4.3: Hydride and Alkyl Migratory Insertions
- Page ID
- 189941
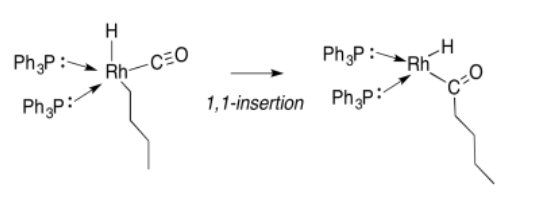
Migratory insertion is a term to describe the transfer of a ligand from a metal to a carbon monoxide that is also bound to the metal. It is a special case of a 1,1-insertion. In a 1,1-insertion, a group is transferred from a metal to an atom attached to the same metal. A general 1,1-insertion is shown in figure \(\PageIndex{1}\).
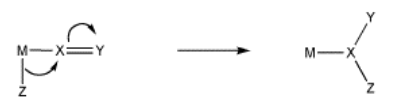
At the end of the 1,1-insertion, the ligand Z has attached to the 1st atom in the next ligand attached to the metal.
Carbonyl groups in organic compounds are electrophilic. The polar carbon-oxygen double bond places positive charge on the carbon, so the carbon atom attracts nucleophiles. One of the nucleophiles that can react with a carbonyl is a complex hydride, such as a borohydride ion or an aluminum hydride ion. Sometimes, these complex hydrides are anionic, making them more nucleophilic. An example is sodium borohydride, NaBH4. Sometimes, the hydride compound is neutral, as in BH3. However, the hydride is still nucleophilic even if the compound is not negatively charged, because of the electronegativity difference between the hydrogen and the boron (or the aluminum). A hydride ion is donated as a nucleophile to the electrophilic carbonyl. Transition metal hydrides, like boron and aluminum hydrides, are frequently nucleophilic. They can donate hydrides to electrophiles.
- A hydrogen attached to a metal atom frequently acts like a hydride.
- A nucleophilic hydride can donate to a carbonyl carbon.

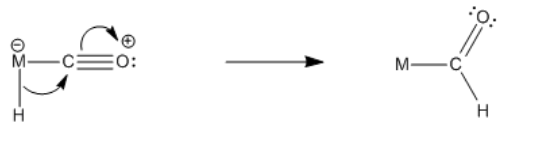
"Inorganic carbonyls", or metal-bound CO compounds, behave in many ways like organic carbonyl compounds. In one sense, the bound CO can be thought of as having a positive formal charge on the oxygen, so it is easy to imagine it as an electrophile. It looks like an "activated" organic carbonyl (for example, a ketone that has been protonated, and has a positively charged oxygen). If a metal has a hydride attached to it (a nucleophile) as well as a CO (an electrophile), then a reaction can occur between them. The hydride can add to the carbonyl. This is one of the most useful things about transition metal chemistry: by binding different, reactive ligands, metals can organize reactants so that they react together.
- This reaction can occur intramolecularly; i.e. from a hydride to a carbonyl on the same metal.
- This event is called a migratory insertion.
Note that the metal does not have to be anionic for the hydride to act as a nucleophile. The electronegativities of transition metals vary from about 1.0 to 1.75, but the electronegativity of hydrogen is about 2.2. Hydrogen is more electronegative than the transition metals, and so a hydrogen attached to a transition metal is usually nucleophilic.
This reaction, migratory insertion of a hydride to a carbonyl, forms a metal "formyl" compound. The "formyl" is the CH=O group attached to the metal. Migratpry insertions can also take place with metal alkyls. Metal alkyls are also nucleophilic, just like metal hydrides. The alkyl carbon is usually more electronegative than the attached transition metal, so it has a partial negative charge.
- Nucleophilic alkyl groups can also undergo migratory insertion reactions.
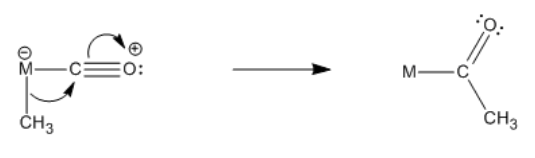
In fact, migratory insertion to a carbonyl is actually much more common with alkyl ligands than it is with hydrides. Conceptually, the reactions are very similar. The reason alkyl migrations are much more common has to do with relative bonds strengths in the reactants compared to the products of the reaction.
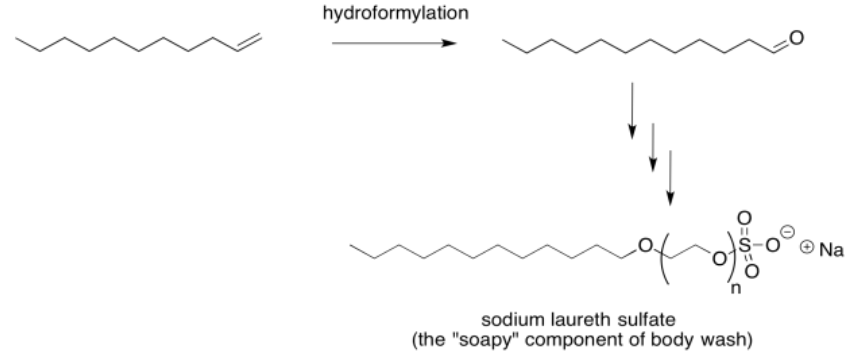
Migratory insertion is industrially important. It is used in the manufacture of things many of us use every day. For example, the main component of body wash. sodium laureth sulfate and related compounds, is synthesized via a key hydroformylation process. The catalyst used for hydroformylation varies from one application to another and from one company to another. In the case of soap synthesis, a rhodium catalyst is usually employed.
Hydroformylation results in an alkene chain being lengthened by one carbon, with an aldehyde at the end of the chain. Overall, it results in the addition of a aldehyde fragment (CHO) to one end of the alkene double bond and a hydrogen atom the the other. A few additional steps are needed to extend the resulting aldehyde and cap the chain with a polar sulfonate group. Of course, the compound works by forming micelles when suspended in water. Those long tails gather together, with the polar heads interacting with the water. Stuff that won't wash off with plain water because it isn't polar enough to dissolve in water may instead dissolve among the soapy tails of the sodium laureth sulfate molecules.
Explain why a coordinated carbon monoxide acts as an electrophile.
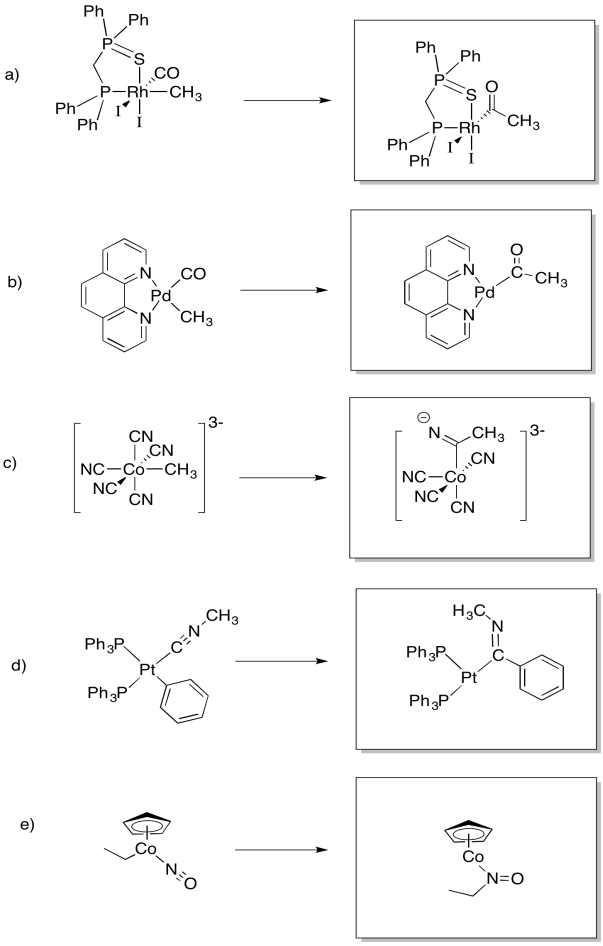
Draw, with arrows, the reaction to give the 1,1- insertion products in the following cases.
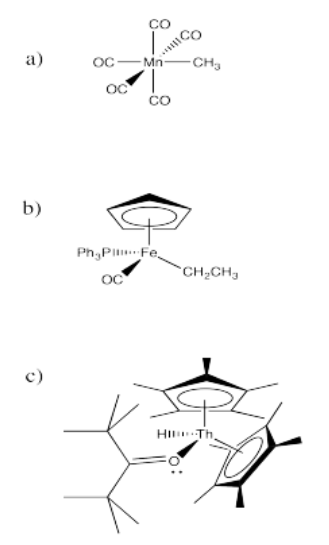
- Answer
-
Binding or coordination to a metal may also occur with organic carbonyl compounds such as ketones, aldehydes, esters and so on.
- Explain why a coordinated carbonyl compound, such as propanal, can be especially electrophilic.
- Compare and contrast the electrophilicity of a coordinated organic carbonyl with the electrophilicity of coordinated carbon monoxide. What atom is the electrophile in each case? What will happen if a nucleophile donates electrons in each case?
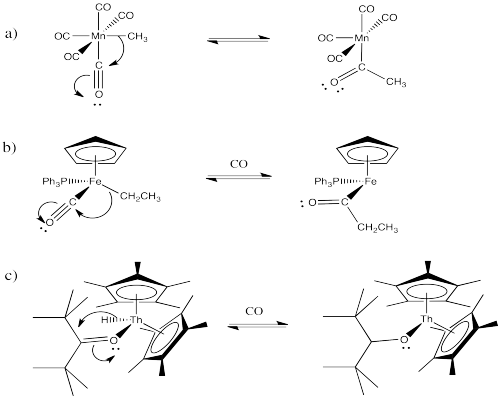
Provide products of the following migration reactions.
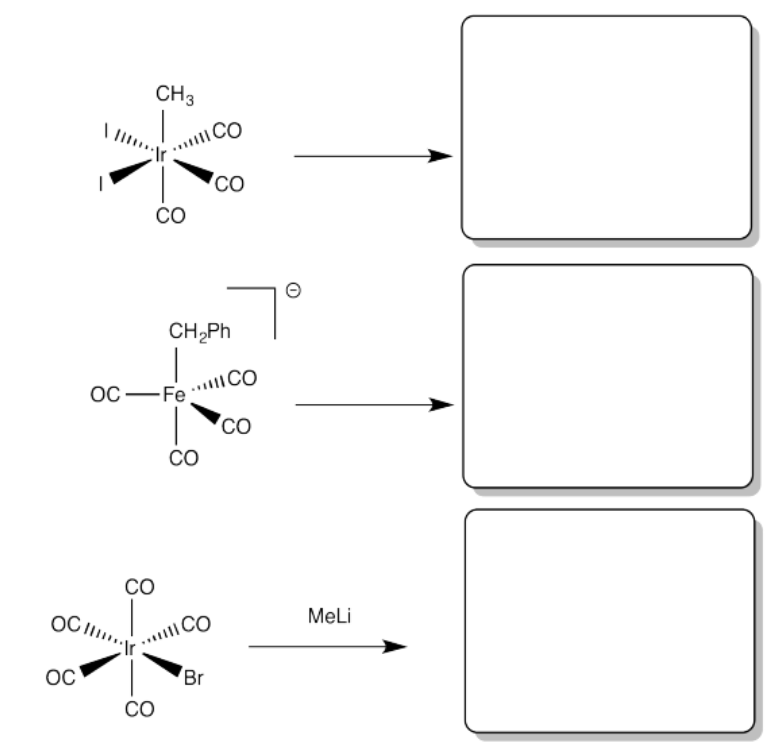
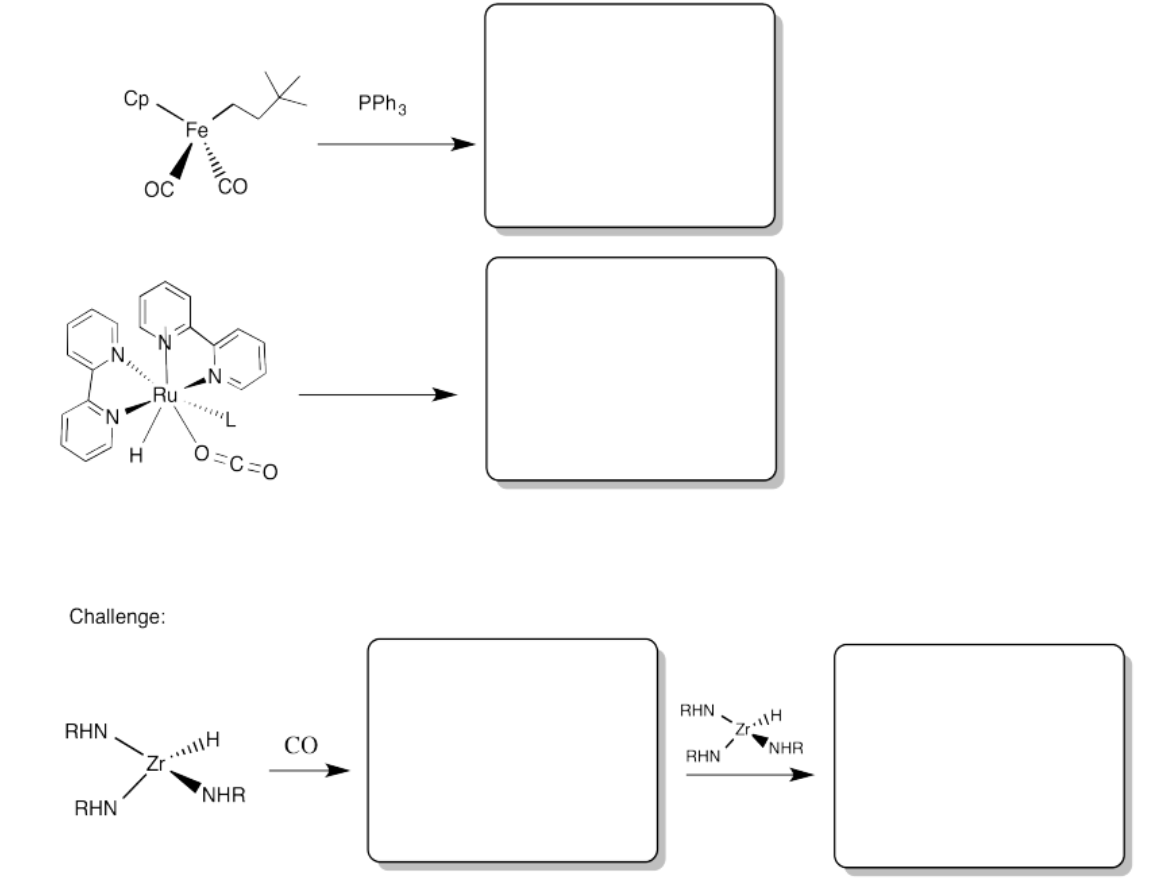
- Answer
-
Provide the products of the following migration reactions.
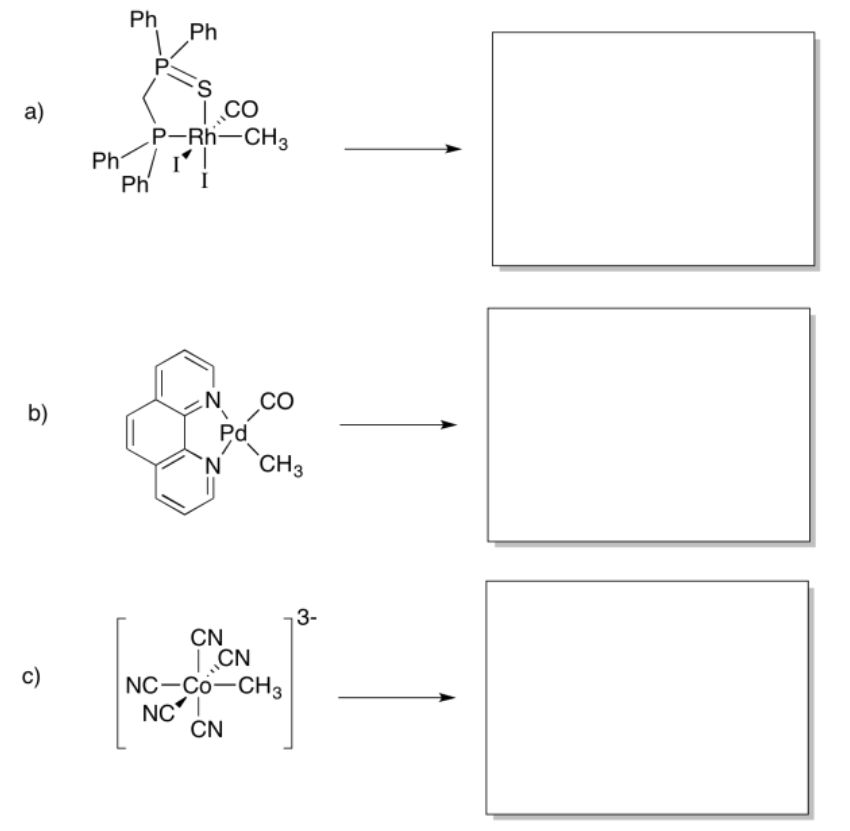
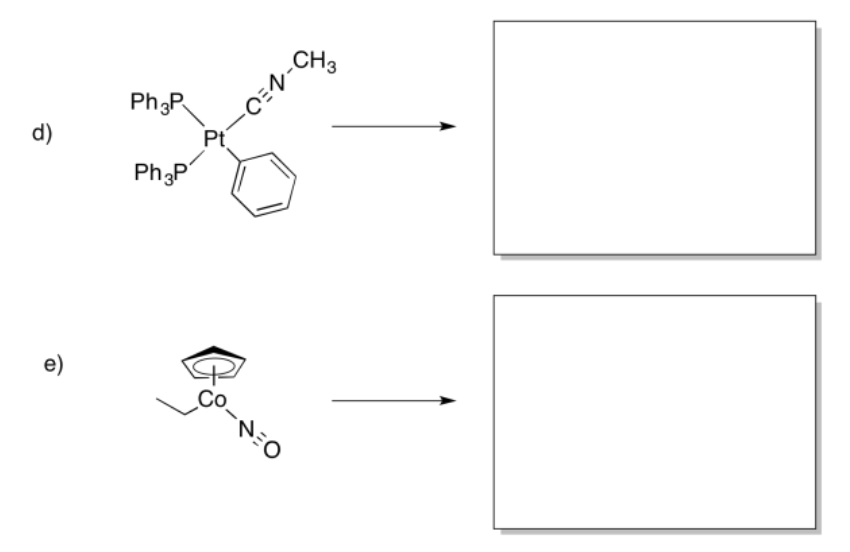
- Answer
-