4.10: ESI-QTOF-MS Coupled to HPLC and its Application for Food Safety
- Page ID
- 55893
ESI-QTOF-MS Coupled to HPLC and its Application for Food Safety
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a very powerful separation method widely used in environmental science, pharmaceutical industry, biological and chemical research and other fields. Generally, it can be used to purify, identify and/or quantify one or several components in a mixture simultaneously.
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a detection technique by measuring mass-to-charge ratio of ionic species. The procedure consists of different steps. First, a sample is injected in the instrument and then evaporated. Second, species in the sample are charged by certain ionized methods, such as electron ionization (EI), electrospray ionization (ESI), chemical ionization (CI), matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). Finally, the ionic species wil be analyzed depending on their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) in the analyzer, such as quadrupole, time-of-flight (TOF), ion trap and fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance.
The mass spectrometric identification is widely used together with chromatographic separation. The most common ones are gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Because of the high sensitivity, selectivity and relatively low price of GC-MS, it has very wide applications in drug detection, environmental analysis and so forth. For those organic chemistry research groups, it is also a daily-used and convenient equipment. However, GC-MS is ineffective if the molecules have high boiling point and/or will be decomposed at high temperature.
In this module, we will mainly talk about liquid chromatography and electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC/ESI-QTOF-MS). As mentioned above, the LC has an efficient capacity of separation and MS has a high sensitivity and strong ability of structural characterization. Furthermore, TOF-MS, has several distinctive properties on top of regular MS, including fast acquisition rates, high accuracy in mass measurements and a large mass range. The combination of LC and ESI-TOF-MS allow us to obtain a powerful in the quantitative and qualitative analysis of molecules in complex matrices by reducing the matrix interferences. It may play an important role in the area of food safety.
How it Works
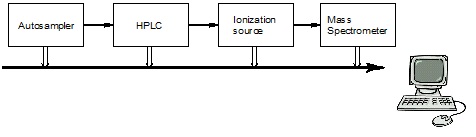
Generally, LC-MS has four components, including an autosampler, HPLC, ionization source and mass spectrometer, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\). Here we need to pay attention to the interface of HPLC and MS so that they can be suitable to each other and be connected. There are specified separation column for HPLC-MS, whose inner diameter (I.D.) is usually 2.0 mm. And the flow rate, which is 0.05 - 0.2 mL/min, is slower than typical HPLC. For the mobile phase, we use the combination of water and methanol and/acetonitrile. And because ions will inhibit the signals in MS, if we want to modify to mobile phase, the modifier should be volatile, such as HCO2H, CH3CO2H, [NH4][HCO2] and [NH4][CH3CO2].
As the interface between HPLC and MS, the ionization source is also important. There are many types and ESI and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) are the most common ones. Both of them are working at atmospheric pressure, high voltage and high temperature. In ESI, the column eluent as nebulized in high voltage field (3 - 5 kV). Then there will be very small charged droplet. Finally individual ions formed in this process and goes into mass spectrometer.
Comparison of ESI-QTOF-MS and Other Mass Spectrometer Methods
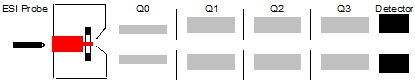
There are many types of mass spectrometers which can connect with the HPLC. One of the most widely-used MS systems is single quadrupole mass spectrometer, whichis not very expensive, shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\). This system has two modes. One mode is total ion monitoring (TIM) mode which can provide the total ion chromatograph. The other is selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode, in which the user can choose to monitor some specific ions, and the latter’s sensitivity is much higher than the former’s. Further, the mass resolution of the single quadrupole mass spectrometer is 1 Da and its largest detection mass range is 30 - 3000 Da.
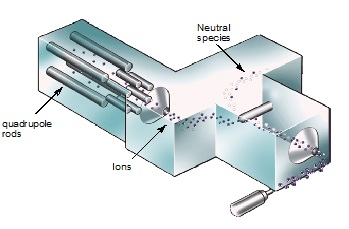
The second MS system is the triple quadrupole MS-MS system, shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). Using this system, people can select the some ions, called parent ions, and use another electron beam to collide them again to get the fragment ions, called daughter ions. In other words, there are two steps to select the target molecules. So it reduces the matrix effect a lot. This system is very useful in the analysis of biological samples because biological samples always have very complex matrix; however, the mass resolution is still 1 Da.
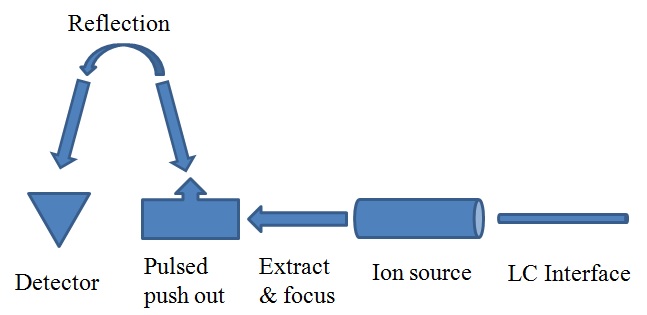
The third system is time-of-flight (TOF) MS, shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), which can provide a higher mass resolution spectrum, 3 to 4 decimals of Da. Furthermore, it can detect a very large range of mass at a very fast speed. The largest detection mass range is 20 - 10000 Da. But the price of this kind of MS is very high. The last technique is a hybrid mass spectrometer, Q-TOF MS, which combines a single quadrupole MS and a TOF MS. Using this MS, we can get high resolution chromatograph and we also can use the MS-MS system to identify the target molecules.
Application of LC/ESI-QTOF-MS in the Detection of Quinolones in Edible Animal Food
Quinolones are a family of common antibacterial veterinary medicine which can inhibit DNA-gyrase in bacterial cells. However, the residues of quinolone in edible animal products may be directly toxic or cause resistant pathogens in humans. Therefore, sensitive methods are required to monitor such residues possibly present in different animal-producing food, such as eggs, chicken, milk and fish. The molecular structures of eight quinolones, ciprofloxacin (CIP), anofloxacin methanesulphonate (DAN), enrofloxacin (ENR), difloxacin (DIF), sarafloxacin (SARA), oxolinic, acid (OXO), flumequine (FLU), ofloxacin (OFL), are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\).
LC-MS is a common detection approach in the field of food safety. But because of the complex matrix of the samples, it is always difficult to detect those target molecules of low concentration by using single quadrupole MS. The following gives an example of the application of LC/ESI-QTOF-MS.
Using a quaternary pump system, a Q-TOF-MS system, a C18 column (250 mm × 2.0 mm I.D., 5 µm) with a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min, and a mixture of solvents as the mobile phase comprising of 0.3% formic acid solution and acetonitrile. The gradient phofile for mobile phase is shown in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\). Since at acidic pH condition, the quinolones carried a positive charge, all mass spectra were acquired in the positive ion mode and summarizing 30,000 single spectra in the mass range of 100-500 Da.
| Time (min) | Volume % of Formic Acid Solution | Volume % of Acetonitrile |
| 0 | 80 | 20 |
| 12 | 65 | 35 |
| 15 | 20 | 80 |
| 20 | 15 | 85 |
| 30 | 15 | 85 |
| 30.01 | 80 | 20 |
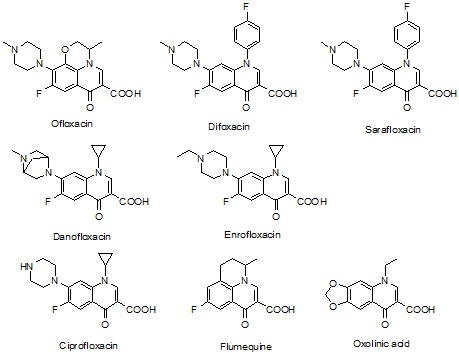
The optimal ionization source working parameters were as follows: capillary voltage 4.5 kV; ion energy of quadrupole 5 eV/z; dry temperature 200 °C; nebulizer 1.2 bar; dry gas 6.0 L/min. During the experiments, HCO2Na (62 Da) was used to externally calibrate the instrument. Because of the high mass accuracy of the TOF mass spectrometer, it can extremely reduce the matrix effects. Three different chromatographs are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\). The top one is the total ion chromatograph at the window range of 400 Da. It’s impossible to distinguish the target molecules in this chromatograph. The middle one is at one Da resolution, which is the resolution of single quadrupole mass spectrometer. In this chromatograph, some of the molecules can be identified. But noise intensity is still very high and there are several peaks of impurities with similar mass-to-charge ratios in the chromatograph. The bottom one is at 0.01 Da resolution. It clearly shows the peaks of eight quinolones with very high signal to noise ratio. In other words, due to the fast acquisition rates and high mass accuracy, LC/TOF-MS can significantly reduce the matrix effects.
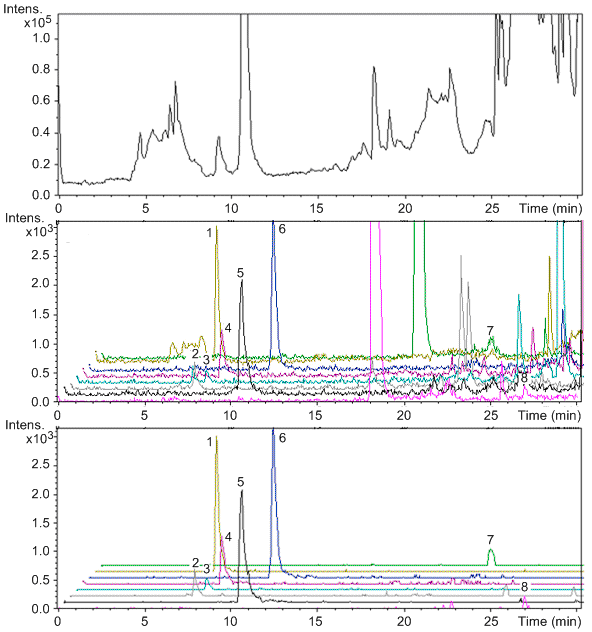
The quadrupole MS can be used to further confirm the target molecules. Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) shows the chromatograms obtained in the confirmation of CIP (17.1 ng/g) in a positive milk sample and ENR (7.5 ng/g) in a positive fish sample. The chromatographs of parent ions are shown on the left side. On the right side, they are the characteristic daughter ion mass spectra of CIP and ENR.
Drawbacks of LC/Q-TOF-MS
Some of the drawbacks of LC/Q-TOF-MS are its high costs of purchase and maintenance. It is hard to apply this method in daily detection in the area of environmental protection and food safety.
In order to reduce the matrix effect and improve the detection sensitivity, people may use some sample preparation methods, such as liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), solid-phase extraction (SPE), distillation. But these methods would consume large amount of samples, organic solvent, time and efforts. Nowadays, there appear some new sample preparation methods. For example, people may use online microdialysis, supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) and pressurized liquid extraction. In the method mentioned in the Application part, we use online in-tube solid-phase microextraction (SPME), which is an excellent sample preparation technique with the features of small sample volume, simplicity solventless extraction and easy automation.


