1.46: Enzymes and Isoenzymes
- Page ID
- 125359
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
- Enzymes accelerate the reaction rate by:
- decreasing the amount of free energy of activation necessary for the reaction
- shifting the equilibrium position of a reaction
- causing thermodynamically incompatible reactions to occur
- increasing the rate of the reaction in one direction only
- c and d
- Enzyme nomenclature is used to describe:
- the reaction taking place
- the physical conditions of the assay
- the conversion of products to substrates
- only two point reactions e. the buffer in the assay
- A substance which when added to the enzyme attaches to a site removed from the active site so that the enzyme cannot bind its natural substrate is a (an):
- competitive inhibitor
- non-competitive inhibitor
- substrate analog
- enzyme cofactor
- coenzyme
- To assure that zero order kinetics is maintained in an enzyme reaction, the substrate concentration should be:
- equal to the Km
- less than the Km
- at least 10 times greater than the Km
- equal to 1/Km
- equal to the enzyme concentration
- For which order of reaction is the rate dependent only on the enzyme concentration?:
- zero order
- first order
- second order
- mixed order
- none of the above
- The point at which an enzyme reaction is proceeding at the greatest rate is:
- the Michaelius constant (Km)
- zero order kinetics
- first order kinetics
- point where the rate of the reaction is dependent on the substrate concentration
- [S] = Km
- Enzymes of metabolism:
- are present in all cells
- are plasma specific enzymes
- have a known function in serum
- have a known function in plasma
- are produced in large quantities after eating
- Isoenzymes are:
- multiple molecular forms of an enzyme family that catalyze the same reaction
- different enzymes which exhibit the same enzymatic specificity
- multiple molecular forms of different enzymes which catalyze the same reaction
- different enzymes which exhibit the same electrophoretic mobility
- enzymes with the same tertiary structure which catalyze the same reaction
- CK isoenzymes are diagnostically important because:
- erythrocyte and cardiac sources of elevation can be distinguished
- cardiac and hepatic sources of elevation can be distinguished.
- statistical analyses of the patterns of the 5 isoenzymes give a diagnostic classification of the various liver diseases
- the isoenzyme pattern indicates the specific tissue involved in a malignancy
- they are absolutely tissue specific
- The distribution of isoenzymes:
- is the same throughout the body
- varies greatly during adult life
- is dependent on physiological needs
- varies by individual
- varies by organ
- Serum from adults contain which isoenzyme of alkaline phosphatase?:
- heart, kidney, liver
- liver, kidney, bone
- kidney, red cells, liver
- red cells, liver, brain
- placenta, lungs, brain
- In coupled enzyme systems, the enzyme in the last reaction:
- is employed as an activator
- must exhibit the same kinetic properties as the enzyme in the primary reaction
- is the one whose product is measured
- is of no significance
- forms the substrate for the enzyme being measured
- The plot of 1/velocity vs. 1/substrate concentration is known as the:
- Arrhenius plot
- initial rate
- Michaelis-Menten plot
- maximal velocity
- Lineweaver-Burk plot
- Situation: You are running an assay of enzyme “X” which utilizes the coenzyme NAD. Its activity is measured in terms of NADH produced. You have obtained the following data:
Micromolar extinction coefficient (\(\epsilon\)) of NADH (at 340 nm) = 6.22 x 10-3 L \(\cdot\) \(\mu\)mol-1 \(\cdot\) c-1; light path (b) = 1 cm total volume of assay = 3.0 mL sample volume = 0.5 mL absorbance change 7 minutes = 0.350
Calculate the enzyme activity in IU/liter:- 0.048
- 1.30
- 48
- 336
- 4.8
- If zero order kinetics are followed, allowing the reaction to run twice the time will:
- cause the product to be denatured
- halve the amount of product formed
- have no effect on the amount of product formed
- double the amount of product formed
- double the absorbance change per minute
- Skeletal muscle tissue contains which of the following CK isoenzymes?
- MM only
- MB only
- BB only
- MM + MB
- MM + BB
- Creatine kinase (CK) isoforms are:
- degradative forms of individual CK isoenzymes
- polymerized forms of individual CK isoenzymes
- intracellular form of individual CK isoenzymes
- imunoglobulin-CK complex of individual isoenzymes
- none of the above.
- If the sample volume is halved in an enzymatic reaction, the final calculated enzyme activity will:
- increase four-fold
- decrease four—fold
- increase two—fold
- decrease two-fold
- remain the same
- According to IUB classification, creatine kinase is a/an:
- oxidoreductase
- transferase
- hydrolase
- lyase
- ligase
Use the following Key to answer Questions 20-27:
- 1, 2, and 3 are correct
- 1 and 3 are correct
- 2 and 4 are correct
- 4 only is correct
- all are correct
- An enzyme is:
- a protein
- highly specific
- not consumed in a reaction
- a catalyst
- The type of curve below shows the effect of enzyme activity in relation to:
- substrate concentration
- temperature
- activator concentration
- pH
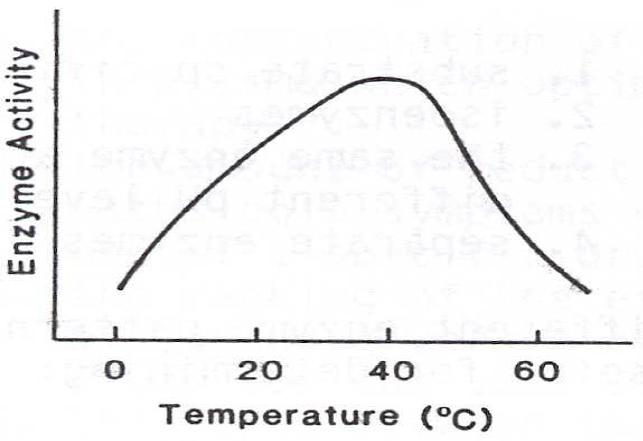
- An advantage of kinetic methods of measuring enzyme activity is that:
- temperature is not critical
- pH is not critical
- there is elimination of the lag phase
- linearity is demonstrable
- Which of the following statements concerning the measurement of serum enzymes is/are true?:
- enzymes are increased in serum following cell destruction and release of cellular constituents.
- enzymes are totally organ specific. A rise in an enzyme tells the physician exactly which organ is diseased.
- enzymes can rise to significant levels over background and help indicate the nature of the disease
- enzymes are depressed after stimulation of the exocrine glands
- Acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase are:
- substrate specific
- isoenzymes
- the same enzyme acting at different pH levels
- separate enzymes
- Different isoenzyme patterns are useful for determining:
- the age of the sample
- the severity of the disease process
- the condition under which the sample was stored
- which tissue was involved in the disease process
- Isoenzymes can be measured by which of the following procedures?
- chromatography
- electrophoresis
- immunoassay
- heat stability
- Which of the following compound(s) is (are) an enzyme cofactor?
- chloride
- pyridoxyl-5-phosphate
- magnesium
- thiamine-pyrophosphate
- Enzyme measurements are usually performed in the:
- lag phase
- linear phase
- substrate depletion phase
- none of the above
- doesn’t matter which phase is used
- An international unit of enzyme activity is defined as the number of:
- \(\mu\)moles product formed/second
- \(\mu\)moles product formed/minute
- mmoles substrate consumed/liter
- mmol substrate consumed/second
- none of the above
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is best considered a enzyme:
- cofactor
- activator
- substrate
- inhibitor
- holoenzyme
- An organ’s isoenzyme composition never changes except as a result of disease.
- True
- False
- Answer
-
- a (p. 1047)
- a (p. 1050-1051)
- b (p. 1057)
- c (p. 1054)
- a (p. 1053-1054)
- b (p. 1053-1054)
- a (p. 1061)
- a (p. 1065)
- b (p. 1067-1070)
- e (p. 1067)
- b (p. 1068)
- c (p. 1060)
- e (p. 1055)
- c (p. 1055)
- d (p. 1054)
- d (p. 1067)
- a (p. 1066)
- e (p. 1055)
- b (p. 1051)
- e (p. 1045, 1046, 1048)
- c (p. 1056, 1059)
- c (p. 1052-1053)
- b (p. 1060-1061)
- d (p. 1051)
- d (p. 1068-1069)
- e (p. 1071)
- c (p. 1057)
- b (p. 1054)
- b (p. 1055)
- c (p. 1044, 1057)
- b (p. 1068)

