2.7: Chapter 2 Problems
- Page ID
- 20461
\( \newcommand{\tx}[1]{\text{#1}} % text in math mode\)
\( \newcommand{\subs}[1]{_{\text{#1}}} % subscript text\)
\( \newcommand{\sups}[1]{^{\text{#1}}} % superscript text\)
\( \newcommand{\st}{^\circ} % standard state symbol\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{^{\text{id}}} % ideal\)
\( \newcommand{\rf}{^{\text{ref}}} % reference state\)
\( \newcommand{\units}[1]{\mbox{$\thinspace$#1}}\)
\( \newcommand{\K}{\units{K}} % kelvins\)
\( \newcommand{\degC}{^\circ\text{C}} % degrees Celsius\)
\( \newcommand{\br}{\units{bar}} % bar (\bar is already defined)\)
\( \newcommand{\Pa}{\units{Pa}}\)
\( \newcommand{\mol}{\units{mol}} % mole\)
\( \newcommand{\V}{\units{V}} % volts\)
\( \newcommand{\timesten}[1]{\mbox{$\,\times\,10^{#1}$}}\)
\( \newcommand{\per}{^{-1}} % minus one power\)
\( \newcommand{\m}{_{\text{m}}} % subscript m for molar quantity\)
\( \newcommand{\CVm}{C_{V,\text{m}}} % molar heat capacity at const.V\)
\( \newcommand{\Cpm}{C_{p,\text{m}}} % molar heat capacity at const.p\)
\( \newcommand{\kT}{\kappa_T} % isothermal compressibility\)
\( \newcommand{\A}{_{\text{A}}} % subscript A for solvent or state A\)
\( \newcommand{\B}{_{\text{B}}} % subscript B for solute or state B\)
\( \newcommand{\bd}{_{\text{b}}} % subscript b for boundary or boiling point\)
\( \newcommand{\C}{_{\text{C}}} % subscript C\)
\( \newcommand{\f}{_{\text{f}}} % subscript f for freezing point\)
\( \newcommand{\mA}{_{\text{m},\text{A}}} % subscript m,A (m=molar)\)
\( \newcommand{\mB}{_{\text{m},\text{B}}} % subscript m,B (m=molar)\)
\( \newcommand{\mi}{_{\text{m},i}} % subscript m,i (m=molar)\)
\( \newcommand{\fA}{_{\text{f},\text{A}}} % subscript f,A (for fr. pt.)\)
\( \newcommand{\fB}{_{\text{f},\text{B}}} % subscript f,B (for fr. pt.)\)
\( \newcommand{\xbB}{_{x,\text{B}}} % x basis, B\)
\( \newcommand{\xbC}{_{x,\text{C}}} % x basis, C\)
\( \newcommand{\cbB}{_{c,\text{B}}} % c basis, B\)
\( \newcommand{\mbB}{_{m,\text{B}}} % m basis, B\)
\( \newcommand{\kHi}{k_{\text{H},i}} % Henry's law constant, x basis, i\)
\( \newcommand{\kHB}{k_{\text{H,B}}} % Henry's law constant, x basis, B\)
\( \newcommand{\arrow}{\,\rightarrow\,} % right arrow with extra spaces\)
\( \newcommand{\arrows}{\,\rightleftharpoons\,} % double arrows with extra spaces\)
\( \newcommand{\ra}{\rightarrow} % right arrow (can be used in text mode)\)
\( \newcommand{\eq}{\subs{eq}} % equilibrium state\)
\( \newcommand{\onehalf}{\textstyle\frac{1}{2}\D} % small 1/2 for display equation\)
\( \newcommand{\sys}{\subs{sys}} % system property\)
\( \newcommand{\sur}{\sups{sur}} % surroundings\)
\( \renewcommand{\in}{\sups{int}} % internal\)
\( \newcommand{\lab}{\subs{lab}} % lab frame\)
\( \newcommand{\cm}{\subs{cm}} % center of mass\)
\( \newcommand{\rev}{\subs{rev}} % reversible\)
\( \newcommand{\irr}{\subs{irr}} % irreversible\)
\( \newcommand{\fric}{\subs{fric}} % friction\)
\( \newcommand{\diss}{\subs{diss}} % dissipation\)
\( \newcommand{\el}{\subs{el}} % electrical\)
\( \newcommand{\cell}{\subs{cell}} % cell\)
\( \newcommand{\As}{A\subs{s}} % surface area\)
\( \newcommand{\E}{^\mathsf{E}} % excess quantity (superscript)\)
\( \newcommand{\allni}{\{n_i \}} % set of all n_i\)
\( \newcommand{\sol}{\hspace{-.1em}\tx{(sol)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\solmB}{\tx{(sol,$\,$$m\B$)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\dil}{\tx{(dil)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\sln}{\tx{(sln)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\mix}{\tx{(mix)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\rxn}{\tx{(rxn)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\expt}{\tx{(expt)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\solid}{\tx{(s)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\liquid}{\tx{(l)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\gas}{\tx{(g)}}\)
\( \newcommand{\pha}{\alpha} % phase alpha\)
\( \newcommand{\phb}{\beta} % phase beta\)
\( \newcommand{\phg}{\gamma} % phase gamma\)
\( \newcommand{\aph}{^{\alpha}} % alpha phase superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\bph}{^{\beta}} % beta phase superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\gph}{^{\gamma}} % gamma phase superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\aphp}{^{\alpha'}} % alpha prime phase superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\bphp}{^{\beta'}} % beta prime phase superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\gphp}{^{\gamma'}} % gamma prime phase superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\apht}{\small\aph} % alpha phase tiny superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\bpht}{\small\bph} % beta phase tiny superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\gpht}{\small\gph} % gamma phase tiny superscript\)
\( \newcommand{\upOmega}{\Omega}\)
\( \newcommand{\dif}{\mathop{}\!\mathrm{d}} % roman d in math mode, preceded by space\)
\( \newcommand{\Dif}{\mathop{}\!\mathrm{D}} % roman D in math mode, preceded by space\)
\( \newcommand{\df}{\dif\hspace{0.05em} f} % df\)
\(\newcommand{\dBar}{\mathop{}\!\mathrm{d}\hspace-.3em\raise1.05ex{\Rule{.8ex}{.125ex}{0ex}}} % inexact differential \)
\( \newcommand{\dq}{\dBar q} % heat differential\)
\( \newcommand{\dw}{\dBar w} % work differential\)
\( \newcommand{\dQ}{\dBar Q} % infinitesimal charge\)
\( \newcommand{\dx}{\dif\hspace{0.05em} x} % dx\)
\( \newcommand{\dt}{\dif\hspace{0.05em} t} % dt\)
\( \newcommand{\difp}{\dif\hspace{0.05em} p} % dp\)
\( \newcommand{\Del}{\Delta}\)
\( \newcommand{\Delsub}[1]{\Delta_{\text{#1}}}\)
\( \newcommand{\pd}[3]{(\partial #1 / \partial #2 )_{#3}} % \pd{}{}{} - partial derivative, one line\)
\( \newcommand{\Pd}[3]{\left( \dfrac {\partial #1} {\partial #2}\right)_{#3}} % Pd{}{}{} - Partial derivative, built-up\)
\( \newcommand{\bpd}[3]{[ \partial #1 / \partial #2 ]_{#3}}\)
\( \newcommand{\bPd}[3]{\left[ \dfrac {\partial #1} {\partial #2}\right]_{#3}}\)
\( \newcommand{\dotprod}{\small\bullet}\)
\( \newcommand{\fug}{f} % fugacity\)
\( \newcommand{\g}{\gamma} % solute activity coefficient, or gamma in general\)
\( \newcommand{\G}{\varGamma} % activity coefficient of a reference state (pressure factor)\)
\( \newcommand{\ecp}{\widetilde{\mu}} % electrochemical or total potential\)
\( \newcommand{\Eeq}{E\subs{cell, eq}} % equilibrium cell potential\)
\( \newcommand{\Ej}{E\subs{j}} % liquid junction potential\)
\( \newcommand{\mue}{\mu\subs{e}} % electron chemical potential\)
\( \newcommand{\defn}{\,\stackrel{\mathrm{def}}{=}\,} % "equal by definition" symbol\)
\( \newcommand{\D}{\displaystyle} % for a line in built-up\)
\( \newcommand{\s}{\smash[b]} % use in equations with conditions of validity\)
\( \newcommand{\cond}[1]{\\[-2.5pt]{}\tag*{#1}}\)
\( \newcommand{\nextcond}[1]{\\[-5pt]{}\tag*{#1}}\)
\( \newcommand{\R}{8.3145\units{J$\,$K$\per\,$mol$\per$}} % gas constant value\)
\( \newcommand{\Rsix}{8.31447\units{J$\,$K$\per\,$mol$\per$}} % gas constant value - 6 sig figs\)
\( \newcommand{\jn}{\hspace3pt\lower.3ex{\Rule{.6pt}{2ex}{0ex}}\hspace3pt} \)
\( \newcommand{\ljn}{\hspace3pt\lower.3ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace-.6pt\raise.45ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace-.6pt\raise1.2ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}} \hspace3pt} \)
\( \newcommand{\lljn}{\hspace3pt\lower.3ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace-.6pt\raise.45ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace-.6pt\raise1.2ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace1.4pt\lower.3ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace-.6pt\raise.45ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace-.6pt\raise1.2ex{\Rule{.6pt}{.5ex}{0ex}}\hspace3pt} \)
2.1
Let \(X\) represent the quantity \(V^2\) with dimensions \((\tx{length})^6\). Give a reason that \(X\) is or is not an extensive property. Give a reason that \(X\) is or is not an intensive property.
2.2
Calculate the relative uncertainty (the uncertainty divided by the value) for each of the measurement methods listed in Table 2.2, using the typical values shown. For each of the five physical quantities listed, which measurement method has the smallest relative uncertainty?
Table 2.5 Helium at a fixed temperature
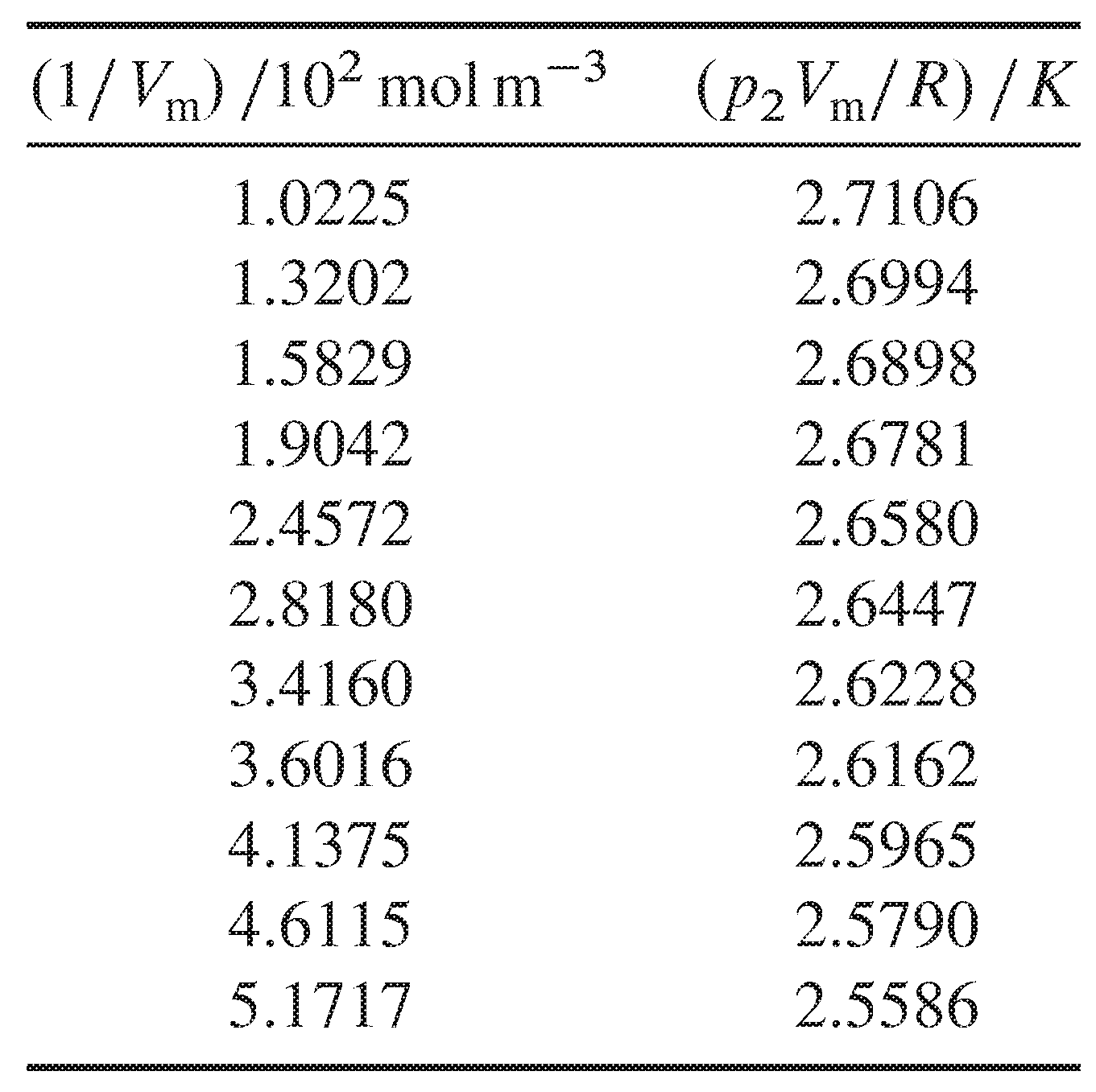
2.3
Table 2.5 lists data obtained from a constant-volume gas thermometer containing samples of varying amounts of helium maintained at a certain fixed temperature \(T_2\) in the gas bulb (K. H. Berry, Metrologia, 15, 89–115, 1979). The molar volume \(V\m\) of each sample was evaluated from its pressure in the bulb at a reference temperature of \(T_1=7.1992\K\), corrected for gas nonideality with the known value of the second virial coefficient at that temperature.
Use these data and Eq. 2.2.2 to evaluate \(T_2\) and the second virial coefficient of helium at temperature \(T_2\). (You can assume the third and higher virial coefficients are negligible.)
2.4
Discuss the proposition that, to a certain degree of approximation, a living organism is a steady-state system.
2.5
The value of \(\Del U\) for the formation of one mole of crystalline potassium iodide from its elements at \(25\units{\(\degC\)}\) and \(1\br\) is \(-327.9\units{kJ}\). Calculate \(\Del m\) for this process. Comment on the feasibility of measuring this mass change.


