9: Organic Functional Groups Structure & Nomenclature: Questions
- Page ID
- 43923
C-O Containing Functional Groups: Alcohols and Ethers
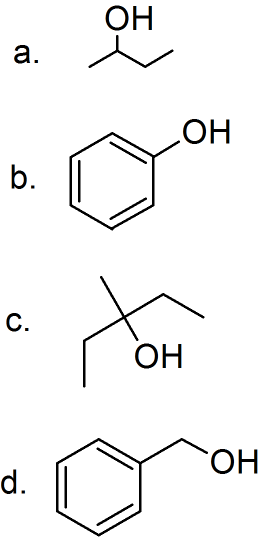
(01) Examine each of the following alcohols and determine whether the alcohol group is primary, secondary, tertiary or phenol. Then rewrite the skeletal structures as condensed formulas.
(02) Using your knowledge of nomenclature, translate the following IUPAC names into their skeletal structures. For each alcohol group, determine whether it is primary, secondary or tertiary.
- 5-methyl-2-octanol
- 2,3-dimethyl-1-heptanol
- cis-3-ethylcyclohexanol
- 2-propanol
- 2-methyl-2-pentanol
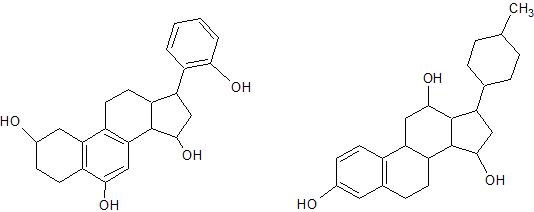
(03) Some very large compounds, such as these steroid derivatives, contain multiple alcohol and phenol groups. Circle each phenol group and put a rectangle around each alcohol group.
(04) From most to least, rank the following compounds in order of water solubility.
a. 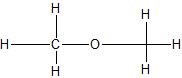
b. 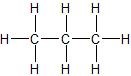
c. 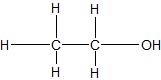
(05) Rank each of the following in order decreasing boiling points.
a. 
b. 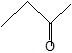
c. 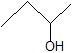
(06) Many carbohydrates have similar structures to the example shown below. Circle the ether functional group, and box the alcohol groups.
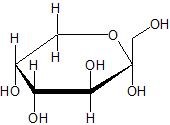
(07) Take the formula C5H12O and sketch an isomer that can be formed for each of the following functional groups: Primary Alcohol, Secondary Alcohol, Tertiary Alcohol, and Ether.
Aldehydes and Ketones
(08) Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following aldehydes and ketones. If there is also a more common name, provide that as well.
a. 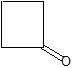
b. 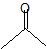
c. 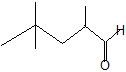
d. 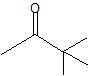
e. 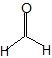
(09) Convert the following IUPAC names into their condensed structural formulas.
- 4-nonanone
- butanal
- 2,3,4-trimethylpentanal
- 3-ethyl-4-heptanone
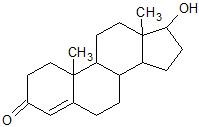
(10) Testosterone, a hormone, contains a number of functional groups. Circle and label each of them. Can any of the rings be called aromatic? Which functional group can be identified from the name, testosterone?
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
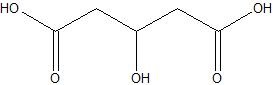
(11) Carboxylic acids and alcohols contain hydroxyl groups. Circle the acid group(s) and box the alcohol group(s) in the compound below.
Esters and Thioesters
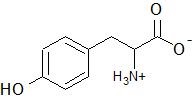
(12) Tyrosine, an amino acid, is shown below. Circle and label each functional group in the molecule.
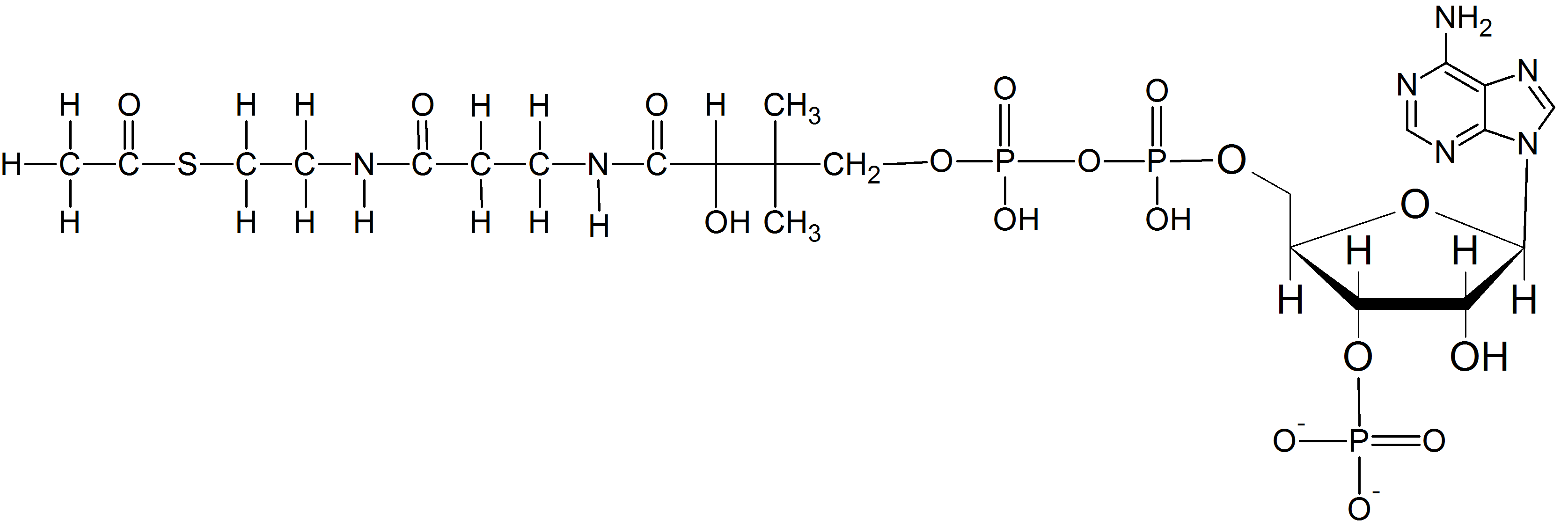
(13) Acetyl CoA is an important biological molecule drawn below. Circle and label the thioester. Box and label any other functional groups.
Amides
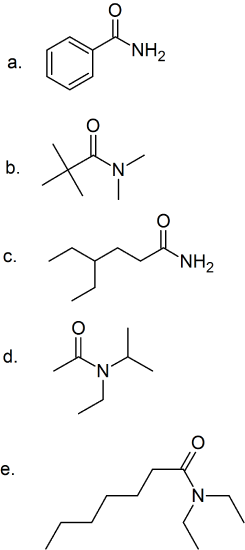
(14) Study the following amide structures and convert them into condensed formulas.
C-N Containing Functional Groups: Amines
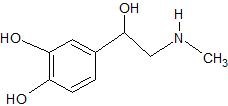
(15) The hormone adrenaline, shown below, is classified as an amine. Box the amine portion; classify it as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary; and determine whether the amino group is in its neutral or ionic form. Circle hydroxyl groups and classify them as primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohols or phenols.
Phosphate Esters and ATP
(16) Phosphoric acid is a triprotic acid; define this term. How many ionizable hydrogens are found in phosphoric acid? Sketch a phosphate ion with one of its bonds to a hydrogen substituted with an alcohol to form a phosphoester bond.

