23.4: Physical Properties of Amines
- Page ID
- 22339
The physical properties of amines depend in an important way on the extent of substitution at nitrogen. Thus primary amines, \(\ce{RNH_2}\), and secondary amines, \(\ce{R_2NH}\), are less volatile than hydrocarbons of similar size, weight, and shape, as the following examples show:
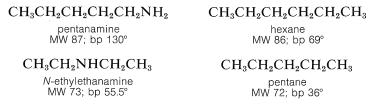
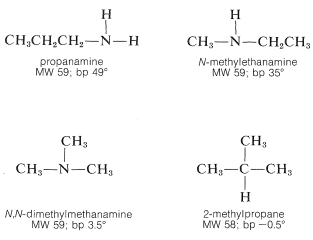
This is because the amines are associated through hydrogen bonding of the type \(\ce{N-H} \cdots \colon \ce{N}\). Generally, \(\ce{N-H} \cdots \colon \ce{N}\) bonds are somewhat weaker than those of the corresponding types, \(\ce{O-H} \cdots \colon \ce{O}\) and \(\ce{F-H} \cdots \colon \ce{F}\), because the electronegativity of nitrogen is less than that of oxygen or fluorine thereby making nitrogen a poorer hydrogen donor. Even so, association through hydrogen bonding is significant in amines of the type \(\ce{RNH_2}\) or \(\ce{R_2NH}\) as the boiling-point comparison shows. With tertiary amines, where \(\ce{N-H} \cdots \colon \ce{N}\) bonding is not possible, the boiling points are much lower and are similar to those of hydrocarbons of similar branching and molecular weights:
The water solubilities of the lower-molecular-weight amines are appreciable, as can be seen from the solubility data in Table 23-1. In fact, amines are more water-soluble than alcohols of similar molecular weights. This is the result of hydrogen bonding, with amine molecules as the hydrogen acceptors and water molecules as the hydrogen donors:
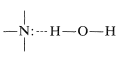
Hydrogen bonds of this type are stronger than \(\ce{O} \colon \cdots \ce{H-O-H}\) bonds.
Amines, especially those with significant volatility, have unpleasant odors. Some of them smell like ammonia, others smell fishy, while others are indescribably revolting. The alkanediamines of structure \(\ce{H_2N(CH_3)}_n \ce{NH_2}\) are notably wretched and two are aptly called putrescine \(\left( n = 4 \right)\) and cadaverine \(\left( n = 5 \right)\). As you may guess from the names, these compounds are among the amines produced by bacterial decay of organic animal matter (putrefaction of protein) and are poisonous components (ptomaines) thereof.
Contributors and Attributions
John D. Robert and Marjorie C. Caserio (1977) Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, second edition. W. A. Benjamin, Inc. , Menlo Park, CA. ISBN 0-8053-8329-8. This content is copyrighted under the following conditions, "You are granted permission for individual, educational, research and non-commercial reproduction, distribution, display and performance of this work in any format."


