Neutralization Reactions
- Page ID
- 282772
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
Learning Objectives
After completing this exercise, students will be able to:
- Write the neutralization reaction between an acid and base.
- Determine if a neutralization reaction goes to completion.
- Calculate the equivalence point of a titration.
- Use stoichiometry to determine the dominate species present after a neutralization reaction.
- Develop a guideline for when the reaction between a weak acid and strong base goes to completion based only on the Ka of the weak acid.
- A 0.219 g sample of primary standard grade Na2CO3 (FM = 105.988 g/mol) is dissolved in 25.0 mL of water. Calculate the first and second equivalence points if the solution is titrated with 0.106 M HCl.
- Maleic acid is the common name for cis-butenedioic acid.
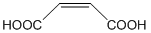
Complete the table below for the reaction of 20.0 mL of 0.150 M maleic acid with the indicated volume of 0.100 M OH-. We will abbreviate maleic acid as H2M.
|
VOH- (mL) |
mmol of H2M |
mmol of HM- |
mmol of M2- |
mmol of OH- |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
30.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
40.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
60.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
75.0 |
|
|
|
|
Contributors and Attributions
- Susan Oxley, St. Mary’s University (San Antonio) (soxley@stmarytx.edu)
- Sourced from the Analytical Sciences Digital Library


