?
Hybridization, Electron Geometry, and Molecular Shape
2-6 What is the hybridization state and geometry of the carbon atom in methane (CH4)?
a) sp, linear
b) sp3, tetrahedral
c) sp2, trigonal planar
d) None of the above
2-7 Identify the electron geometry of the following compounds.
a) H2O
b) PF5
c) NH4+
d) The carbonyl carbon of acetone (CH3)2CO. (Note that double bonds between carbon and oxygen must be recognized.)
2-8 For the following compounds, identify which atoms have sp2 hybridization.
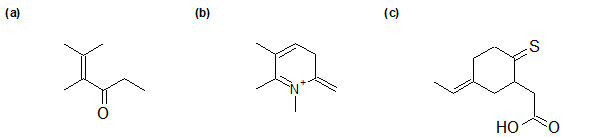
2-9 Draw the orbitals showing the geometric shape of ammonia (NH3). Identify its geometric shape.
2-10 What is the geometric shape of the boron atom in BH3? What is the bond angle of the hydrogen atoms?
Bond Rotation
2-11 Will the following compound experience free rotation around the middle bond? Explain why or why not.
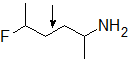
2-12 Will the following compound experience free rotation around the middle bond? Explain why or why not.
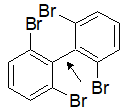
2-13 Can a molecule of ethylene experience free rotation around the C=C bond?
Polarity of Bonds and Molecules
2-14 For the following compounds, draw an arrow to show the direction of the dipole moment (if any).

2-15 In the following pairs of compounds, identify the compound with the larger dipole moment (if any).
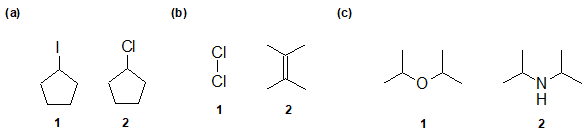
2-16 True or False: Generally, the larger the difference in electronegativity of connected atoms, the greater the dipole moment.
Intermolecular Forces (IMFs)
2-17 Identify which of the following compounds can form hydrogen bonds.
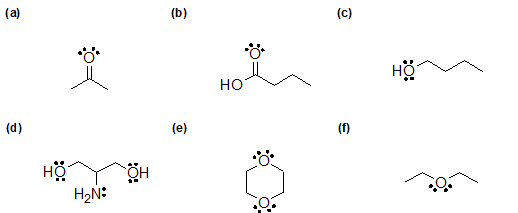
2-18 For the compounds in the previous problem ( 2-17 above) that can hydrogen bond, draw how they can form those bonds.
2-19 Identify what type of intermolecular force the following compounds experience.
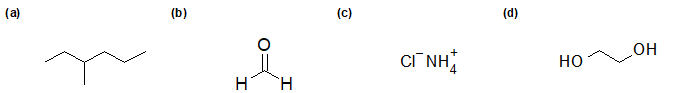
IMFs and Solubility
2-20 Identify whether the following compounds are miscible or soluble in water.
2-21 Identify which solvent, hexanes or dichloromethane (DCM), would be the better solvent to dissolve 3.0 grams of caffeine. Explain your answer.
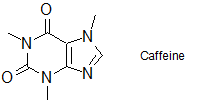
Hydrocarbons and an Introduction to Isomerism
2-22 Identify whether the following hydrocarbons are alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes.

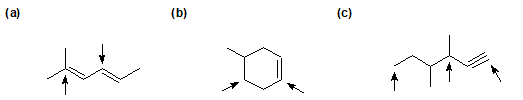
2-23 For the following compounds, identify the hybridization state of each labeled carbon.
2-24 Draw all possible isomers for the following compounds.
a) C4H10
b) C6H14
c) C3H6
2-25 Does (CH3)2CHCCCH3 show cis/trans isomerism? Explain why or why not.
Organic Compounds with Oxygen
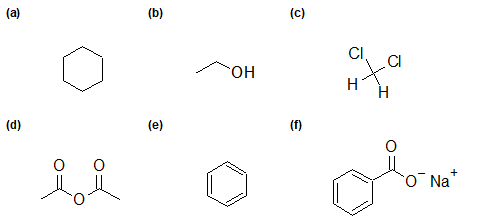
2-26 Identify the functional group(s) of each compound.
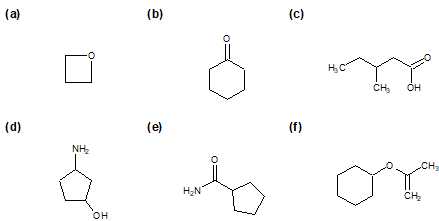
2-27 What functional groups are found in the following compounds?
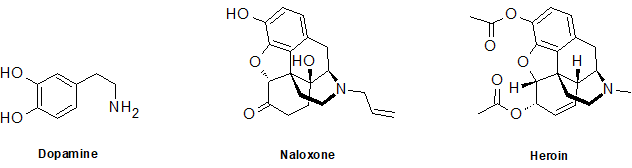
2-28 What oxygen-containing functional groups are present in the following compounds. The nitrogen-containing group is a challenge question.
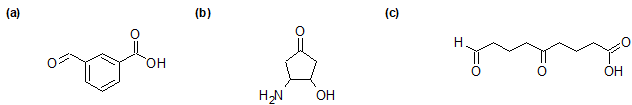
2-29 Identify whether the functional groups on the following compounds are classified correctly. If not, give the correct classification.
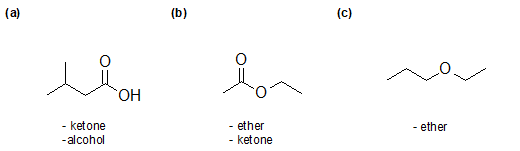
Organic Compounds with Nitrogen
2-30 First, identify which of the following compounds has a dipole moment. Then, predict which of the following compounds will have the higher boiling point and explain why.
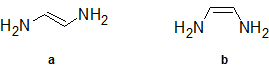
2-31 Identify whether the functional groups of the following compounds are classified correctly. If not, give the correct classification.


