6.1: Basic Principles of Chromatography
- Page ID
- 212589
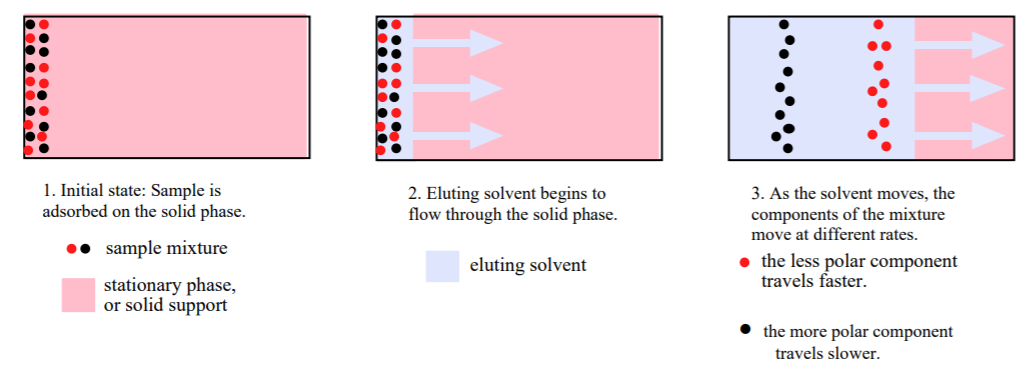
Chromatography is yet another technique for the analysis and separation of chemical mixtures. The technique is based on a polarity interplay between the sample and two other substances called the solid (or stationary) phase, and the mobile phase, which can be a liquid or a gas. As their names indicate, the stationary phase does not move, whereas the mobile phase flows across, or through the solid phase.
In this “love triangle,” the sample to be separated first becomes adsorbed onto the surface of the solid phase through polar interactions. More polar samples adhere (or bind) more strongly than less polar ones. The mobile phase then comes in and sweeps across the stationary phase, competing for the sample. If the mobile phase is a solvent, it is called the eluting solvent. The more polar the solvent, the greater its capacity to carry the components of the mixture with it, “yanking” them away from the solid phase as it moves. Different components with different polarities will travel at different rates as the solvent moves, causing their separation.
Some of the most common solid adsorbents used as stationary phases in chromatography are listed in table 19.1, p. 760. In the organic chemistry lab the most commonly used are silica gel and alumina due to their versatile polarity range. Likewise, some common eluting solvents are listed in table 19.2, p. 761 by order of increasing polarity, and therefore increasing eluting power. Methylene chloride, ethyl acetate, and ethanol are among the most commonly used.
Table 19.3, p. 762, lists some functional groups by order of elution, meaning how fast they move in a chromatographic separation. Again, the more polar ones (alcohols, amines, and acids) move slower, whereas the less polar ones (hydrocarbons and ethers) move faster.


