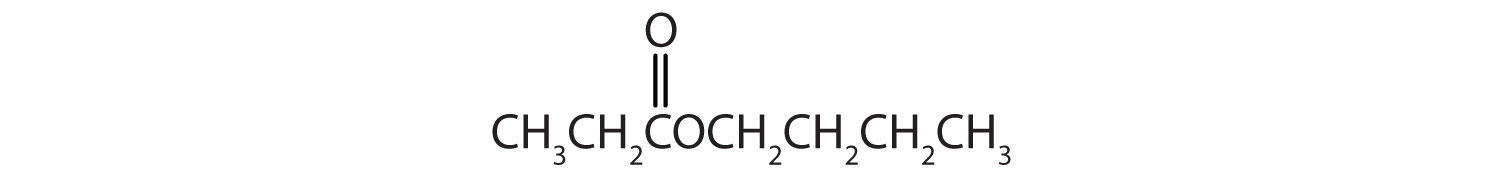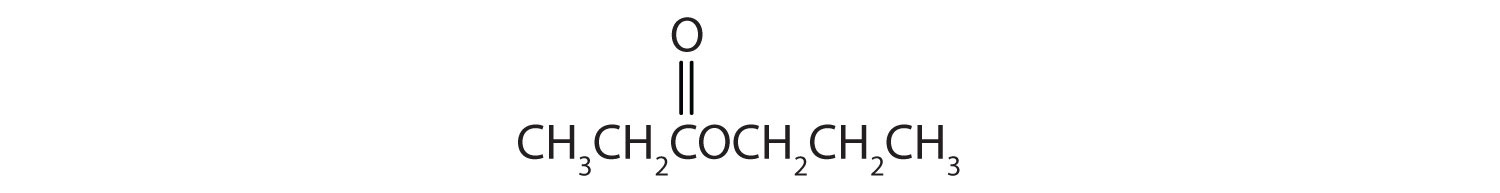11.3 Alcohols, Acids, and Esters
- Page ID
- 218439
Alcohols
An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl (OH) functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols, we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH, where R is an alkyl group. Alcohols are common in nature. Most people are familiar with ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, but this compound is only one of a family of organic compounds known as alcohols. The family also includes such familiar substances as cholesterol and the carbohydrates. Methanol (CH3OH) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH) are the first two members of the homologous series of alcohols.
Alcohols with one to four carbon atoms are frequently called by common names, in which the name of the alkyl group is followed by the word alcohol:
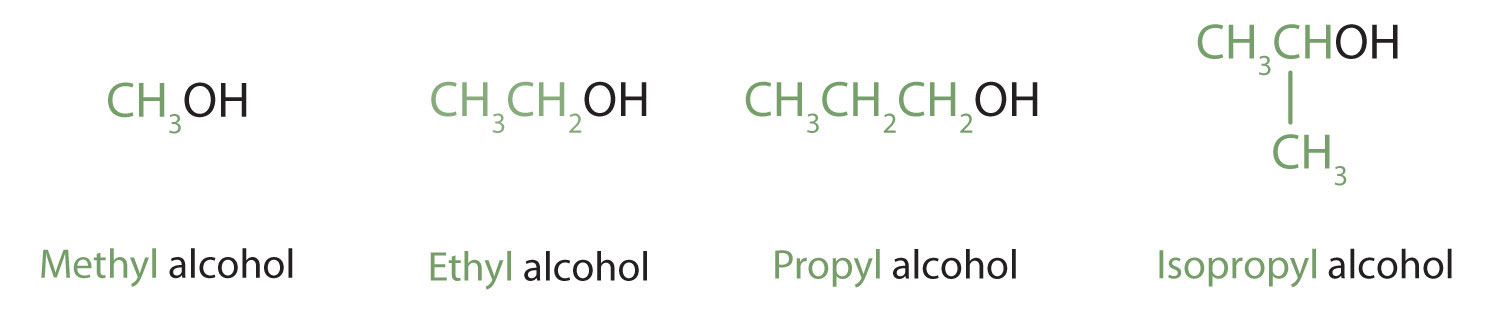
According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), alcohols are named by changing the ending of the parent alkane name to -ol.
Alcohols can be considered derivatives of water (H2O; also written as HOH).

Like the H–O–H bond in water, the R–O–H bond is bent, and alcohol molecules are polar. This relationship is particularly apparent in small molecules and reflected in the physical and chemical properties of alcohols with low molar mass. Replacing a hydrogen atom from an alkane with an OH group allows the molecules to associate through hydrogen bonding (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
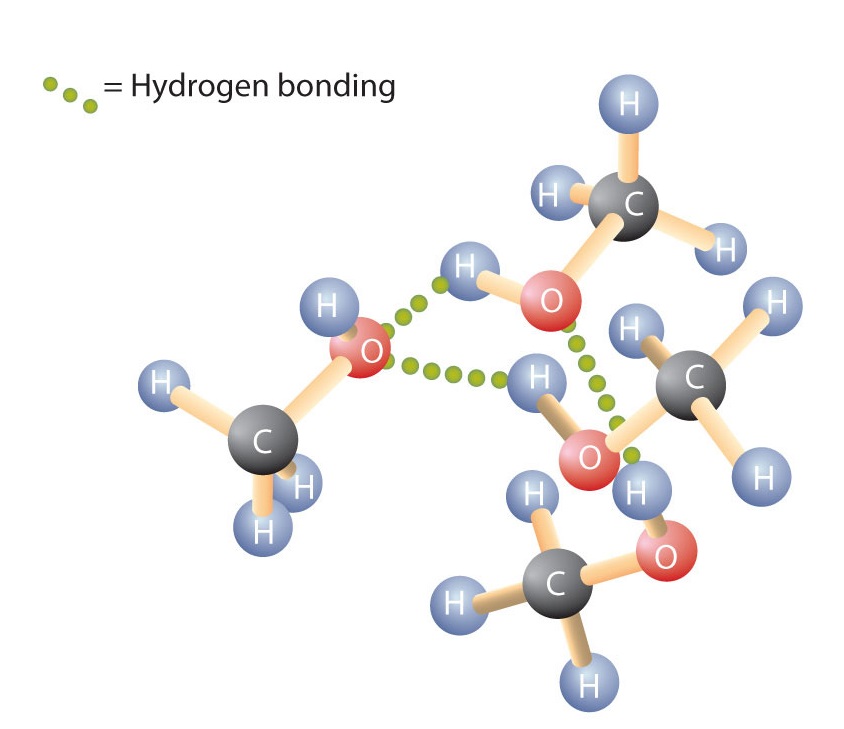
Recall that physical properties are determined to a large extent by the type of intermolecular forces. Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) lists the molar masses and the boiling points of some common compounds. The table shows that substances with similar molar masses can have quite different boiling points.
| Formula | Name | Molar Mass | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | methane | 16 | –164 |
| HOH | water | 18 | 100 |
| C2H6 | ethane | 30 | –89 |
| CH3OH | methanol | 32 | 65 |
| C3H8 | propane | 44 | –42 |
| CH3CH2OH | ethanol | 46 | 78 |
| C4H10 | butane | 58 | –1 |
| CH3CH2CH2OH | 1-propanol | 60 | 97 |
Alkanes are nonpolar and are thus associated only through relatively weak dispersion forces. Alkanes with one to four carbon atoms are gases at room temperature. In contrast, even methanol (with one carbon atom) is a liquid at room temperature. Hydrogen bonding greatly increases the boiling points of alcohols compared to hydrocarbons of comparable molar mass. The boiling point is a rough measure of the amount of energy necessary to separate a liquid molecule from its nearest neighbors. If the molecules interact through hydrogen bonding, a relatively large quantity of energy must be supplied to break those intermolecular attractions. Only then can the molecule escape from the liquid into the gaseous state.
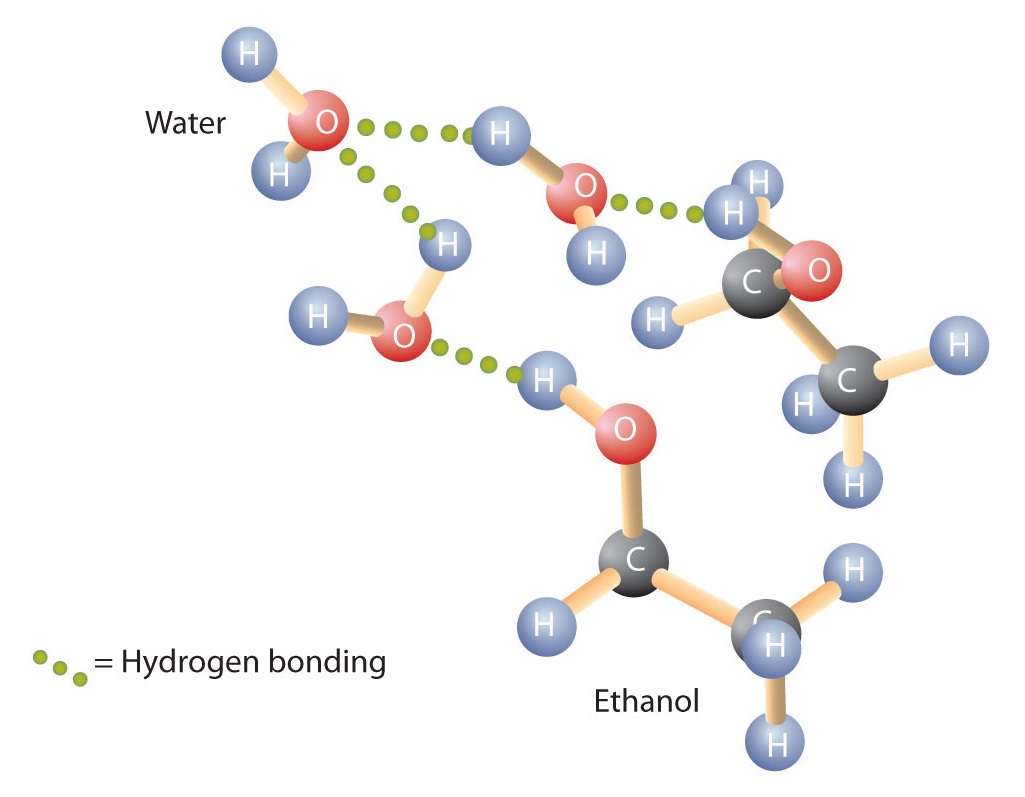
Alcohols can also engage in hydrogen bonding with water molecules (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Thus, whereas the hydrocarbons are insoluble in water, alcohols with one to three carbon atoms are completely soluble. As the length of the chain increases, however, the solubility of alcohols in water decreases; the molecules become more like hydrocarbons and less like water. The alcohol 1-decanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH) is essentially insoluble in water. We frequently find that the borderline of solubility in a family of organic compounds occurs at four or five carbon atoms.
Carboxylic Acids
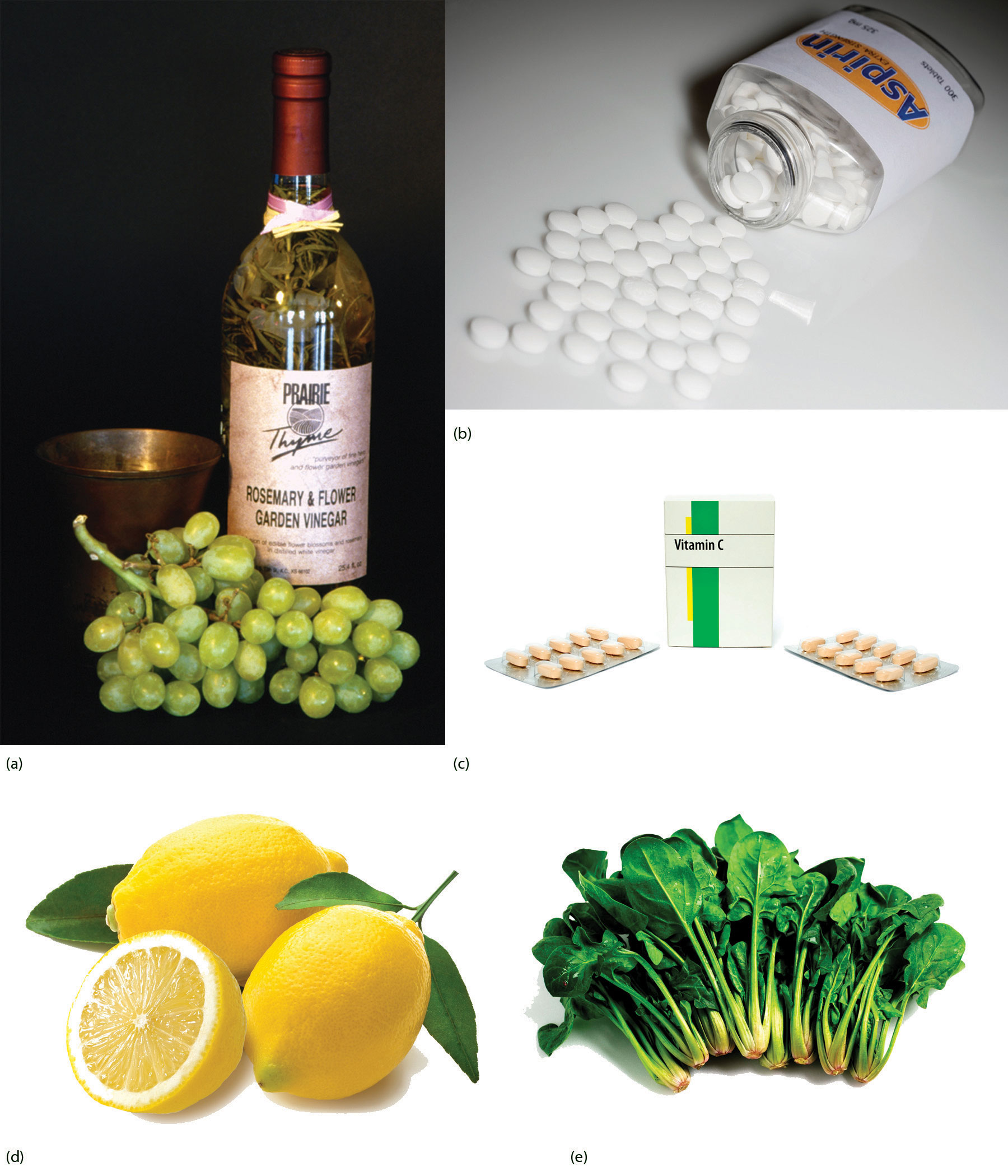
Carboxylic acids occur widely in nature, often combined with alcohols or other functional groups, as in fats, oils, and waxes. They are components of many foods, medicines, and household products (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Not surprisingly, many of them are best known by common names based on Latin and Greek words that describe their source.

The simplest carboxylic acid, formic acid (HCOOH), was first obtained by the distillation of ants (Latin formica, meaning “ant”). The bites of some ants inject formic acid, and the stings of wasps and bees contain formic acid (as well as other poisonous materials).

The next higher homolog is acetic acid, which is made by fermenting cider and honey in the presence of oxygen. This fermentation produces vinegar, a solution containing 4%–10% acetic acid, plus a number of other compounds that add to its flavor. Acetic acid is probably the most familiar weak acid used in educational and industrial chemistry laboratories.
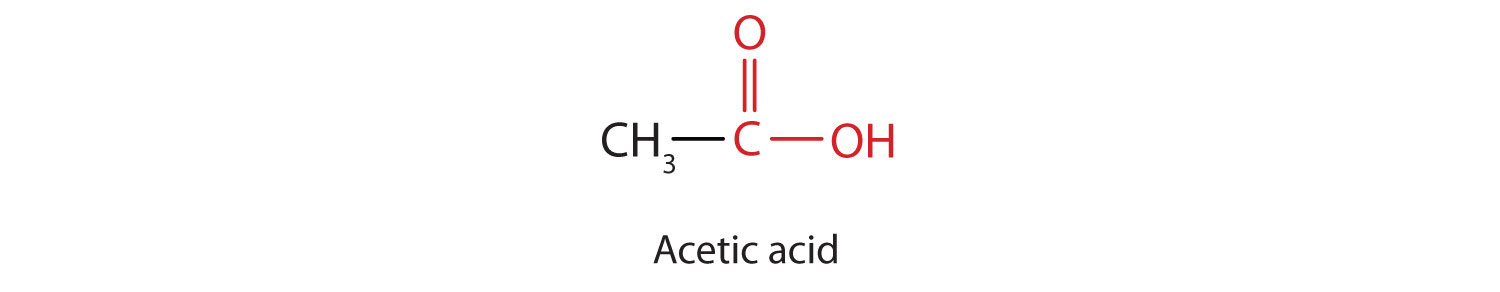
Pure acetic acid solidifies at 16.6°C, only slightly below normal room temperature. In the poorly heated laboratories of the late 19th and early 20th centuries in northern North America and Europe, acetic acid often “froze” on the storage shelf. For that reason, pure acetic acid (sometimes called concentrated acetic acid) came to be known as glacial acetic acid, a name that survives to this day.
The third homolog, propionic acid (CH3CH2COOH), is seldom encountered in everyday life. The fourth homolog, butyric acid (CH3CH2CH2COOH), is one of the most foul-smelling substances imaginable. It is found in rancid butter and is one of the ingredients of body odor. By recognizing extremely small amounts of this and other chemicals, bloodhounds are able to track fugitives. Models of the first four carboxylic acids are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\).
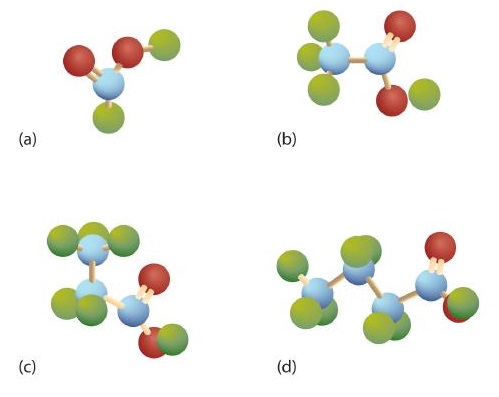
The acid with the carboxyl group attached directly to a benzene ring is called benzoic acid (C6H5COOH).

Many carboxylic acids are colorless liquids with disagreeable odors. The carboxylic acids with 5 to 10 carbon atoms all have “goaty” odors (explaining the odor of Limburger cheese). These acids are also produced by the action of skin bacteria on human sebum (skin oils), which accounts for the odor of poorly ventilated locker rooms. The acids with more than 10 carbon atoms are waxlike solids, and their odor diminishes with increasing molar mass and resultant decreasing volatility.
Carboxylic acids exhibit strong hydrogen bonding between molecules. They therefore have high boiling points compared to other substances of comparable molar mass.
The carboxyl group readily engages in hydrogen bonding with water molecules (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). The acids with one to four carbon atoms are completely miscible with water. Solubility decreases as the carbon chain length increases because dipole forces become less important and dispersion forces become more predominant. Hexanoic acid [CH3(CH2)4COOH] is barely soluble in water (about 1.0 g/100 g of water). Palmitic acid [CH3(CH2)14COOH], with its large nonpolar hydrocarbon component, is essentially insoluble in water. The carboxylic acids generally are soluble in such organic solvents as ethanol, toluene, and diethyl ether.
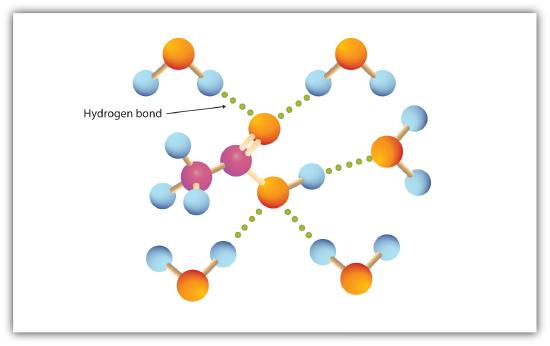
Table 15.4.1 lists some physical properties for selected carboxylic acids. The first six are homologs. Notice that the boiling points increase with increasing molar mass, but the melting points show no regular pattern.
| Condensed Structural Formula | Name of Acid | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) | Solubility (g/100 g of Water) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCOOH | formic acid | 8 | 100 | miscible |
| CH3COOH | acetic acid | 17 | 118 | miscible |
| CH3CH2COOH | propionic acid | –22 | 141 | miscible |
| CH3(CH2)2COOH | butyric acid | –5 | 163 | miscible |
| CH3(CH2)3COOH | valeric acid | –35 | 187 | 5 |
| CH3(CH2)4COOH | caproic acid | –3 | 205 | 1.1 |
| C6H5COOH | benzoic acid | 122 | 249 | 0.29 |
Esters
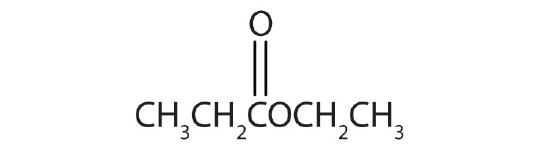
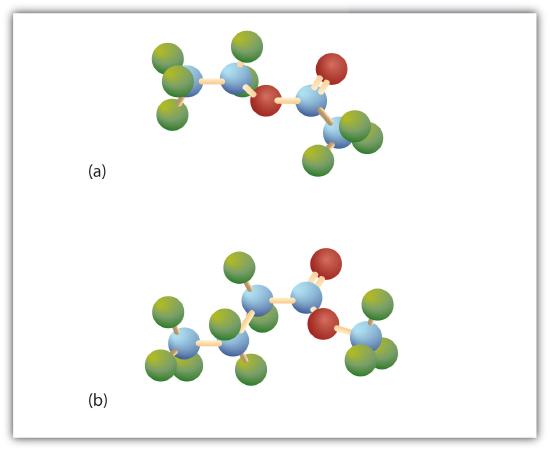
Esters have the general formula RCOOR′, where R may be a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, or an aryl group, and R′ may be an alkyl group or an aryl group but not a hydrogen atom. (If it were hydrogen atom, the compound would be a carboxylic acid.) Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows models for two common esters.
Esters occur widely in nature. Unlike carboxylic acids, esters generally have pleasant odors and are often responsible for the characteristic fragrances of fruits and flowers. Once a flower or fruit has been chemically analyzed, flavor chemists can attempt to duplicate the natural odor or taste. Both natural and synthetic esters are used in perfumes and as flavoring agents.
Fats and vegetable oils are esters of long-chain fatty acids and glycerol. Esters of phosphoric acid are of the utmost importance to life.
Names of Esters
Although esters are covalent compounds and salts are ionic, esters are named in a manner similar to that used for naming salts. The group name of the alkyl or aryl portion is given first and is followed by the name of the acid portion. In both common and International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature, the -ic ending of the parent acid is replaced by the suffix -ate (Table \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
| Condensed Structural Formula | Common Name | IUPAC Name |
|---|---|---|
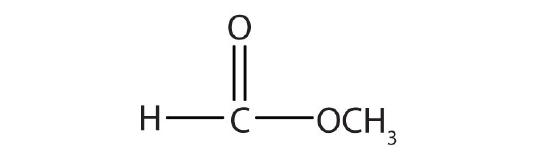
| HCOOCH3 | methyl formate | methyl methanoate |
| CH3COOCH3 | methyl acetate | methyl ethanoate |
| CH3COOCH2CH3 | ethyl acetate | ethyl ethanoate |
| CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 | ethyl propionate | ethyl propanoate |
| CH3CH2CH2COOCH(CH3)2 | isopropyl butyrate | isopropyl butanoate |
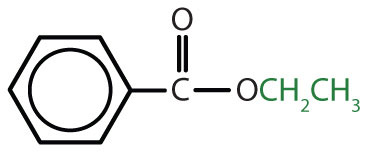 |
ethyl benzoate | ethyl benzoate |
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Give the common and IUPAC names for each compound.
Solution
- The alkyl group attached directly to the oxygen atom is a butyl group (in green).
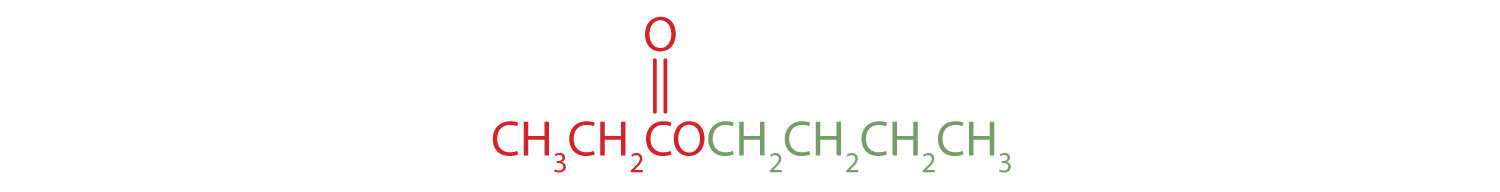
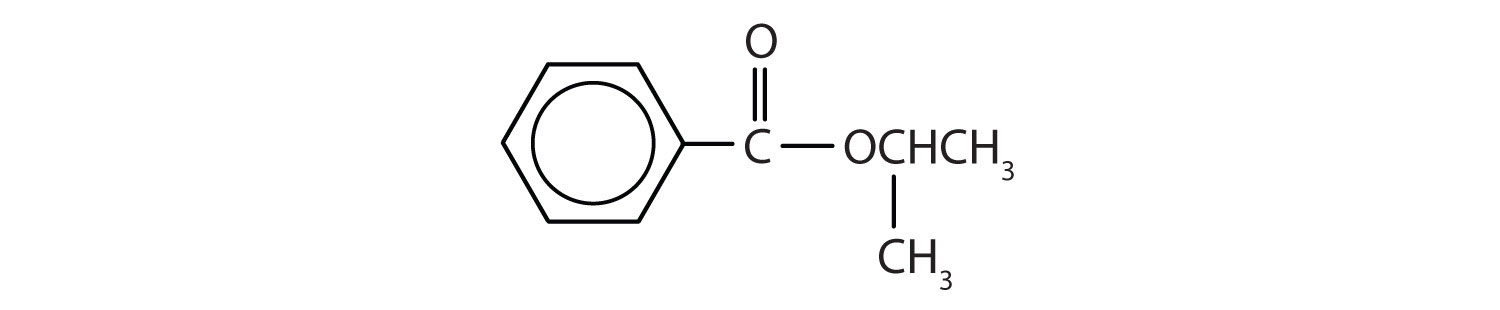
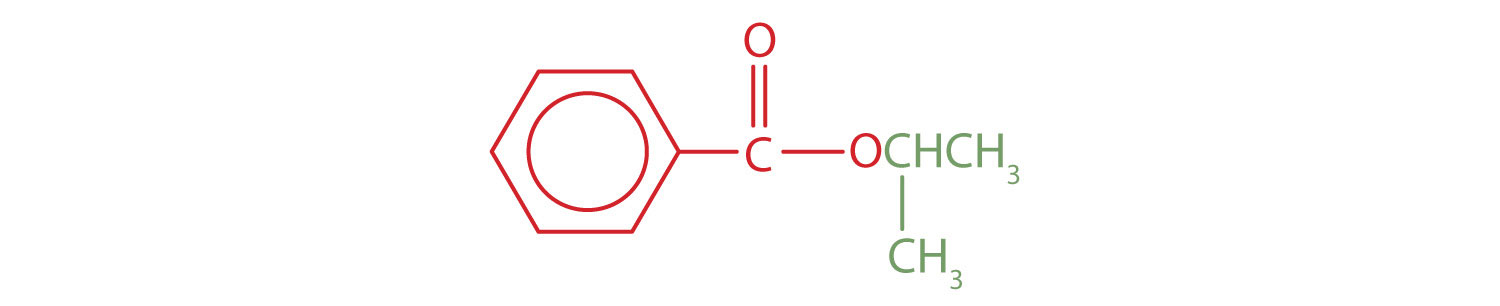
The part of the molecule derived from the carboxylic acid (in red) has three carbon atoms. It is called propionate (common) or propanoate (IUPAC). The ester is therefore butyl propionate or butyl propanoate. - An alkyl group (in green) is attached directly to the oxygen atom by its middle carbon atom; it is an isopropyl group. The part derived from the acid (that is, the benzene ring and the carbonyl group, in red) is benzoate. The ester is therefore isopropyl benzoate (both the common name and the IUPAC name).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Give the common and IUPAC names for each compound.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
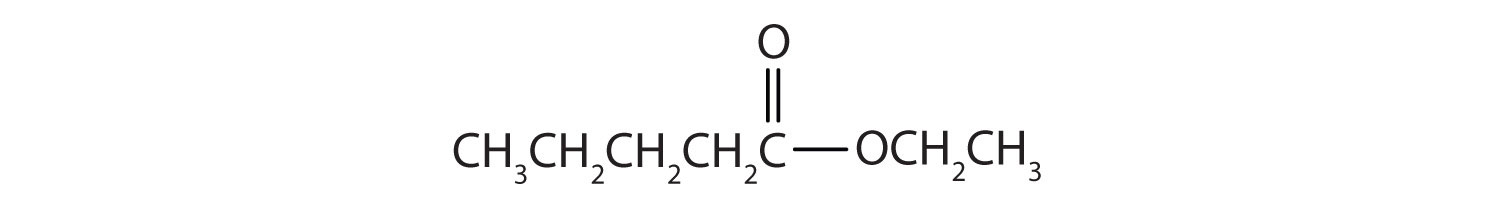
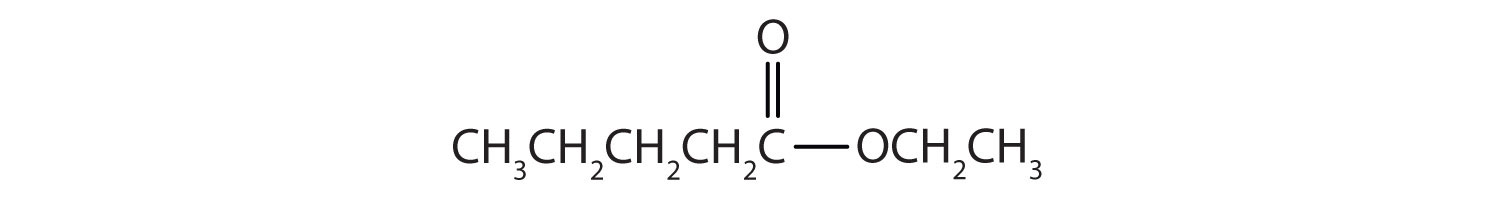
Draw the structure for ethyl pentanoate.
Solution
Start with the portion from the acid. Draw the pentanoate (five carbon atoms) group first; keeping in mind that the last carbon atom is a part of the carboxyl group.
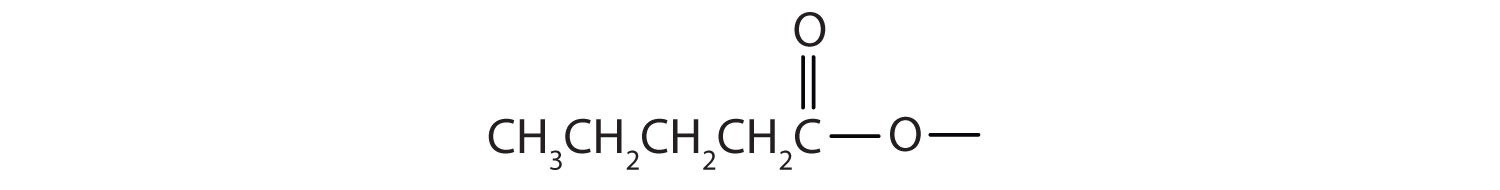
Then attach the ethyl group to the bond that ordinarily holds the hydrogen atom in the carboxyl group.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Draw the structure for phenyl pentanoate.
Preparation of Esters
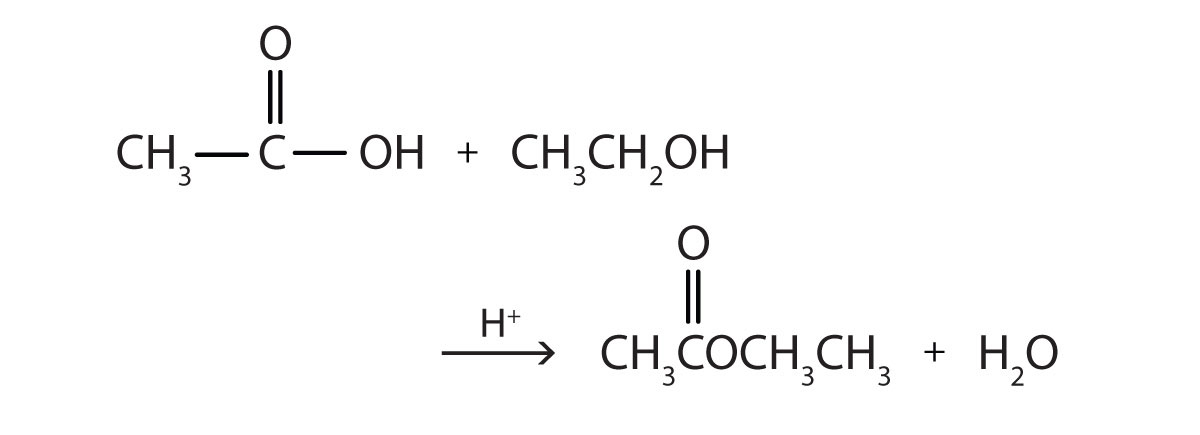
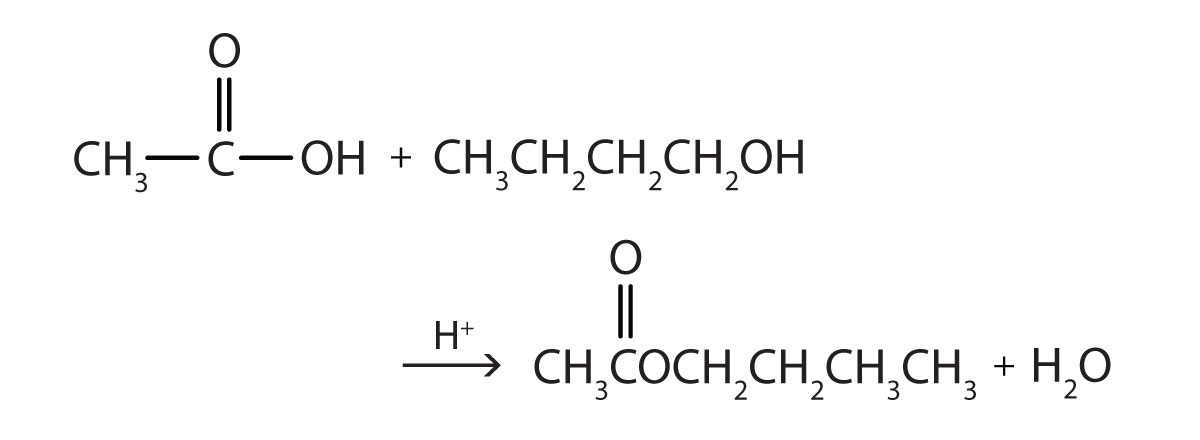
Some esters can be prepared by esterification, a reaction in which a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, heated in the presence of a mineral acid catalyst, form an ester and water:
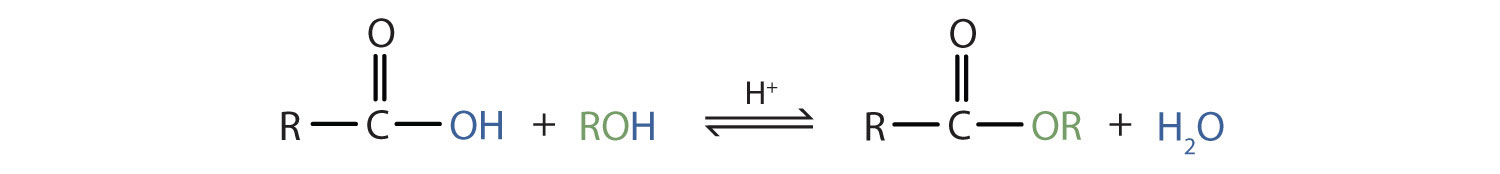
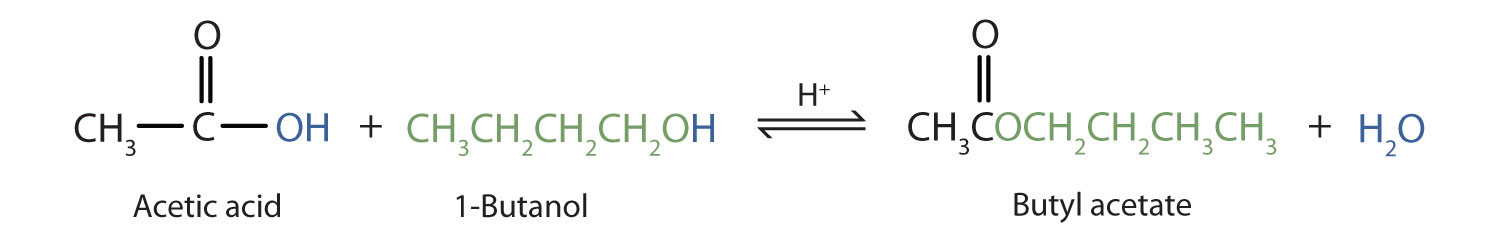
The reaction is reversible. As a specific example of an esterification reaction, butyl acetate can be made from acetic acid and 1-butanol.
A Closer Look: Condensation Polymers
A commercially important esterification reaction is condensation polymerization, in which a reaction occurs between a dicarboxylic acid and a dihydric alcohol (diol), with the elimination of water. Such a reaction yields an ester that contains a free (unreacted) carboxyl group at one end and a free alcohol group at the other end. Further condensation reactions then occur, producing polyester polymers.
The most important polyester, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is made from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol monomers:
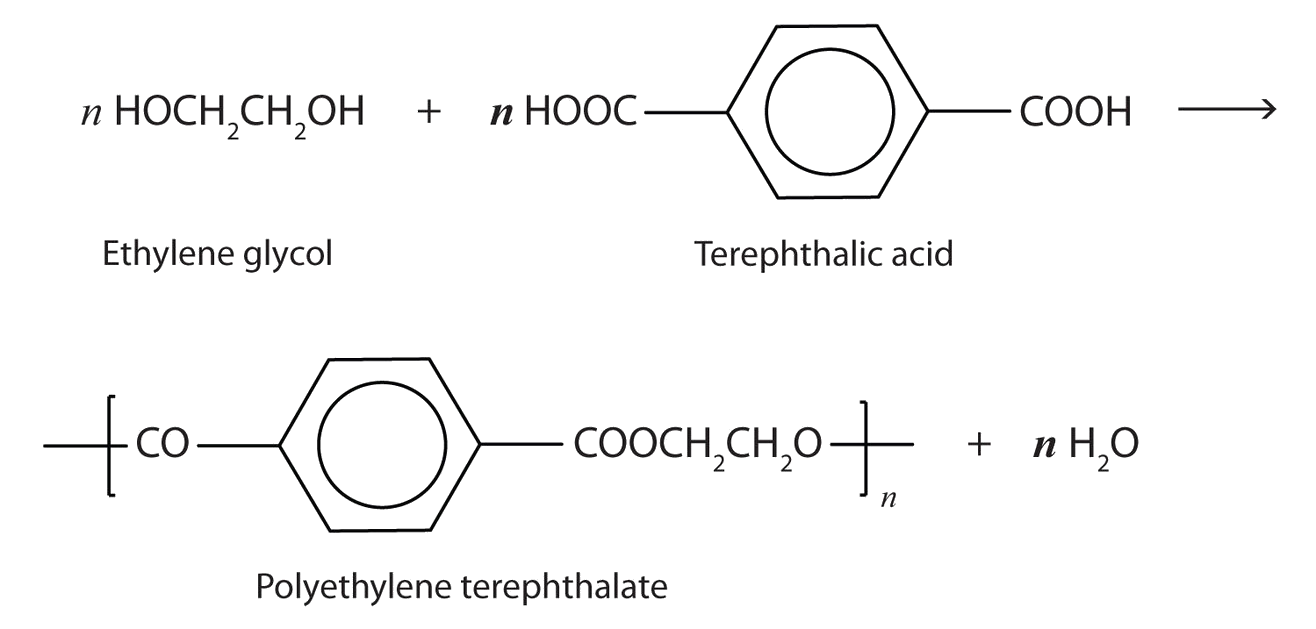
Polyester molecules make excellent fibers and are used in many fabrics. A knitted polyester tube, which is biologically inert, can be used in surgery to repair or replace diseased sections of blood vessels. PET is used to make bottles for soda pop and other beverages. It is also formed into films called Mylar. When magnetically coated, Mylar tape is used in audio- and videocassettes. Synthetic arteries can be made from PET, polytetrafluoroethylene, and other polymers.
Summary
Esters are made by the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol, a process that is called esterification.
Concept Review Exercises
- From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can the ester isopropyl nonanoate be made?
- From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can the ester cyclobutyl butyrate be made?
Exercises
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- methyl acetate
- ethyl pentanoate
- phenyl acetate
- isopropyl propionate
-
Name each compound with both the common name and the IUPAC name.
-
3. Write the equation for the reaction of acetic acid with each compound.
- ethanol
- 1-butanol in the presence of a mineral acid catalyst
Answers
-
-
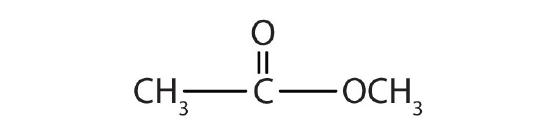
-
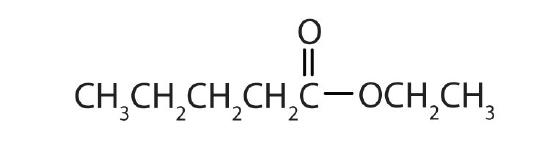
-
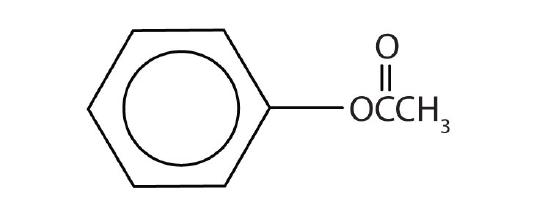
-
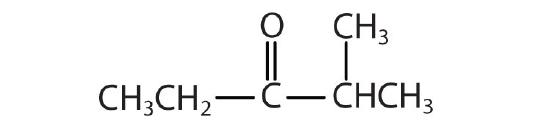
-
methyl formate; methyl methanoate
-
-
- ethyl propionate; ethyl propanoate