Electrochemistry: Basic Concepts
- Page ID
- 283158
A REDOX Example
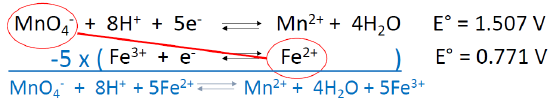
- One would predict a spontaneous reaction between….
- What is the coefficient in front of Fe2+ in the balanced reaction?
- What is E° for the total reaction?
ΔG, E and K Example
Eo for the following reaction (as written) is 0.736 volts. Calculate ΔG and K for the reaction.
\[\ce{MnO4- + 8H+ + 5Fe^2+ ⇌ Mn^2+ + 4H2O + 5Fe^3+}\nonumber\]
Calculating Potential of a Cell (Nernst equations)
Calculate the potential for the following cell:
\[\mathrm{Pt \mid Sn^{2+}(0.400\: M),\: Sn^{4+}(0.500\: M) \mid\mid NO_3^-(0.100\: M),\: H^+(pH=2.00),\: HNO_2(0.400\: M) \mid Pt}\nonumber\]
Potentiometry – Cells (line notation with REF)
Calculate the cell potential of the following cell:
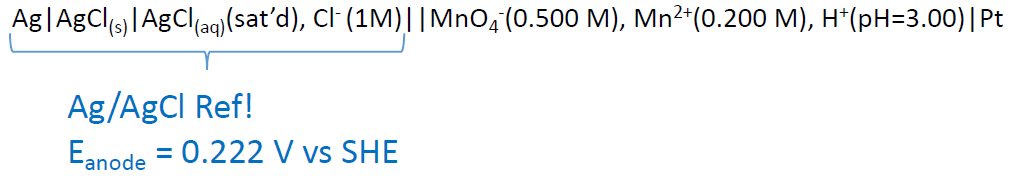
Bringing in Ksp
Think about the previous problem…
Calculate the cell potential of the following cell:
\[\mathrm{Ag \mid AgCl_{(s)} \mid AgCl_{(aq)}(sat’d),\: Cl^- (1.00\: M) \mid\mid \textrm{reduction half cell} \mid Pt}\nonumber\]
Couldn’t one use the Ag+ + e- ⇌ Ag(s) half cell at Eo = 0.799?
“Adding” Reactions
When you “add” chemical reactions, you multiply the K values and/or add the E values.
Given the following Eo values:
\[\ce{Ag+ + e- ⇌ Ag_{(s)}} \textrm{ (0.799 V vs SHE) and}\nonumber\]
\[\ce{AgCl_{(s)} + e- ⇌ Ag_{(s)} + Cl-} \textrm{ (0.222 V vs SHE)}\nonumber\]
Calculate the Ksp for AgCl.
“Mixing” Problems
30.00 mL of 0.120 F NaNO3 is mixed with 20.00 mL of 0.150 F SnCl2 and the solutions is buffered at pH=2.00. (NOTE: no gas or solid is observed)
- Calculate Eo and K for the spontaneous reaction that will occur.
- Calculate the solution potential of the resulting solution.
Potentiometry Problems (mixing, then measuring)
Calculate the cell potential, as measured at a Pt/SCE electrode pair, for a solution prepared by mixing 30.00 mL of 0.120 F NaNO3 and 20.00 mL of 0.150 F SnCl2. The solution is buffered at pH=2.00. (except for SCE, this is the same problem as the previous exercise)
Potentiometry Problems, II (mixing, then measuring, EP)
Calculate the cell potential, as measured at a Pt/SCE electrode pair, for a solution prepared by mixing 25.00 mL of 0.120 F NaNO3 and 20.00 mL of 0.150 F SnCl2. The solution is buffered at pH=2.00.
KEY: Reactant conc’ns are “Not really zero, just really small….AND in a defined ratio” …as indicated by coefficients in balanced eqn!
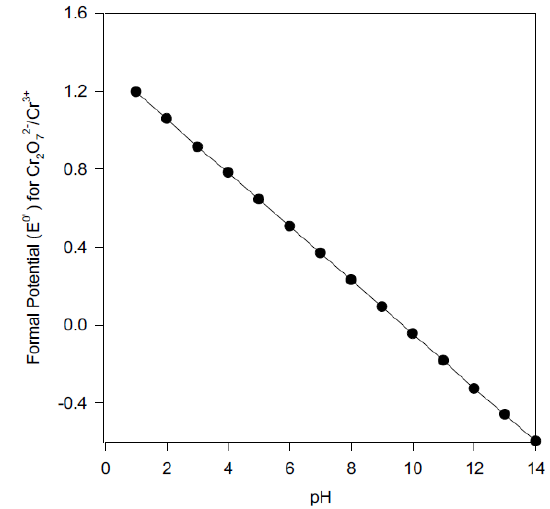
Formal Potential (Eo’)
Derive an equation for the pH-dependent formal potential for the dichromate/ chromium III half reaction, and calculate the Eo’ at pH 7.00.
\[\ce{Cr2O7^2- + 14H+ + 6e- ⇌ 2Cr^3+ + 7H2O} \hspace{30px} \mathrm{E^o} = \textrm{1.33 V vs SHE}\nonumber\]
\[E^{0'}_{Cr_2O_7^{2-}/Cr^{3+}} = E^0_{Cr_2O_7^{2-}/Cr^{3+}} - \dfrac{0.0591}{6} \log\left(\dfrac{1}{[H^+]^{14}}\right)\nonumber\]
\[E^{0'}_{Cr_2O_7^{2-}/Cr^{3+}} = E^0_{Cr_2O_7^{2-}/Cr^{3+}} - \dfrac{0.0591(14)}{6} pH\nonumber\]
\[\mathrm{E^{o’}}\textrm{ at pH 7.00 = 0.365 V vs SHE}\nonumber\]
Redox Titration
Consider the titration of 50.00 mL of 0.100 M Cr2O72- with 0.300 M Fe2+ as monitored with a Pt/SCE electrode pair...calculate the measured cell potential and construct the expected titration plot. The pH is maintained at 0.00.
\[\ce{Cr2O7^2- + 14H+ + 6e- ⇌ 2Cr^3+ + 7H2O} \hspace{30px} \mathrm{E^o} = \textrm{1.33 V vs SHE}\nonumber\]
\[\ce{Fe^3+ + e- ⇌ Fe^2+} \hspace{30px} \mathrm{E^o} = \textrm{0.771 V vs SHE}\nonumber\]
Contributors and Attributions
- Timothy Strein, Bucknell University (strein@bucknell.edu)
- Sourced from the Analytical Sciences Digital Library


