20.9: Vitamin C
- Page ID
- 22308
The "antiscorbutic" factor of fresh fruits, which prevents the development of the typical symptoms of scurvy in humans, is a carbohydrate derivative known as vitamin C or ascorbic acid. This substance is not a carboxylic acid, but a lactone, and owes its acidic properties (and ease of oxidation) to the presence of an enediol grouping. It belongs to the \(L\) series by the glyceraldehyde convention:
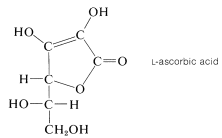
Most animals are able to synthesize vitamin C in their livers but, in the course of evolution, man has lost this capacity.
Contributors and Attributions
John D. Robert and Marjorie C. Caserio (1977) Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry, second edition. W. A. Benjamin, Inc. , Menlo Park, CA. ISBN 0-8053-8329-8. This content is copyrighted under the following conditions, "You are granted permission for individual, educational, research and non-commercial reproduction, distribution, display and performance of this work in any format."


