13.1: Naming the Aldehydes and Ketones
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 201223
Objectives
After completing this section, you should be able to
- provide the IUPAC name of an aldehyde or ketone, given its Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure.
- draw the structure of an aldehyde or ketone, given its IUPAC name.
- draw the structure of the following aldehydes and ketones, given their trivial names: formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, benzaldehyde, acetone, acetophenone, benzophenone.
Study Notes
We only use those trivial names listed under Objective 3, above. We use systematic names in all other cases. For example, the systematic name of the compound shown below is benzenecarbaldehyde, but it has the trivial name of benzaldehyde.
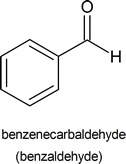
When naming unsaturated aldehydes and ketones, you must give the carbonyl group “priority” over the double bond when you are deciding which end of the carbon chain to begin numbering The carbonyl‑carbon of an aldehyde will always be at the end of the carbon chain in an acyclic compound; and therefore numbering always starts at this carbon. It is for this reason, too, that the number “1” is not required when naming a compound such as 2‑ethyl‑4‑methylpentanal.
The most potent and varied odors are aldehydes. Ketones are widely used as industrial solvents. Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl group. Aldehydes are considered the most important functional group. They are often called the formyl or methanoyl group. Aldehydes derive their name from the dehydration of alcohols. Aldehydes contain the carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom. Ketones contain the carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms.
Introduction
Aldehydes and ketones are organic compounds which incorporate a carbonyl functional group, C=O. The carbon atom of this group has two remaining bonds that may be occupied by hydrogen, alkyl or aryl substituents. If at least one of these substituents is hydrogen, the compound is an aldehyde. If neither is hydrogen, the compound is a ketone.
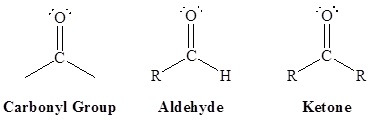
Naming Aldehydes
The IUPAC system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix -al to aldehydes. For example, H2C=O is methanal, more commonly called formaldehyde. Since an aldehyde carbonyl group must always lie at the end of a carbon chain, it is always is given the #1 location position in numbering and it is not necessary to include it in the name. There are several simple carbonyl containing compounds which have common names which are retained by IUPAC.
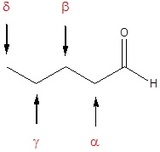
Also, there is a common method for naming aldehydes and ketones. For aldehydes common parent chain names, similar to those used for carboxylic acids, are used and the suffix –aldehyde is added to the end. In common names of aldehydes, carbon atoms near the carbonyl group are often designated by Greek letters. The atom adjacent to the carbonyl function is alpha, the next removed is beta and so on.
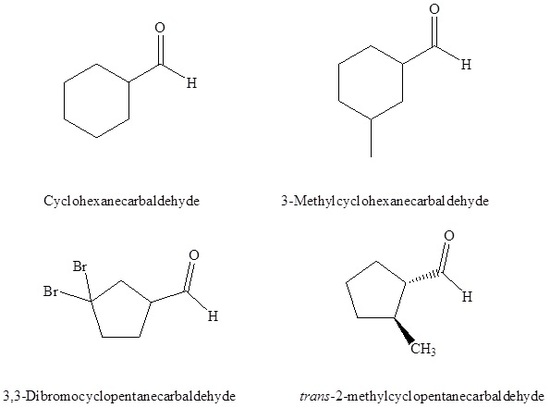
If the aldehyde moiety 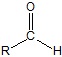 (-CHO) is attached to a ring the suffix –carbaldehyde is added to the name of the ring. The carbon attached to this moiety will get the #1 location number in naming the ring.
(-CHO) is attached to a ring the suffix –carbaldehyde is added to the name of the ring. The carbon attached to this moiety will get the #1 location number in naming the ring.
Summary of Aldehyde Nomenclature rules
- Aldehydes take their name from their parent alkane chains. The -e is removed from the end and is replaced with -al.
- The aldehyde funtional group is given the #1 numbering location and this number is not included in the name.
- For the common name of aldehydes start with the common parent chain name and add the suffix -aldehyde. Substituent positions are shown with Greek letters.
- When the -CHO functional group is attached to a ring the suffix -carbaldehyde is added, and the carbon attached to that group is C1.
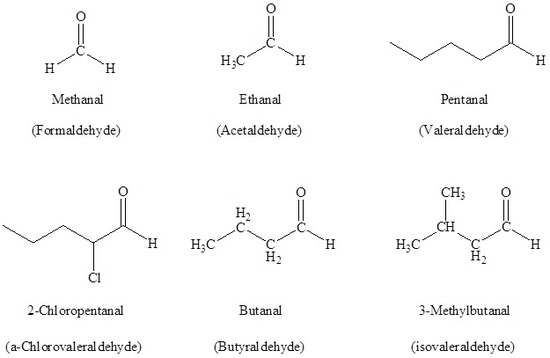
Example 19.1.1
The IUPAC system names are given on top while the common name is given on the bottom in parentheses.
Naming Ketones
The IUPAC system of nomenclature assigns a characteristic suffix of -one to ketones. A ketone carbonyl function may be located anywhere within a chain or ring, and its position is usually given by a location number. Chain numbering normally starts from the end nearest the carbonyl group. Very simple ketones, such as propanone and phenylethanone do not require a locator number, since there is only one possible site for a ketone carbonyl function
The common names for ketones are formed by naming both alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl then adding the suffix -ketone. The attached alkyl groups are arranged in the name alphabetically.
Summary of Ketone Nomenclature rules
- Ketones take their name from their parent alkane chains. The ending -e is removed and replaced with -one.
- The common name for ketones are simply the substituent groups listed alphabetically + ketone.
- Some common ketones are known by their generic names. Such as the fact that propanone is commonly referred to as acetone.
Example 19.1.2
The IUPAC system names are given on top while the common name is given on the bottom in parentheses.
Naming Aldehydes and Ketones in the Same Molecule
As with many molecules with two or more functional groups, one is given priority while the other is named as a substituent. Because aldehydes have a higher priority than ketones, molecules which contain both functional groups are named as aldehydes and the ketone is named as an "oxo" substituent. It is not necessary to give the aldehyde functional group a location number, however, it is usually necessary to give a location number to the ketone.
Example 19.1.3
Naming Dialdehydes and Diketones
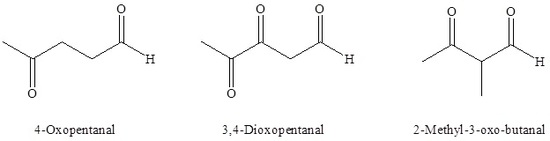
For dialdehydes the location numbers for both carbonyls are omitted because the aldehyde functional groups are expected to occupy the ends of the parent chain. The ending –dial is added to the end of the parent chain name.
Example 19.1.4
For diketones both carbonyls require a location number. The ending -dione or -dial is added to the end of the parent chain.
Example 19.1.5
Naming Cyclic Ketones and Diketones
In cyclic ketones the carbonyl group is assigned location position #1, and this number is not included in the name, unless more than one carbonyl group is present. The rest of the ring is numbered to give substituents the lowest possible location numbers. Remember the prefix cyclo is included before the parent chain name to indicate that it is in a ring. As with other ketones the –e ending is replaced with the –one to indicate the presence of a ketone.
With cycloalkanes which contain two ketones both carbonyls need to be given a location numbers. Also, an –e is not removed from the end but the suffix –dione is added.
Example 19.1.6
Naming Carbonyls and Hydroxyls in the Same Molecule
When and aldehyde or ketone is present in a molecule which also contains an alcohol functional group the carbonyl is given nomenclature priority by the IUPAC system. This means that the carbonyl is given the lowest possible location number and the appropriate nomenclature suffix is included. In the case of alcohols the OH is named as a hydroxyl substituent. However, the l in hydroxyl is generally removed.
Example 19.1.7
Naming Carbonyls and Alkenes in the Same Molecule
When and aldehyde or ketone is present in a molecule which also contains analkene functional group the carbonyl is given nomenclature priority by the IUPAC system. This means that the carbonyl is given the lowest possible location number and the appropriate nomenclature suffix is included.
When carbonyls are included with an alkene the following order is followed:
(Location number of the alkene)-(Prefix name for the longest carbon chain minus the -ane ending)-(an -en ending to indicate the presence of an alkene)-(the location number of the carbonyl if a ketone is present)-(either an –one or and -anal ending).
Remember that the carbonyl has priority so it should get the lowest possible location number. Also, remember that cis/tran or E/Z nomenclature for the alkene needs to be included if necessary.
Example 19.1.8
Aldehydes and Ketones as Fragments
- Alkanoyl is the common name of the
 fragment, though the older naming, acyl, is still widely used.
fragment, though the older naming, acyl, is still widely used. - Formyl is the common name of the
 fragment.
fragment. - Acety is the common name of the CH3-C=O- fragment.
Example 19.1.9
acetyl chloride |
acetylaldehyde |
formyl fluoride |
Exercises
Exercise 19.1.1
Give the IUPAC name for each compound:
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
A) 3,4-dimethylhexanal
B) 5-bromo-2-pentanone
C) 2,4-hexanedione
D) cis-3-pentenal
E) 6-methyl-5-hepten-3-one
F) 3-hydroxy-2,4-pentanedione
G) 1,2-cyclobutanedione
H) 2-methyl-propanedial
I) 3-methyl-5-oxo-hexanal
J) cis-2,3-dihydroxycyclohexanone
K) 3-bromo-2-methylcyclopentanecarboaldehyde
L) 3-bromo-2-methylpropanal
Exercise 19.1.2
Give the structure corresponding to each IUPAC name:
A) butanal
B) 2-hydroxycyclopentanone
C) 2,3-pentanedione
D) 1,3-cyclohexanedione
E) 3,4-dihydoxy-2-butanone
F) (E) 3-methyl-2-hepten-4-one
G) 3-oxobutanal
H) cis-3-bromocyclohexanecarboaldehyde
I) butanedial
J) trans-2-methyl-3-hexenal
- Answer
-
References
- Vollhardt, K. Peter C., and Neil E. Schore. Organic Chemistry. 5th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman, 2007.
- Zumdahl, Steven S., and Susan A. Zumdahl. Chemistry. 6th ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin College Division, 2002.
Contributors and Attributions
Dr. Dietmar Kennepohl FCIC (Professor of Chemistry, Athabasca University)
Prof. Steven Farmer (Sonoma State University)
William Reusch, Professor Emeritus (Michigan State U.), Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry

