SC16. E and Z Alkene Isomers
- Page ID
- 4122
SC16. Another kind of stereochemistry: E and Z alkene isomers
Double bonds can exhibit stereoisomerism if there is more than one way to arrange two groups at opposite ends of a double bond: either on the same side of the bond axis (commonly cis) or opposite sides of the double bond axis (commonly trans). There is a different way of denoting these two stereochemical configurations that is always used if the compound has a more complicated structure. Compounds that have more than one non-hydrogen group at either end of the double bond are not normally referred to as cis or trans isomers, but are instead called E or Z isomers.
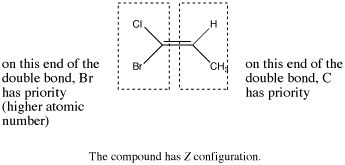
- In Z isomers, the highest-priority groups at each end of an alkene are on the same side of the double bond axis. The double bond axis is a straight line drawn through the two atoms that are double bonded to each other.
- Z is from the German zusammen (together).
- In E isomers, the highest-priority groups at each end of an alkene are on opposite sides of the double bond axis.
- E is from the German entgegen (against).
Highest-priority is decided based on atomic number.
Figure SC16a. An example of an E alkene.
Figure SC16b. An example of a Z alkene.
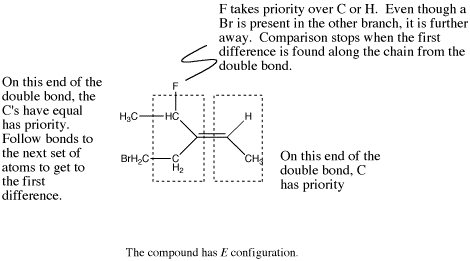
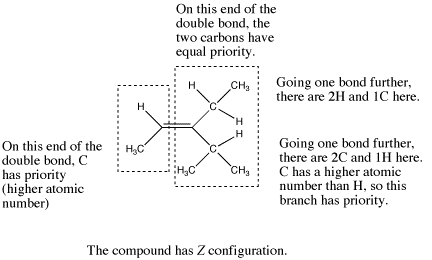
If the first atoms attached to one end of the double bond are the same, go one bond further on each chain and compare all the atoms that come next. If one of the chains at this point contains an atom with a higher atomic number than any of the atoms on the other chain, it is given higher priority.
Figure SC16c. A more complicated example of an E alkene.
Sometimes, going one bond further leads to the same set of atomic numbers along both branches, but there are more of the higher atomic numbered atom on one branch than the other.
Figure SC16d. Another complicated example, this time of a Z alkene.
Remember, this is an arbitrary set of rules that have been adopted to name these compounds so that people can refer to one isomer or the other. They may not be the rules that you would have come up with on your own.