2.3: Nomenclature for Coordination Compounds
- Page ID
- 364646
The name of a coordination compound must communicate several things: the number and identity of ligands present, counterions, metal identity, and oxidation state. You'll notice that the names for coordination compounds tend to be quite complex.
Ligand Prefixes
Ligands are named as a prefix to the central metal ion name. In Table \(\PageIndex{1}\), the prefixes used for several common ligands are listed. In general, if the ligand is an anion ending in "-ide", the "-ide" is converted into "-o". (Recent changes to IUPAC naming rules favor dropping only the "e" and replacing it with "o". For example, "fluoride" would become "fluorido-".) When the anion ends in "-ate", then the "e" is dropped and replaced with an "-o" (e.g. oxalate becomes oxalato).
When the ligand is a neutral, the general rule is to keep the name of the compound. A few common ligands are exceptions to this that you must memorize. These are \(\ce{H2O}\) (called aqua), \(\ce{NH3}\) (called ammine), \(\ce{CO}\) (called carbonyl), and \(\ce{NO}\) (called nitrosyl).
Table \(\PageIndex{1}\). Common Ligands and their Prefixes for Coordination Compounds
| Ligand | Prefix |
|---|---|
| F− | fluoro |
| Cl− | chloro |
| Br− | bromo |
| I− | iodo |
| CN− | cyano |
| \(\ce{NO3-}\) | nitrato |
| \(\ce{OH-}\) | hydroxo |
| \(\ce{O^2-}\) | oxo |
| \(\ce{C2O4^2-}\) | oxalato |
| \(\ce{CO2^2-}\) | carbonato |
| \(\ce{H2O}\) | aqua |
| \(\ce{NH3}\) | ammine |
| \(\ce{CO}\) | carbonyl |
| \(\ce{NO}\) | nitrosyl |
| \(\ce{NH2CH2CH2NH2}\) | ethylenediamine |
We need to communicate not only the identity of the ligand(s), but the number of each present. To indicate the number of a particular ligand we use Greek prefixes (Table \(\PageIndex{2}\)).
Table \(\PageIndex{2}\). Greek prefixes associated with the number of ligands in a coordination compound.
| Number | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Prefix | di | tri | tetra | penta | hexa |
Nomenclature of Complexes with Anionic Coordination Spheres
We can now develop the full name of a coordination compound. Let us consider compounds with complex anions first. We can name them according to three steps.
1. Name the counter cation. We do not account for the number of counter cations in the name.
2. Determine the name and the number of ligands. If the ligand is anionic it gets the suffix “o”. Generally, when an anion ends with “-ide”, the “-ide” is omitted, and replaced by “-o”. The greek numerical prefix will immediately precede the name of the ligand. For example, if there are three chloride ligands, the name would contain "trichloro-".
3. Name the metal ion and add the suffix “ate” to the name. You add the oxidation number of the metal in roman numerals after the name of the metal. Note that if the element symbol of the metal is derived from a latin name then the latin name is used. For example if silver is the metal then the complex anion is an argentate, if lead is the metal the complex anion is a plumbate. Also here abbreviations are often used to make pronunciation easier. If the name ends with “um” that ending is replaced by “ate”.
Name this coordination compound.
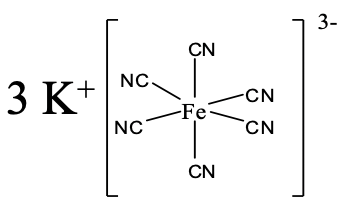
Solution
There are three K+ cations, so the name starts with potassium. We realize next, that there are six cyanide anions as ligands, so the name continues “hexacyano”. The name of the metal is iron, but we use the latin name ferrum, and replace the ending “um” with the ending “ate”. The oxidation number of the iron is +3. We can see that from the fact that the complex ion has a 3- charge, and the six cyano ligands have a 1- charge each.
So overall it would be either a potassium hexacyanoferrate (III).
How would you name this complex?
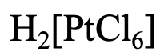
- Answer
-
First, we need to name the cation. What is it? It is just “hydrogen”. Next we need to determine the name and number of ligands. We have six chloro ligands, so the name continues with “hexachloro”. The name of metal is platinum. We replace the ending “um” by “ate”. The roman numeral would be (IV) because the oxidation state of the Pt is +4. We can see this from the fact that the complex anion has a 2- charge, and the six chloro ligands have a 1- charge each. We must add +4 to -6 to get to -2.
Therefore, the name would be hydrogen hexachloroplatinate (IV).
How would you name this complex?
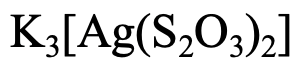
- Answer
-
This example has three K+ cations, so the name starts with potassium. What is the name of the ligand? The name of the anion is thiosulfate. In this case we replace the ending “e” by the ending “o”. We have two ligands, so it is a “dithiosulfato”. The metal is silver, but we use the latin name “argentum”, and replace the ending “um” by the ending “ate”. So it is an “argentate” . Fusing the parts together gives “potassium dithiosulfato argentate”. The oxidation number of Ag is +1, the charge at the anion is -3.
Therefore the name would be potassium dithiosulfatoargenate (I).
Nomenclature of Complexes with Cationic Coordination Spheres
Now let us name complexes with complex cations. We name the complex cation first, and then the anion. Then, we determine the name and the number of the ligands and prefixes accordingly. If there is an anionic ligand we give it the suffix “o” again. Then, we name the metal. In this case, we always use English names. As before, we place the oxidation number in roman numerals.
Name the coordination compound here.
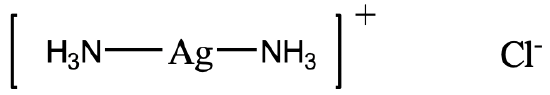
Solution
There are two NH3 ligands which are neutral. We have to consider that NH3 as a ligand is called an “ammine” ligand. Note that it is spelled with two “m” in the middle. So the name starts “diammine”. The name of the metal is silver, and the oxidation state of silver is +1. This is because the complex has a 1+ charge and the ammine ligands are neutral. The anion is a chloride anion.
Therefore then name would be diamminesilver (I) chloride.
Name this coordination compound.
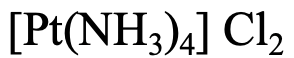
- Answer
-
The complex has four NH3 ligands, so the name starts with tetraammine. Platinum is the metal, so the name continues “platinum”. The oxidation state of Pt is +2 because the complex cation has a 2+ charge, and the ligands are charge-neutral. The name of the anion is “choride”.
So overall it is a tetraammineplatinum (II) chloride.
Name this coordination compound.
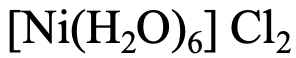
- Answer
-
The complex has six water ligands, therefore the name starts with “hexaaqua” followed by the name of the metal with is “nickel”. The oxidation state of Ni is 2+ because the charge at the complex cation is +2, and the ligands are charge-neutral. The name of the anion is “chloride”.
Therefore, the name is hexaaaquanickel (II) chloride.
Nomenclature of Complexes with Cationic and Anionic Coordination Spheres
There is also the possibility that a coordination compound is made of a complex cation and a complex anion. In this case, the rules discussed previously hold, the only new thing to learn is that we name the complex cation first and the complex anion second.
Name this coordination compound.
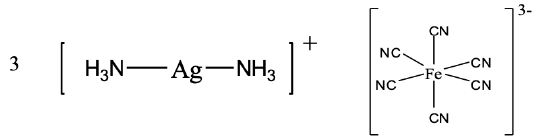
- Answer
-
In the compound, we have a diamminesilver (I) cation and a hexacyanoferrate (III) anion.
The name of the compound is diamminesilver (I) hexacyanoferrate (III).
Nomenclature of Complexes with Multiple Ligand Identities
What if there are different ligands in a coordination compound? In this case, we name the ligands in alphabetical order, and give each ligand a prefix according to its number.
What is the name for this complex?
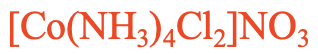
Solution
This is a compound with a complex cation containing ammine and chloro ligands. Because “a” comes before “c” in the alphabet we have to name the ammine ligand first. There are four ammine ligands and two chloro ligands. Therefore, we use the prefixes “tetra” in front of “ammine” and “di” in front of “chloro”. So the name starts “tetraamminedichloro”. Then, we name the metal which is cobalt. The oxidation number of cobalt is +3 because there are four charge-neutral ammine ligands, two anionic chloro ligands, and the charge at the complex cation is +1. +3 -2 = +1.
So the compound is called tetramminedichlorocobalt(III) nitrate.
What is the name of this coordination compound?

- Answer
-
In the compound [Pt(NH3)BrCl(H2O)]SO4 there is a complex cation with four different ligands: an “ammine” ligand, a “bromo”-ligand, a "chloro"-ligand, and an "aqua" ligand. What is the order of them? According to the alphabet, “ammine” comes first, “aqua” is second, “bromo” is third, and “chloro” is fourth. They do not get a prefix because there is just one of them for each. The metal is platinum, and its oxidation state is +4 because the complex cation has a 2+ charge, and there are two neutral ligands, namely the aqua and the ammine ligands, and two anionic ones, namely the bromo and the chloro ligands: +4 - 2 = +2.
Therefore the compound's name is ammineaquabromochloroplatinum(IV) sulfate.
Nomenclature of Complexes with Complicated Ligands in a Coordination Sphere
So far we only considered relatively simple ligands that were either monoatomic, or contained a few atoms only. However, many ligands, in particular chelating ligands, contain more atoms, and have more complex names. These names may already contain prefixes that we use to number ligands. For example the ethylenediamine ligand is a chelating ligand with a longer name that already contains the prefix “di”. In such cases, to avoid ambiguity, we put the ligand name in parentheses, and place a somewhat different prefix in front of it to account for the number of the ligands.
Table \(\PageIndex{3}\). Greek prefixes and prefixes for complicated ligands used for number of ligands in a coordination compound.
| Number | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Simple Prefix | di | tri | tetra | penta | hexa |
| Alternative Prefix | bis | tris | tetrakis | pentakis | hexakis |
Instead of “di” we use “bis”, instead of “tri” we use “tris”, instead of “tetra” we use “tetrakis”, and so on (Table \(\PageIndex{3}\) ). When we use these alternative prefixes, the name of the ligand should always be included in parentheses.
What is the name of the complex cation shown here?
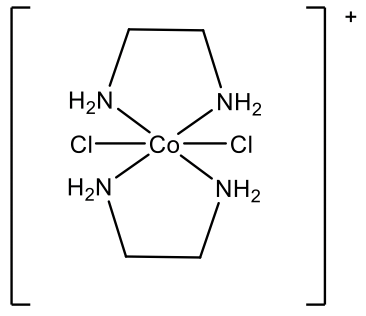
Solution
We first need to realize that there are two different ligands: chloro ligands and ethylenediamine ligands. We need to name the chloro ligands first, because they come first in the alphabet. Because there are two chloro ligands we use the prefix “di”. The ethylenediamine ligand is placed in parentheses, and the prefix “bis” is used instead of “di”. The metal is cobalt in the oxidation state +3 because the complex cation has a 1+ charge, and there are two chloro ligands with a 1- charge each, and two charge-neutral ethylenediamine ligands: +3 -2 = +1.
The name of the complex ion is dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) ion.
Dr. Kai Landskron (Lehigh University). If you like this textbook, please consider to make a donation to support the author's research at Lehigh University: Click Here to Donate.


