Reduction of Carboxylic Acids with \(LiAlH_4\)
- Page ID
- 3927
This page looks at the reduction of carboxylic acids to primary alcohols using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III) (lithium aluminium hydride), LiAlH4. The "(III)" is the oxidation state of the aluminium. Since aluminium only ever shows the +3 oxidation state in its compounds, the "(III)" is actually unnecessary.
The reaction
Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate has the structure:
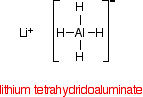
In the negative ion, one of the bonds is a co-ordinate covalent (dative covalent) bond using the lone pair on a hydride ion (H-) to form a bond with an empty orbital on the aluminium.
The reduction of a carboxylic acid
The reaction happens in two stages - first to form an aldehyde and then a primary alcohol. Because lithium tetrahydridoaluminate reacts rapidly with aldehydes, it is impossible to stop at the halfway stage. Equations for these reactions are usually written in a simplified form with the "[H]" in the equations represents hydrogen from a reducing agent. Because of the impossibility of stopping at the aldehyde, there is not much point in giving an equation for the two separate stages. The overall reaction is:
\[ RCOOH + 4[H] \rightarrow RCH_2OH + H_2O\]
"R" is hydrogen or a hydrocarbon group. For example, ethanoic acid will reduce to the primary alcohol, ethanol.
\[ CH_3COOH + 4[H] \rightarrow CH_3CH_2OH + H_2O\]
Sodium tetrahydridoborate (sodium borohydride) will not work! If you are familiar with the reduction of aldehydes and ketones using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate, you are probably aware that sodium tetrahydridoborate is often used as a safer alternative. It CAN'T be used with carboxylic acids. The sodium tetrahydridoborate isn't reactive enough to reduce carboxylic acids.
Reaction conditions
Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate reacts violently with water and so the reactions are carried out in solution in dry ethoxyethane (diethyl ether or just "ether"). The reaction happens at room temperature. At the end of the reaction, the product is a complex aluminum salt. This is converted into the alcohol by treatment with dilute sulfuric acid.
![]()
Contributors
Jim Clark (Chemguide.co.uk)


